A Design Method for Optimum Coal Pillar Stagger in Shallow Coal Seam Group Working Face
A technology of working face and coal seam group, applied in calculation, ground mining, earthwork drilling and mining, etc., can solve the problems of safety production and surface environmental protection, and achieve the effect of reducing surface subsidence disturbance and slowing down surface damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
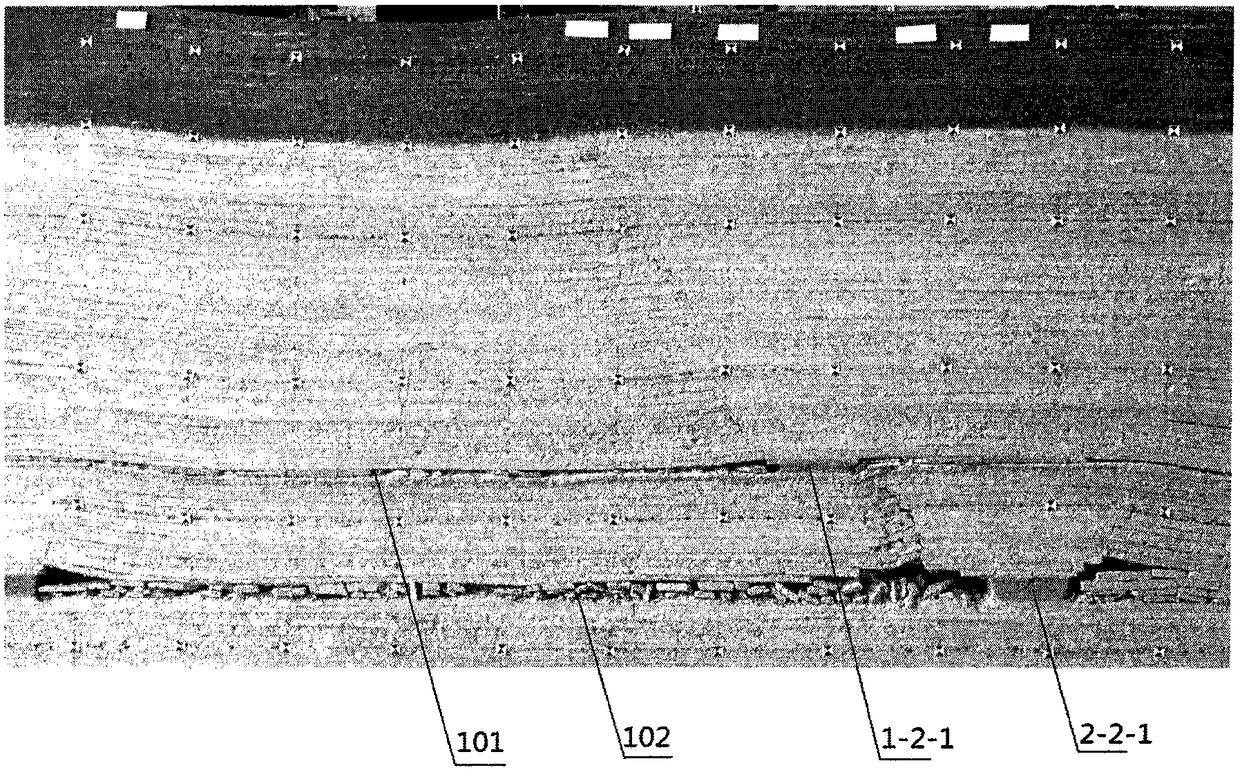
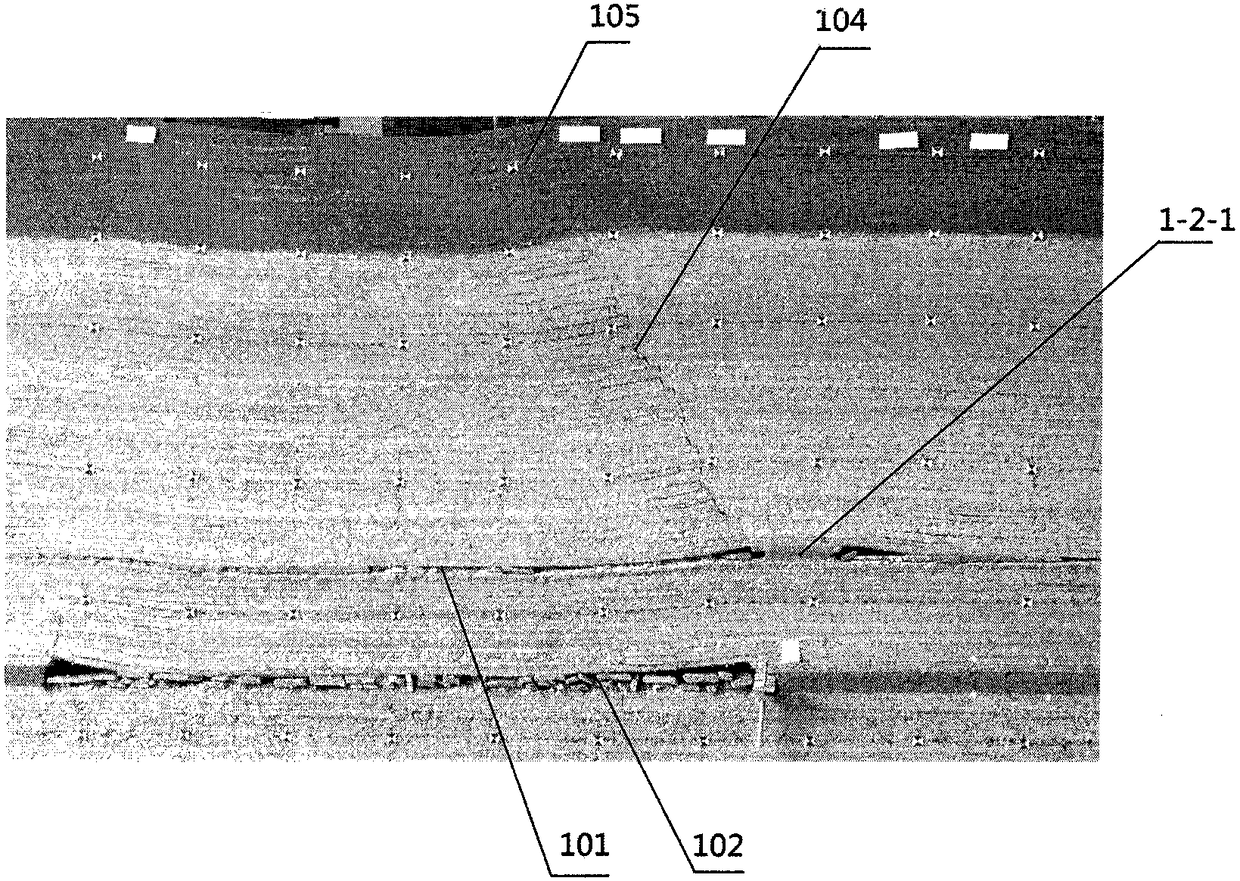
[0075] Take the north wing east area of a coal mine as an example to illustrate the application of this method. The inclination angle of the coal seam in this mining area is about 1°. There are 2 main coal seams, namely 1-2 coal seam (upper coal seam) and 2-2 coal seam (lower coal