A path programming method for a plane redundancy robot to avoid obstacles and avoid singularities
A technology for path planning and robotics, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control and other directions, and can solve problems such as
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
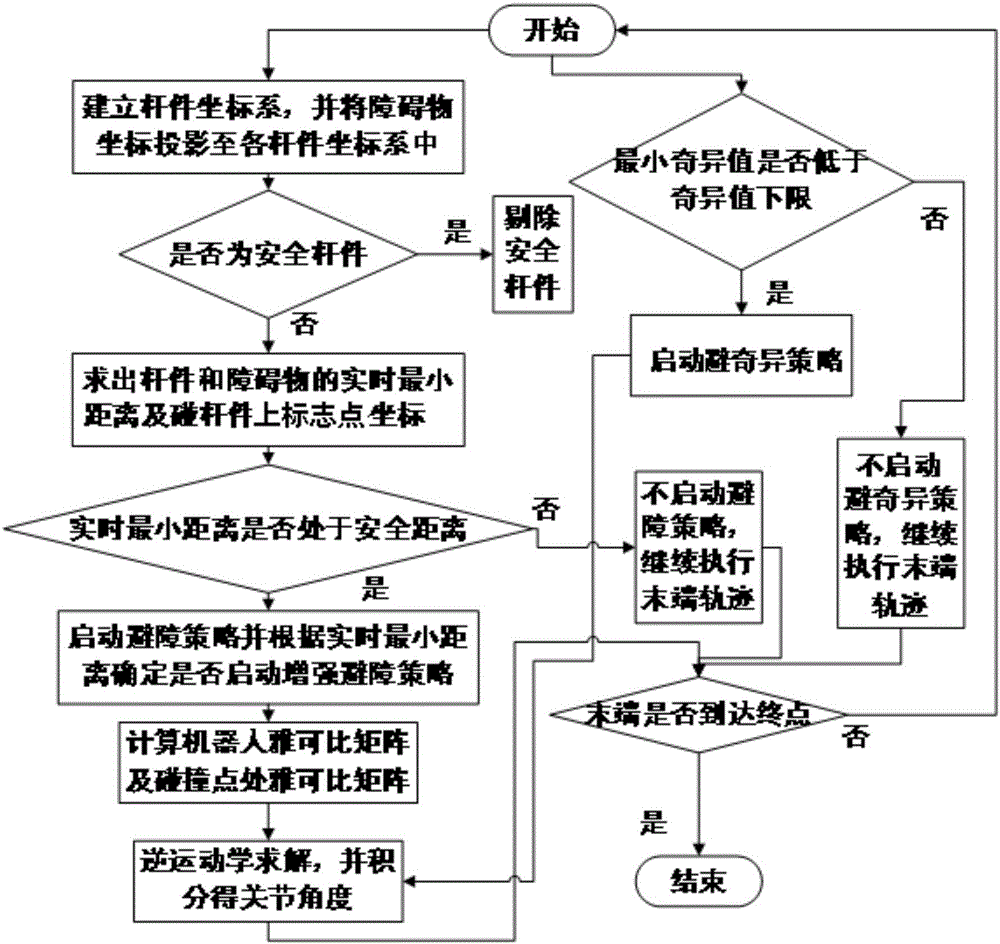
[0111] DETAILED DESCRIPTION One. The method for path planning for obstacle avoidance and singularity avoidance of a planar redundant robot described in this embodiment is performed according to the following steps:
[0112] The method of the present invention involves two simultaneous processes:
[0113] Process 1: The path planning steps for obstacle avoidance are as follows:
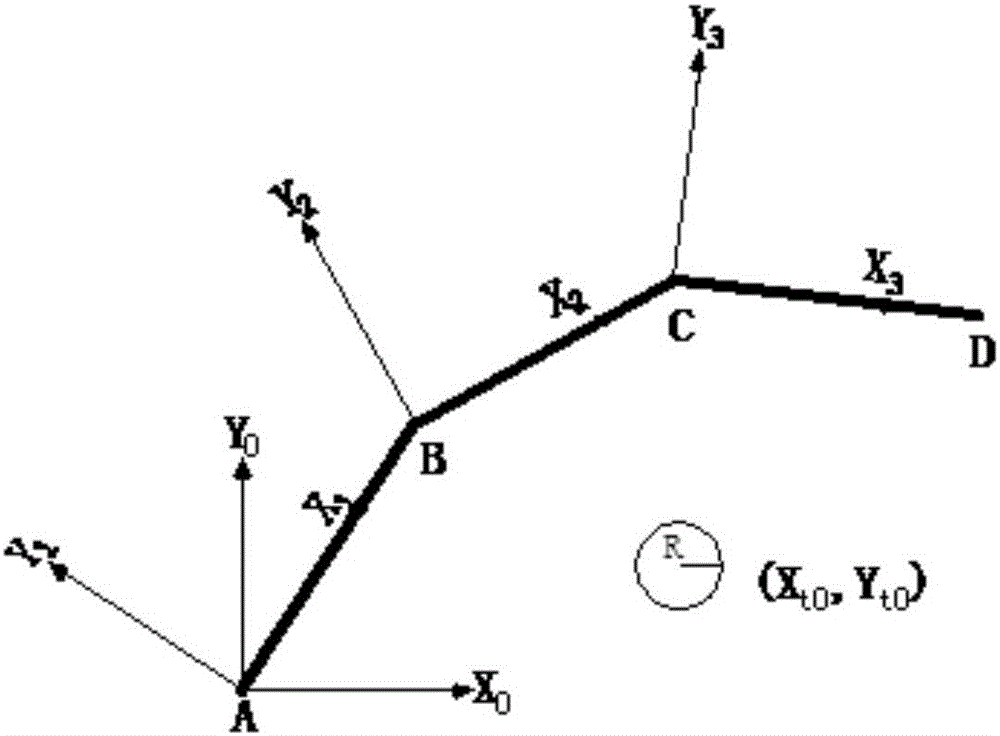
[0114] Step 1: Establish the coordinate system of each member, and project the coordinates of each obstacle to the coordinate system of each member;
[0115] Step 2: Judge whether the rod is a safe rod;
[0116] Step 2. One: If the rod is a safety rod, then the rod will be rejected without any treatment;
[0117] Step 2. Two: If the rod is not a safety rod, go to step three;
[0118] Step 3: Find the real-time minimum distance between the connecting rod and the obstacle and the coordinates of the mark points on each rod;
[0119] Step 4: Judge whether the real-time minimum distance is at a safe distance;
[0120] St...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0139] Specific implementation manner 2. This implementation manner is a further description of a planar redundant robot obstacle avoidance and singularity avoidance path planning method described in specific implementation manner 1. The specific process of step one is:
