Structure stability determining method and system for polymeric ComplexingAgent
A surfactant and structural stability technology, applied in the field of structural stability judgment of polymer surfactants, can solve the problems of long research and development cycle and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
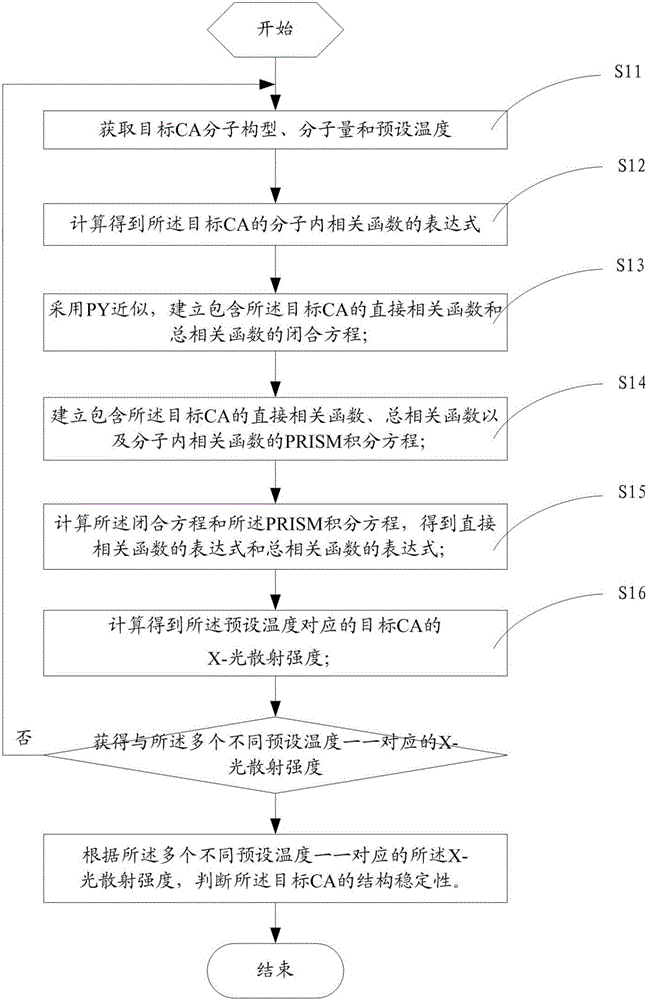
[0080] This embodiment provides a method for judging the structural stability of polymeric surfactants, comprising the following steps:
[0081] Step S0: Determine the molecular configuration, molecular weight and multiple preset temperatures of the surfactant.
[0082] This step is mainly used to determine the molecular configuration of the polymer surfactant and the molecular weight of the surfactant. CAs with different molecular weights have different microstructures. Moreover, at different temperatures, the structure of the surfactant will also be different
[0083] Step S1: For each preset temperature, perform the following steps respectively until the X-ray scattering intensities corresponding to the multiple different preset temperatures are obtained.
[0084] By calculating the X-ray scattering intensities at different preset temperatures, the structural changes of the polymeric surfactants at different temperatures can be compared, thereby determining the structural...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Compared with the previous embodiment, this embodiment regards the establishment of the reference action point model of the surfactant CA in step S112 as an independent step, and the specific step 1 is divided into the following steps:
[0124] Step S120: Obtain the molecular configuration, molecular weight and preset temperature of the surfactant CA.
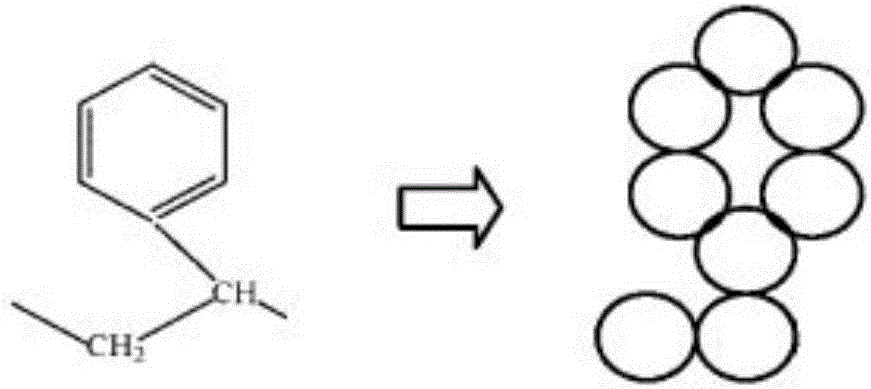
[0125] Step S121: According to the molecular configuration and molecular weight of the surfactant, establish a reference action point model of the surfactant CA.
