Structure capable of preventing railroad bed mud pumping and paving method thereof
A technology for railway subgrade and mud-flurrying, which is applied to roads, tracks, ballast layers, etc., can solve problems such as failure to improve the strength of the subgrade, not allowing the filling of the subgrade, and inability to reduce the dynamic stress of the train load.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
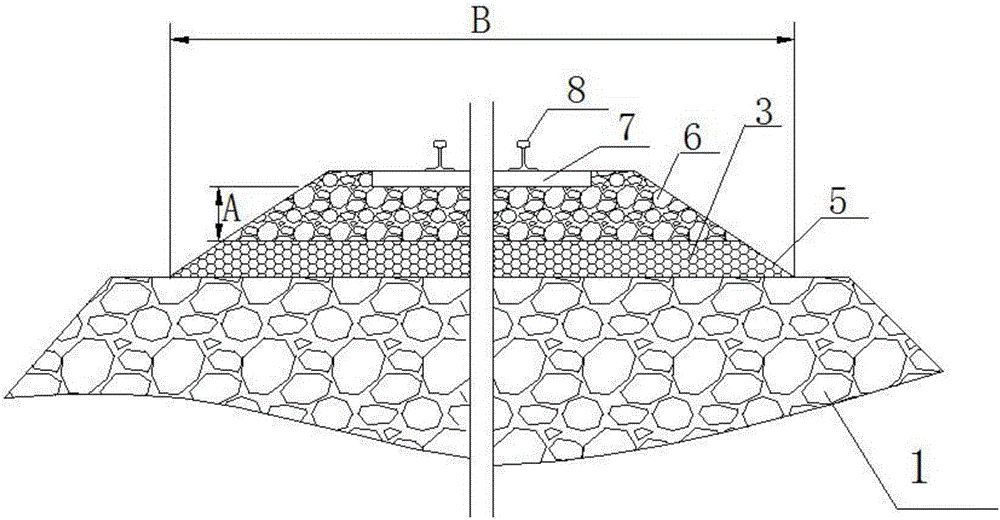
[0016] Such as figure 1 As shown, the structure to prevent the mud and mud of the railway embankment is the first protective layer 3 arranged between the surface of the railway embankment 1 and the ballast 6. The ballast 6 is laid with sleepers 7 and rails 8, and the first protective layer 3 is formed by stacking Composed of crushed stones on the surface of the railway subgrade 1 and polyurethane waterproof paint filled in the gaps between the crushed stones, the first protective layer 3 has a 5% double-sided drainage slope 5, and the water that seeps down to the first protective layer 3 is covered by the first protective layer. Layer 3 is isolated and then drained through drainage slope 5. Simultaneously, the mud that rises up is isolated by the first protection layer 3, prevents mud from turning outwards to the ballast 6 or through the ballast 6 to squeeze out.
[0017] The laying method of the structure to prevent the mud from pouring out of the railway subgrade is as foll...