[0140] The connecting rod of the present invention is composed of rod 1, rod 2 and rod 3;
[0141] The position of the center of the known obstacle in the coordinate system {0} (x t0 ,y t0 ), the connecting rod section is a square with side length a, and the obstacle radius is R. According to the rotation matrix of the coordinate system {1} relative to the coordinate system {0}, the position of the obstacle center in the coordinate system {1} is obtained (x t1 ,y t1 ),which is
[0142] x t 1 y t 1 0 = cosθ 1 - sinθ 1 0 sinθ 1 cosθ 1 0 0 0 1 x t 0 y t 0 0
[0143] By...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0145] Embodiment 3 This embodiment is a further explanation of a planar redundant robot obstacle avoidance and singularity avoidance path planning method described in Embodiment 1 or 2. The specific process of step 2 is:
[0146] If (x t1 ,y t1 )Satisfy
[0147] | y A 1 - y t 1 | ≥ R + a x t 1 ≥ x B 1 + R
[0148] or | y A 1 - y t 1 | ≥ R + a x A 1 - R ≥ x t 1
[0149] Bar 1 is a safety bar, so there is no need to calculate the distance between it and the obstacle;
[0150] If (x t1 ,y t1 )Satisfy
[0151] | y A 1 - y t 1 | ≤ R + a x A 1 - R ≤ x t 1 ≤ x B 1 + R - - - ( 4 )
[0152] Where x A1 , Y A1 Is the position coordinate of point A on the member 1 in the coordinate system {1}, x B1 Is the abscissa of the posit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com