Application of citric acid in preparation of weak-acid electrolyzed water and preparation method of weak-acid electrolyzed water
A weakly acidic, potential water technology is applied in the preparation of weakly acidic potential water. The application of citric acid in the preparation of weakly acidic potential water can solve the problems of difficulty in control, and the pH of weakly acidic potential water changes too quickly, so as to ensure the elimination of water. Bacteria quality and effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride solution: Weigh 12g of sodium chloride and dissolve in 6L of purified water.
[0024] (2) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride + 0.04% diluted hydrochloric acid mixed solution: Dissolve 12g sodium chloride and 2.4ml diluted hydrochloric acid in 6L purified water.
[0025] (3) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride + 0.04% citric acid mixed solution: Dissolve 12g sodium chloride and 2.4g citric acid monohydrate in 6L purified water
[0026] (4) Use high-concentration potential water device (Riande AnyWhere-320W) to electrolyze the above three solutions separately for 1, 3, 5, and 10 minutes (additives add electrolysis group for 7 minutes).
[0027] (5) Take 1L of electrolytic solution after electrolysis, and measure its available chlorine, pH and oxidation-reduction potential.
[0028] (6) Repeat the above steps three times to obtain parallel data. The results are shown in Table 1 to Table 3.
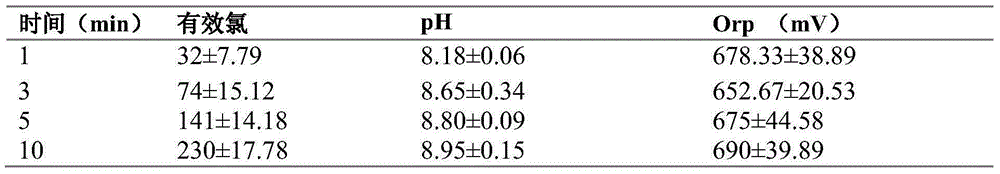
[0029] Table 1 shows the electrolysis data of 0.2%NaCl+6L water
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride solution: Weigh 24g sodium chloride and dissolve it in 6L purified water.
[0040] (2) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride + 0.04% diluted hydrochloric acid mixed solution: Dissolve 24g sodium chloride and 3.6ml diluted hydrochloric acid in 6L purified water.
[0041] (3) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride + 0.04% citric acid mixed solution: Dissolve 24g sodium chloride and 3.6g citric acid monohydrate in 6L purified water
[0042] (4) The above three solutions were electrolyzed for 1, 3, 5, and 10 minutes respectively using a high-concentration potential water device (the additive group adds the electrolysis group for 7 minutes).
[0043] (5) Take 1L of electrolytic solution after electrolysis, and measure its available chlorine, pH and redox potential.
[0044] (6) Repeat the above steps three times to obtain parallel data. The results are shown in Table 4 to Table 6.
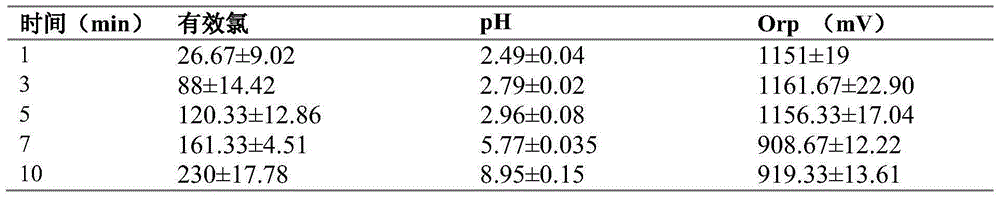
[0045] Table 424g sodium chloride dissolved in 6L purified water
[0046]
[0047] Ta...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) Prepare 0.2% sodium chloride solution: Weigh 6g sodium chloride and dissolve it in 6L purified water.
[0053] (2) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride + 0.04% diluted hydrochloric acid mixed solution: take 6g sodium chloride and 1.2ml diluted hydrochloric acid and dissolve in 6L purified water.
[0054] (3) Configure 0.2% sodium chloride + 0.04% citric acid mixed solution: take 6g sodium chloride and 1.2g citric acid monohydrate and dissolve in 6L purified water
[0055] (4) The above three solutions were electrolyzed for 1, 3, 5, and 10 minutes respectively using a high-concentration potential water device (the additive group adds the electrolysis group for 7 minutes).
[0056] (5) Take 1L of electrolytic solution after electrolysis, and measure its available chlorine, pH and redox potential.
[0057] (6) Repeat the above steps three times to obtain parallel data, and the results are shown in Table 7-9.
[0058] Table 76g sodium chloride dissolved in 6L purified water
[0059]
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com