Ground object classification method based on electric power corridor airborne LiDAR point cloud data
A technology of point cloud data and power corridors, which is applied to computer parts, instruments, character and pattern recognition, etc., and can solve problems such as insufficient information utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
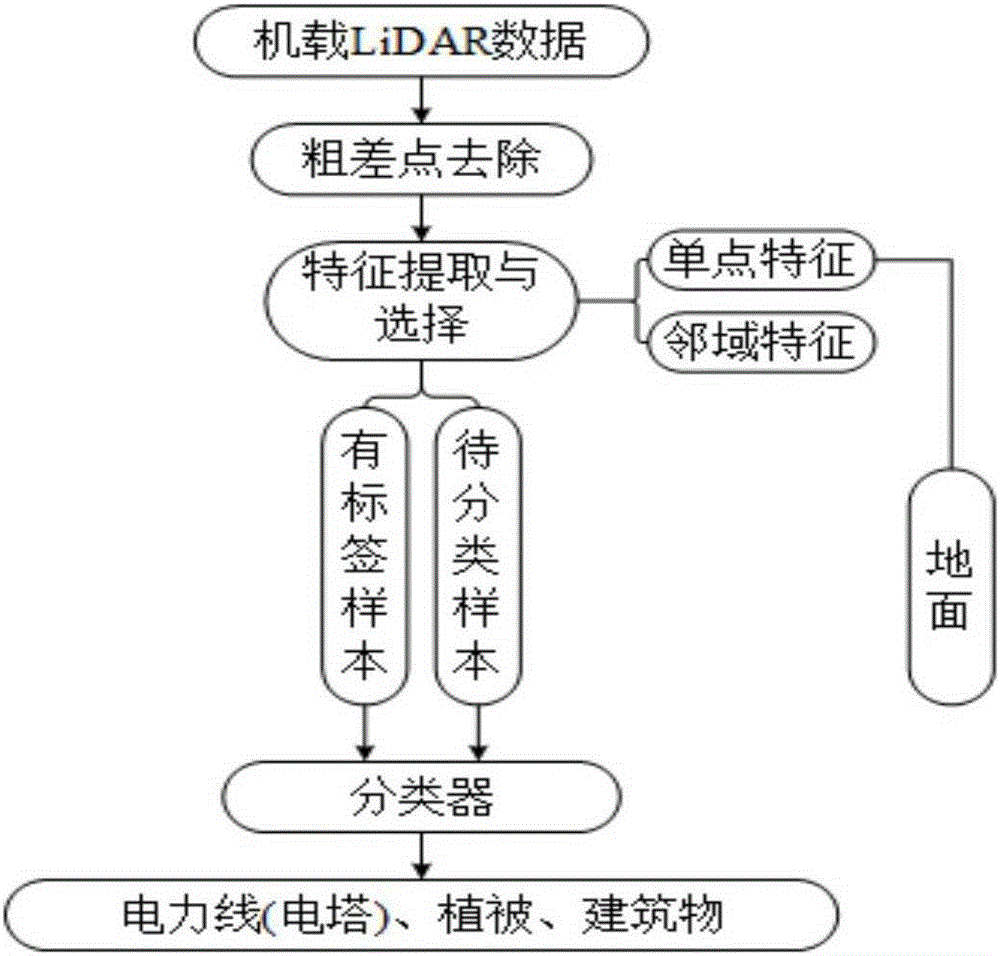
[0046] Specific implementation mode 1: Combination figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the method for classification of ground features of airborne LiDAR data of the power corridor in this embodiment includes the following steps:
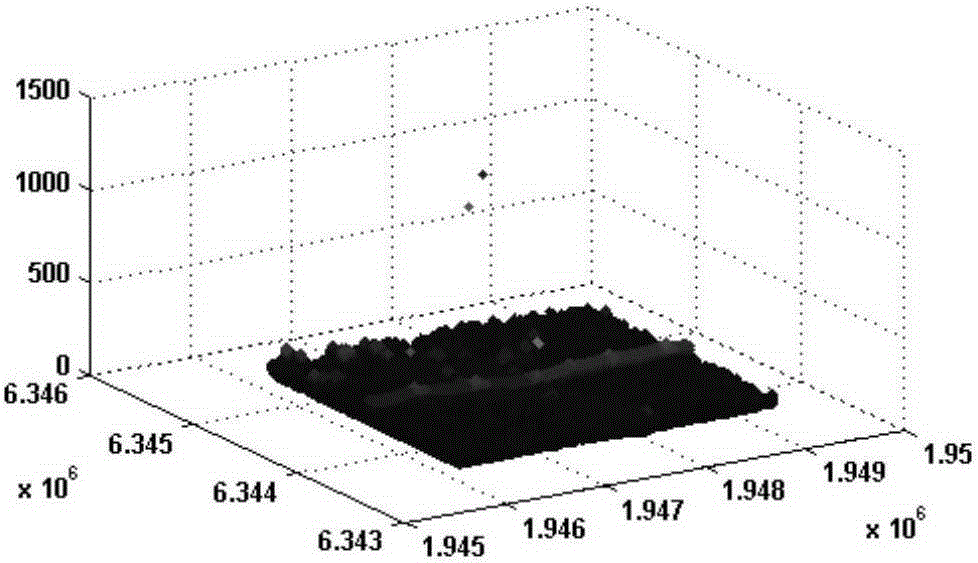
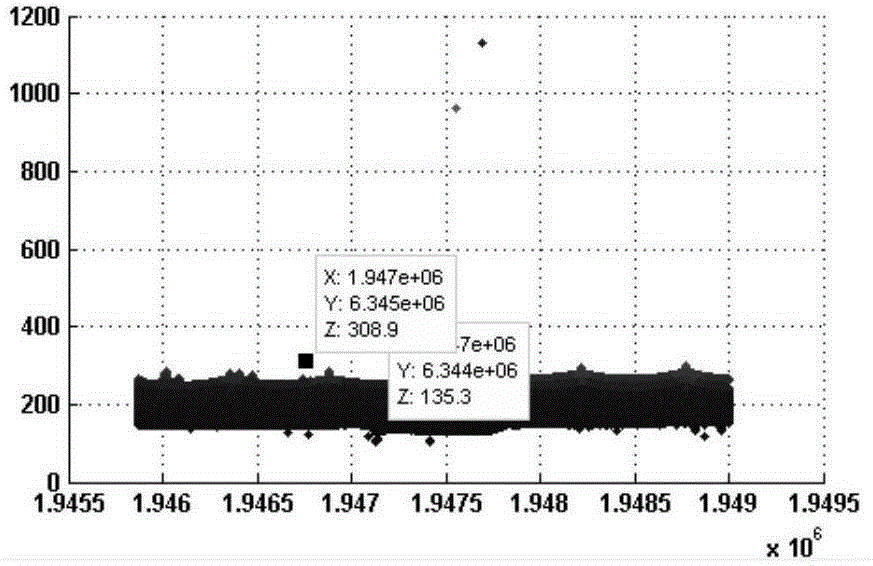
[0047] Step 1: Obtain LiDAR point cloud data, display the LiDAR point cloud data in three-dimensional visualization, and remove gross points according to the set elevation threshold;
[0048] Step 2: Perform feature extraction and feature processing on LiDAR point cloud data;
[0049] Step 3: Randomly select labeled samples from LiDAR point cloud data;
[0050] Step 4. Use the labeled samples to classify the LiDAR point cloud data samples to be classified by the classifier, namely the k-nearest neighbor criterion classification method, to obtain the power facilities, vegetation, buildings, and surface point cloud data;
[0051] Step 1. Calculate the Euclidean distance between the sample to be classified and all labeled samples y represents the sample to ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0055] Specific implementation manner 2: The difference between this implementation manner and the specific implementation manner 1 is: the gross error removal described in step 1 of this implementation manner, the specific steps are as follows:
[0056] Step 1: Use MATLAB software to read the point cloud data into the work area and display it visually;
[0057] Step 1. Determine the elevation interval [L, H] of the ground object point according to not lower than the ground and not higher than the highest ground object point in the scene, where L represents the lowest point of elevation threshold, and H represents the highest elevation threshold Point, remove the points whose elevation threshold is less than L and the elevation threshold is greater than H.
[0058] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is: in this embodiment, the feature extraction and feature processing described in step 2 are performed, and the specific steps are as follows: ...
specific Embodiment approach 4
[0062] Specific embodiment 4: The difference between this embodiment and the third embodiment is that the specific steps of extracting single point features described in step 21 of this embodiment are as follows:
[0063] Step 21: Use the height, intensity, number of echoes, and echo position information in the LiDAR point cloud data as a feature of the point;
[0064] Step 212: Divide the LiDAR point cloud data into blocks, select the lowest point in each block as the ground point for surface model fitting, and subtract the original point cloud height from the ground surface height to obtain the relative height information of the point as a feature; The relative height is less than 1m as the ground point.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com