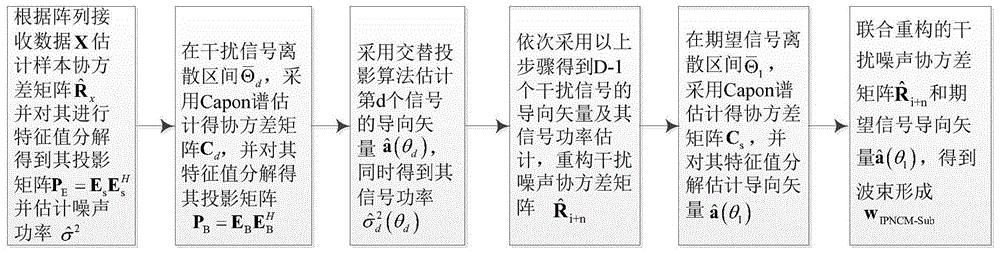
Beam forming method based on subspace interference-plus-noise covariance matrix reconstruction
A technology of covariance matrix and interference noise, applied in radio wave measurement systems, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as relying on prior information, interference signal guidance vector error is very sensitive, and correlation coefficient is small
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
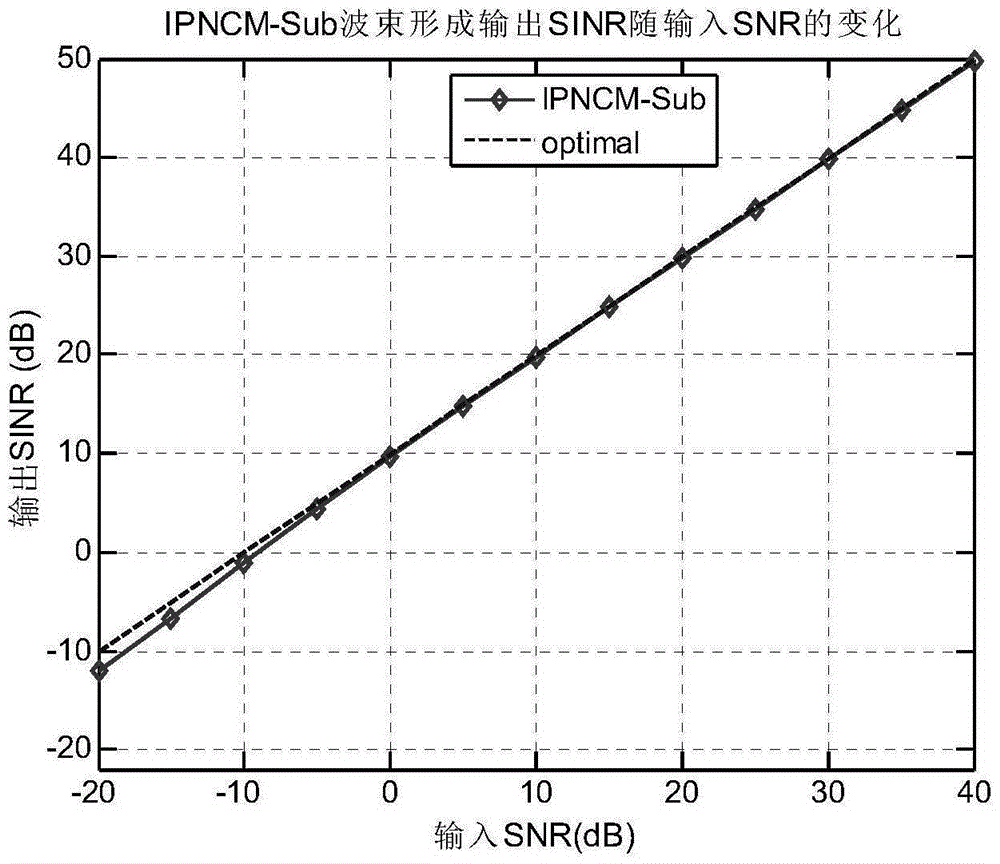
[0036] A uniform linear array composed of 10 array elements receives narrowband signals emitted by 3 far-field sources, and the preset directions of arrival are respectively and The first signal is the desired signal; the corresponding angle intervals are and It is discretized by adopting an angle interval Δθ=0.1°, and the parameter ρ is set to ρ=0.9 to determine the dimension K of the signal subspace in step S32. The input signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the two interference signals is both 30dB, the number of snapshots received by the array is 30, and the input signal-to-noise ratio of the expected signal ranges from -20dB to 40dB, and 200 Monte Carlo experiments are carried out. This implementation mainly considers the robustness of the beamforming algorithm of the present invention to the error of the direction of arrival of the interference signal and the desired signal, so it is assumed that the error of the direction of arrival of all the array received signals (in...