[0126] Step S122: Calculate and obtain the expression of the intramolecular correlation function of the surfactant CA.
[0127] In this step, calculation is performed directly according to the model parameters in step 121 to obtain the expression of the intramolecular correlation function of the surfactant CA.
[0128] Step S123: using PY approximation to establish a closed equation including the direct correlation function and the total correlation function ...
Embodiment 3
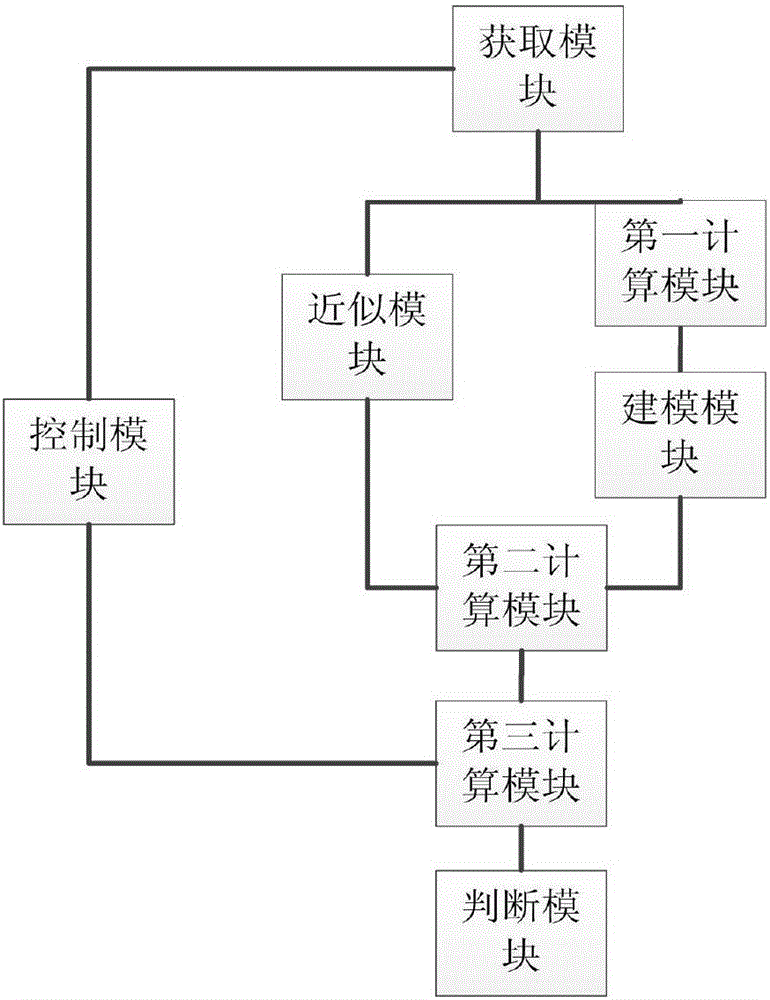
[0151] Corresponding to the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment provides a system for judging the structural stability of polymer surfactants, combining image 3 It can be seen that the system described in this embodiment specifically includes:
[0152] The acquisition module is used to acquire the molecular configuration, molecular weight and multiple different preset temperatures of the surfactant;
[0153] Specifically, the acquisition module includes:
[0154] The structure acquisition unit is used to determine the molecular configuration and molecular weight of the surfactant;
[0155] By obtaining the molecular configuration and molecular weight, the molecular chain structure of the surfactant is determined.
[0156] The temperature acquisition unit is used to determine the preset temperature of the surfactant.
[0157]The control module is used to control the corresponding module to perform calculation operations for each preset temperature until the X-ray s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com