Magnetic negative stiffness damper
A negative stiffness and damper technology, applied in the direction of magnetic springs, springs/shock absorbers, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as complex sensor structures, and achieve simple and compact structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
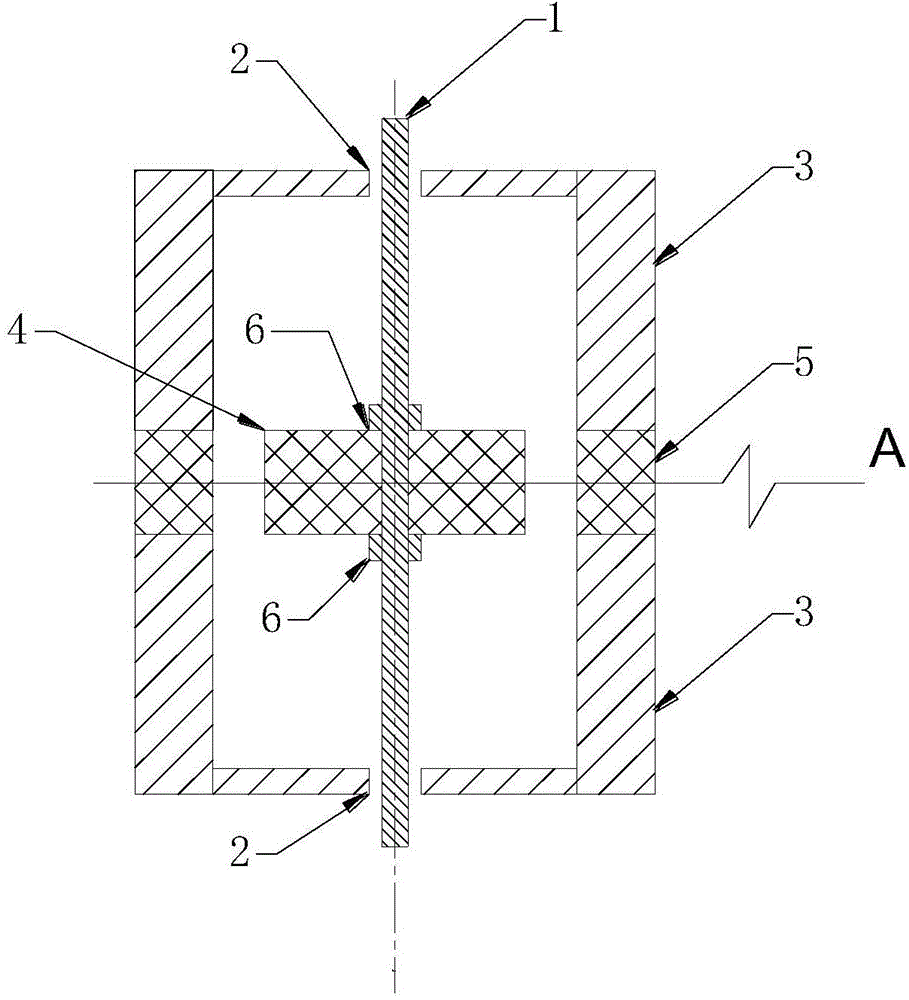
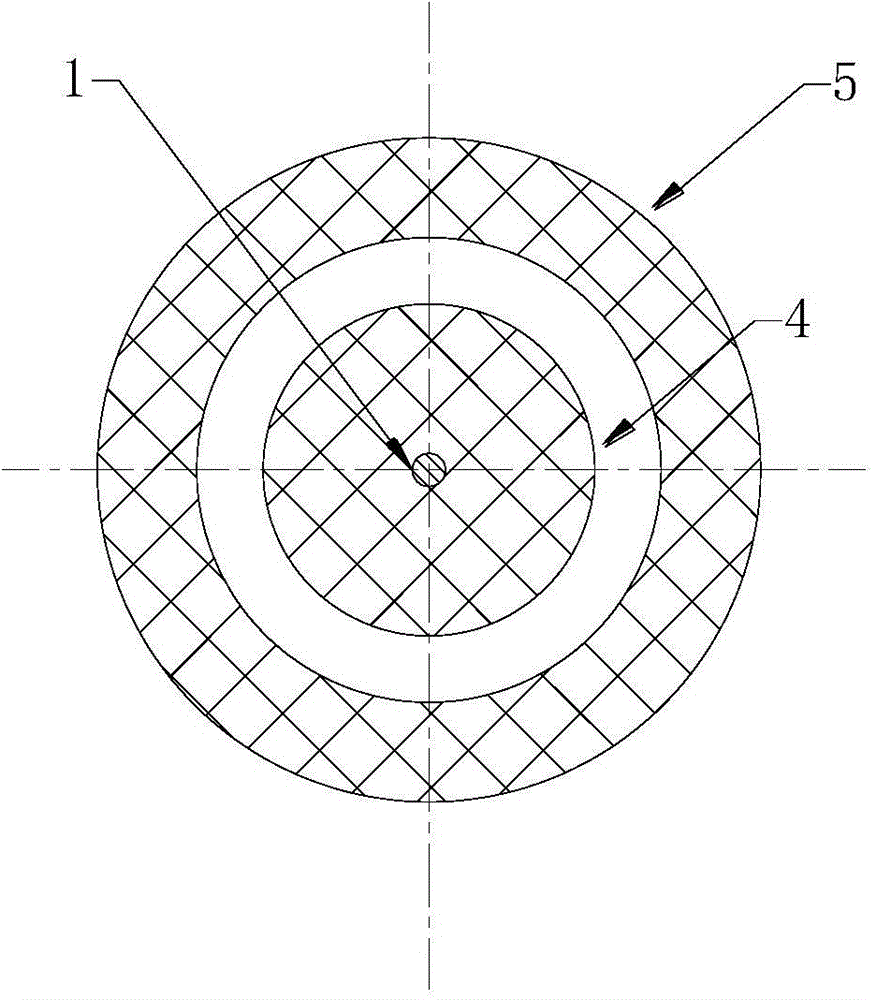
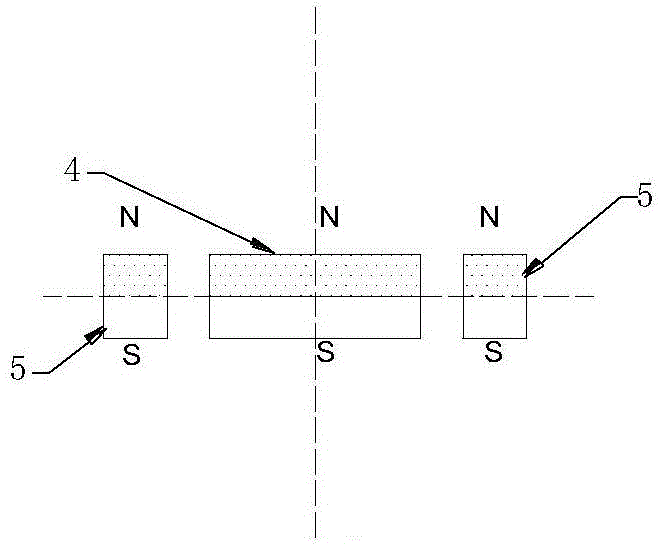
[0029] see Figure 1a and 1b They are the vertical sectional view and the horizontal sectional view of the first embodiment of the magnetic negative stiffness damper according to the present invention, respectively. in Figure 1a is the sectional view of the plane along the vertical longitudinal axis of the magnetic negative stiffness damper, Figure 1b for Figure 1a Sectional view along the horizontal cross-section at A. Such as Figure 1a and 1b As shown, the magnetic negative-stiffness damper (magnetic negative-stiffness damper, MNSD) provided by this embodiment includes a mounting shaft 1 , a sliding bearing 2 , and a pair of magnets arranged along the axial direction of the conductive tube 3 . The pair of magnets includes a first magnet 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com