Embodiment 2
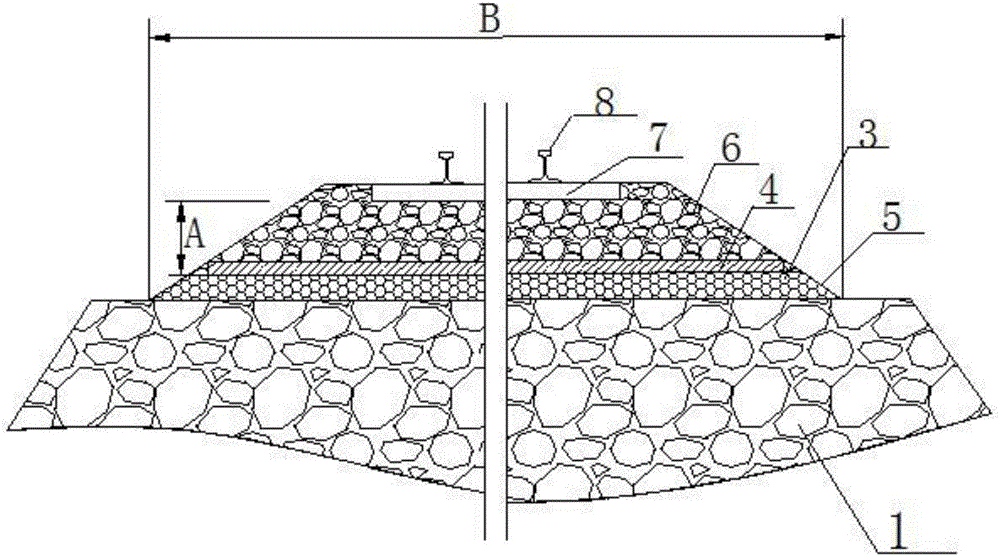
[0019] Such as figure 2 As shown, the structure for preventing the mud and mud of the railway embankment includes a first protective layer 3 and a second protective layer 4 sequentially arranged on the surface of the railway embankment 1 , and a sleeper 7 and a steel rail 8 are laid on the ballast 6 . Wherein, the first protective layer 3 is composed of crushed stones accumulated on the surface of the railway subgrade 1 and polyurethane waterproof paint filled in the gaps of the crushed stones, and the first protective layer 3 has a 5% double-sided drainage slope 5 . The second protection layer 4 is formed by curing two-component polyurea waterproof coating. The water that seeps down to the second protective layer 4 is isolated by the second protective layer 4 , and then the water is discharged through the drainage slope 5 of the first protective layer 3 . Simultaneously, the mud that rises up is isolated by the first protection layer 3, and the second protection layer 4 for...
Embodiment 3
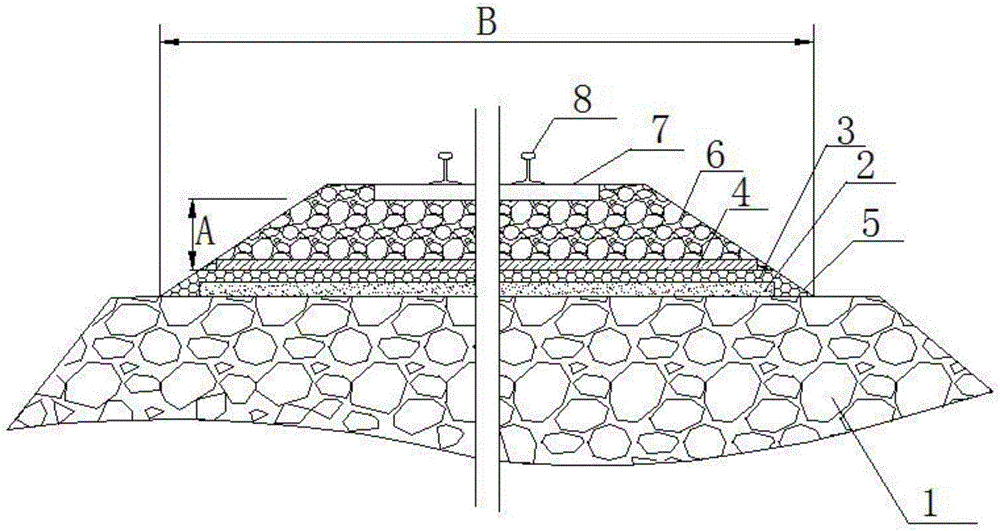
[0024] The laying method of the structure that prevents the railway subgrade from turning mud and mud is as follows: first, a uniform, dense and smooth sand cushion 2 is laid. The average particle size of the sand material in the sand cushion 2 is 3mm, and the laying thickness of the sand cushion 2 is 5cm. Then the crushed stones with an average particle diameter of 6mm are laid on the surface of the above-mentioned sand cushion 2, the laying thickness is 5cm, the transverse width B on the main line is 5m, and the distance A between its upper surface and the bottom of the sleeper 7 is 30cm; First, spray the polyurethane waterproof coating into the gravel gap along the direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the line, and then spray the polyurethane waterproof coating into the gravel gap along the direction parallel to the longitudinal direction of the line, so that the polyurethane waterproof coating fills all the gravel pores, After the polyurethane waterproof...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com