Design method of few-leaf parabolic isostress steel plate spring provided with ends of different structures
A leaf spring and parabolic technology, applied in the field of stress leaf springs, can solve the problems of unable to provide analytical design formula, unable to meet design requirements, difficult to parameter design values, etc., to improve transportation efficiency and driving safety, reduce design and test. Expenses, quality and cost reduction effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
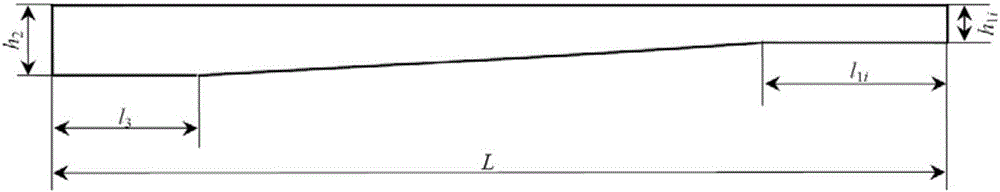
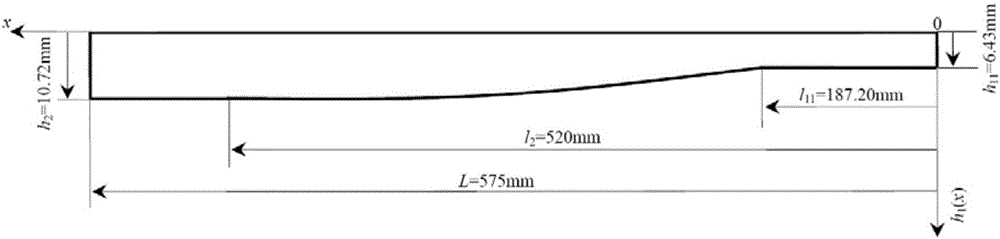
[0049] Embodiment 1: The structure schematic diagram of half of the single-leaf spring of a few-piece parabolic equal-stress leaf spring with non-isomorphic ends is as follows figure 2 As shown, among them, half length L of each leaf spring = 575mm, width b = 60mm, half of the installation distance l 3 =55mm, half load P=1200N acting on the free end of the leaf spring, elastic modulus E=200GPa, safe allowable stress [σ]=500MPa. Half of the rigidity design requirement K M =24N / mm, design the leaf spring with few pieces of parabolic equal stress with non-isomorphic end.
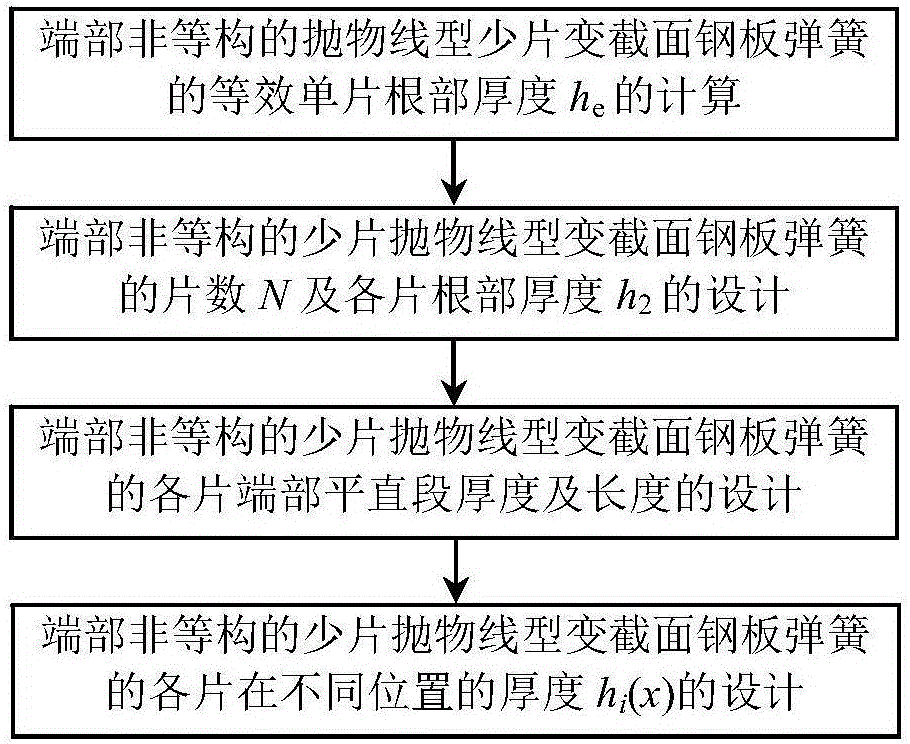
[0050] The design method of the few-sheet parabolic type equal stress leaf spring provided by the examples of the present invention is not isostructural, and its design process is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) The equivalent single root thickness h of the few-piece parabolic equal-stress leaf spring e The calculation of:
[0052] First, select the thickness ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2: The structure schematic diagram of half of the single-leaf spring of a few-piece parabolic type equal-stress leaf spring with non-isomorphic end portion is as follows figure 2 As shown, among them, half length L of each leaf spring = 600mm, width b = 60mm, half of the installation distance l 3 =60mm, half load P=3500N acting on the free end of the leaf spring, elastic modulus E=200GPa, safe allowable stress [σ]=500MPa. Half of the rigidity design requirement K M =52N / mm, design the leaf spring with few pieces of parabolic equal stress with non-isomorphic end.
[0087] The design method of the few-sheet parabolic type equal stress leaf spring provided by the examples of the present invention is not isostructural, and its design process is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0088] (1) The equivalent single root thickness h of the few-piece parabolic equal-stress leaf spring e The calculation of:
[0089] First, select th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com