Laminate for light emitting device and process of preparing same
A light-emitting device and stacking technology, which is applied in the semiconductor devices of light-emitting elements, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, and electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of loss of optical properties of light-emitting devices and increase of bubble concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
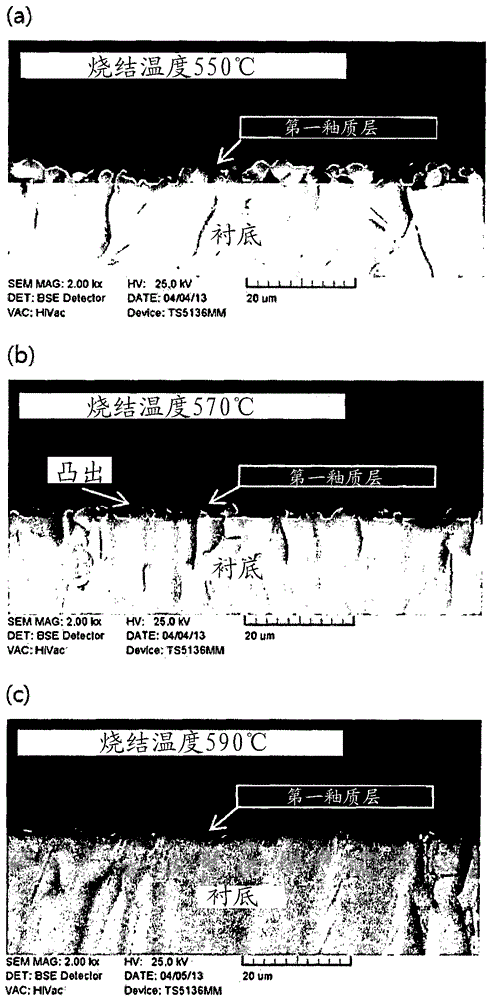
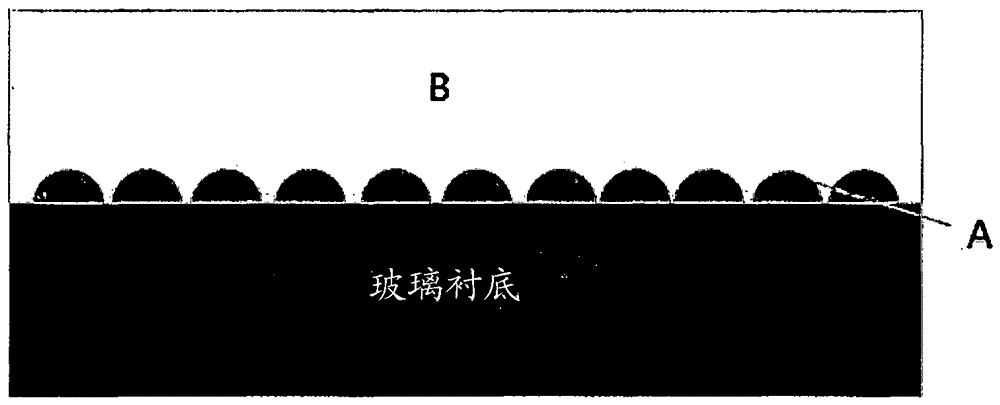
[0172] Example 1: Fabrication of stacks for light emitting devices
[0173] Prepared as follows: a soda lime glass substrate having a thickness of 0.7 mm; a first glass frit paste comprising (based on the total weight of the paste) 20% by weight of a glass frit comprising 28.4% by weight of SiO 2 , 3.6% Al by weight 2 o 3 , 39.5% by weight of B 2 o 3 , 11.6% by weight of ZnO, 3% by weight of P 2 o 5 and (based on the total weight of the first glass frit paste) by weight 13.9% Na 2 O, and (based on the total weight of the paste) 80% by weight of ethyl cellulose as a binder and diethylene glycol butyl ether acetate as a solvent; and a second glass frit paste comprising (based on the total weight of the paste of) 75% by weight of glass frit which includes 70% by weight of Bi 2 o 3 , 10% by weight ZnO, 3% by weight Al 2 o 3 , 7% SiO by weight 2 , 9% by weight of B 2 o 3 and (based on the total weight of the second glass frit paste) by weight 1% Na 2 O and (based on...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com