seam). The average thickness of -2 coal seam is 1.8m, and the average thickness of 2-2 coal seam is 5m. The average distance between 1-2 coal seam and 2-2 coal seam is 35m. The buried depth of the 1-2 coal seam is about 110m, the thickness of the bedrock is 70m, and the thickness of the loose soil layer is 40m, which is a typical shallow-buried coal seam group.
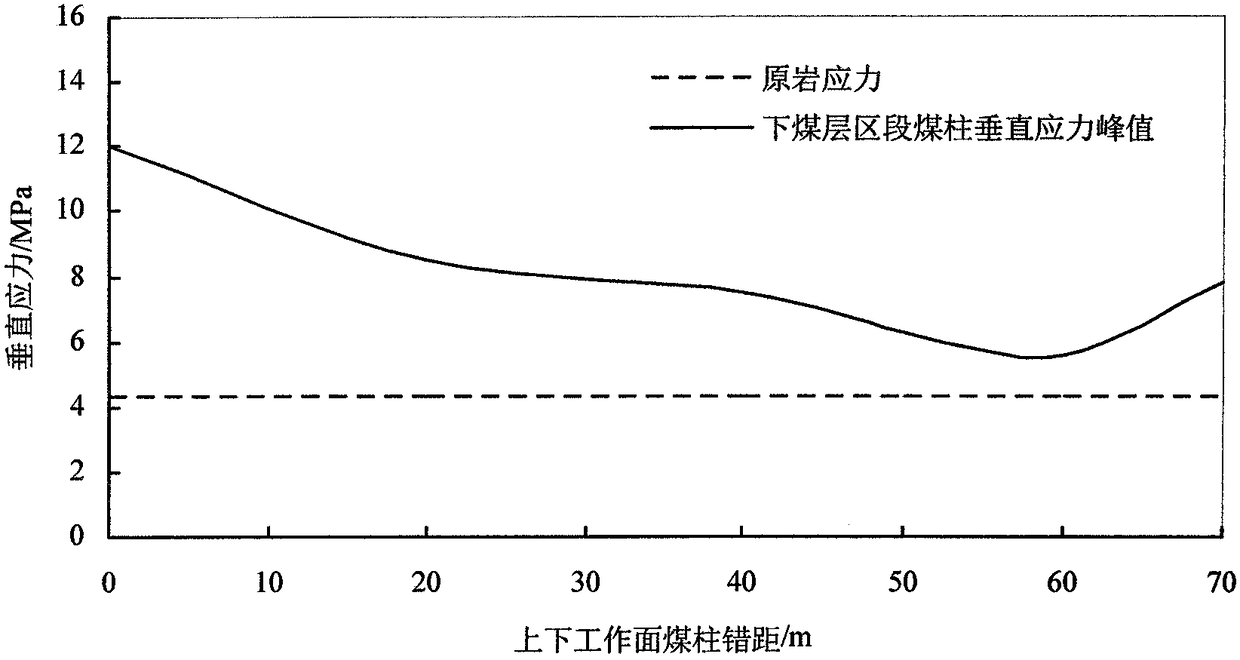
[0076] The mine originally used the upper and lower coal seams to overlap. In order to avoid the stress-increasing area of the upper coal seam, the 2-2 coal seam face must be mined after the 1-2 coal seam face was mined, which caused continuous tight production of the working face. In addition, the stress on the coal pillars on the working...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com