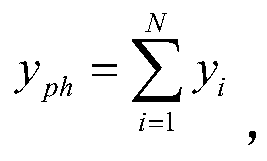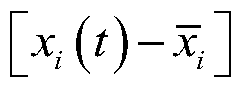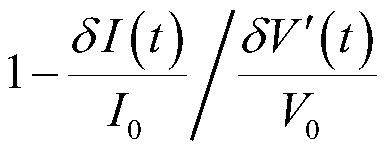A Real-time Error Compensation Method for Atomic Clocks
An error compensation and atomic clock technology, applied in the field of real-time error compensation for atomic clocks to reduce frequency offsets, can solve the problems of limited environmental control, can no longer produce significant effects, cannot be used as a reference or secondary frequency standard, etc. , to achieve the effect of improving frequency stability and reducing frequency shift uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0027] We performed experimental verification on the atomic fountain system. The second-order Zeeman effect is selected as the compensation object, and its noise is amplified so that its contribution to the fountain frequency standard uncertainty is much greater than other effects, and its correlation function is detected to test the change of the fountain frequency standard uncertainty before and after noise compensation.
[0028] In the present embodiment, atomic clock (b) adopts fountain atomic clock (h), figure 2 The resistor (j) and the acquisition part of the control card (k) in the figure 1 The first detector (c) in , figure 2 The detector (i) in is equivalent to figure 1 In the second detector (d), the specific steps of implementing the real-time error compensation method are as follows:
[0029] ① Turn on the fountain atomic clock (h), an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com