Embodiment 2
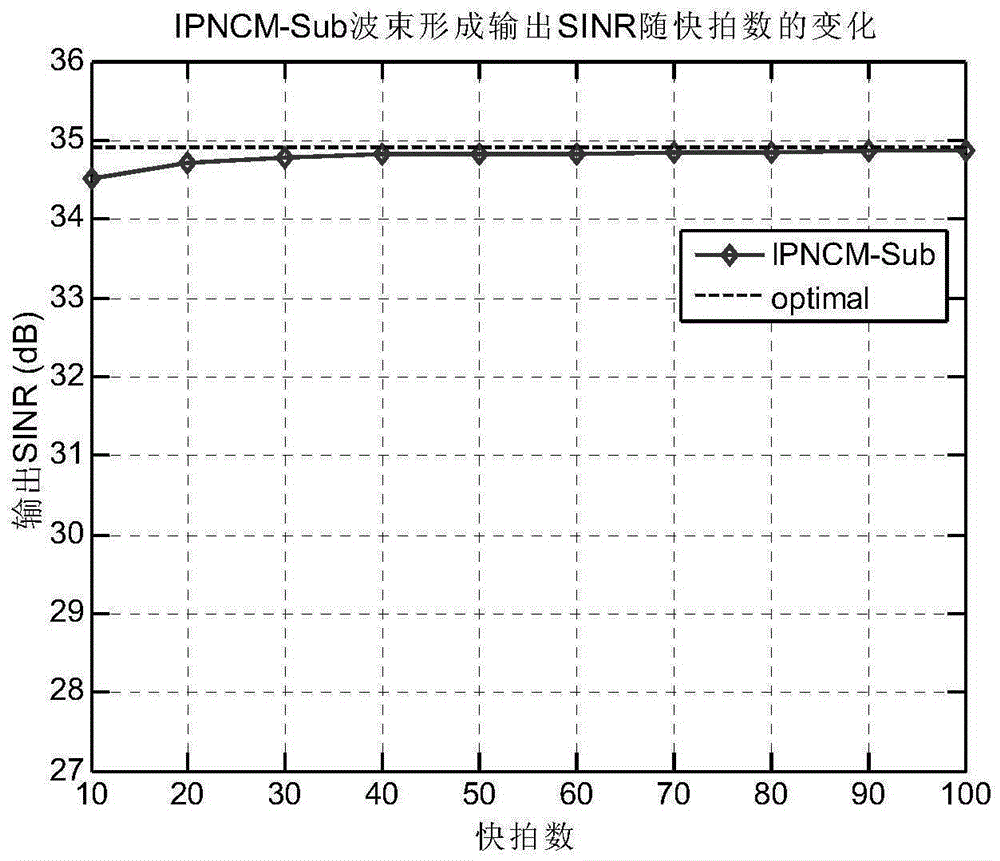
[0044] A uniform linear array composed of 10 array elements receives narrowband signals emitted by 3 far-field sources, and the preset directions of arrival are respectively and The first signal is the desired signal; the corresponding angle intervals are and It is discretized by adopting an angle interval Δθ=0.1°, and the parameter ρ is set to ρ=0.9 to determine the dimension K of the signal subspace in step S32. The input signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the two interference signals is both 30dB, the input signal-to-noise ratio of the desired signal is 25dB, and the number of snapshots received by the array ranges from 10 to 100, and 200 Monte Carlo experiments are carried out. This implementation mainly considers the robustness of the beamforming algorithm of the present invention to the error of the direction of arrival of the interference signal and the desired signal, so it is assumed that the error of the direction of arrival of all the array received signals (inclu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com