Temperature self compensation method for LAPS (Light Addressable Potentiometric Sensor)
A potential sensor, self-compensation technology, applied in the sensor field, can solve the problems of no LAPS temperature self-compensation, affecting the output stability and measurement accuracy of the LAPS sensor, limiting practical applications, etc., to improve the detection accuracy and reduce the external environment temperature cross-sensitivity the effect of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but is not limited to this embodiment.
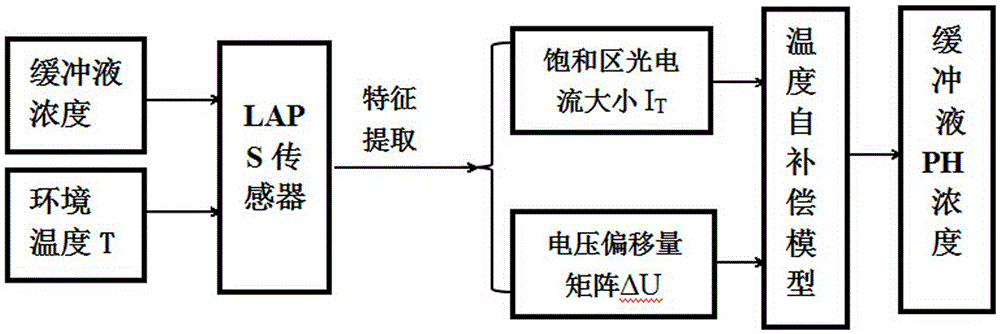
[0018] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the principle of LAPS temperature self-compensation. The LAPS system was used to detect the concentration of PBS buffer solution at different temperatures, the LAPS temperature self-compensation model was established by the support vector machine (SVM) algorithm, and the temperature compensation effect was finally evaluated. The specific steps are as follows:
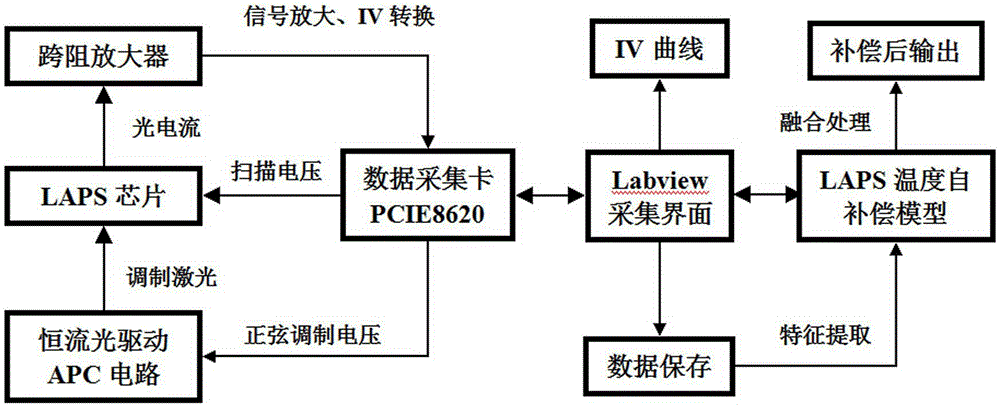
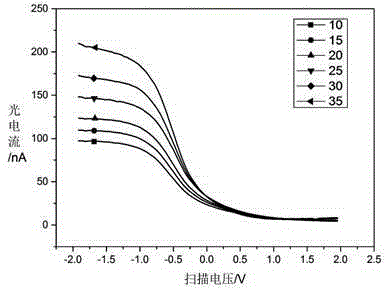
[0019] 1. Acquisition of training samples: figure 2 Schematic diagram of the LAPS test system. pass figure 2 The LAPS test system shown, for PBS buffers at different temperatures (10°C, 15°C, 20°C, 25°C, 30°C, 35°C) and different pH values (pH=6.00, 6.50, 7.00, 7.50, 8.00) Each test was performed 5 times, and a total of 150 groups of data samples were measured.
[0020] 2. Feature extraction: Use ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com