Device and method of inhibiting potential induced degeneration
A potential-induced attenuation, photovoltaic system technology, applied in circuit devices, output power conversion devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and affect the reliability of photovoltaic systems, and achieve low cost, low power consumption, and small capacity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
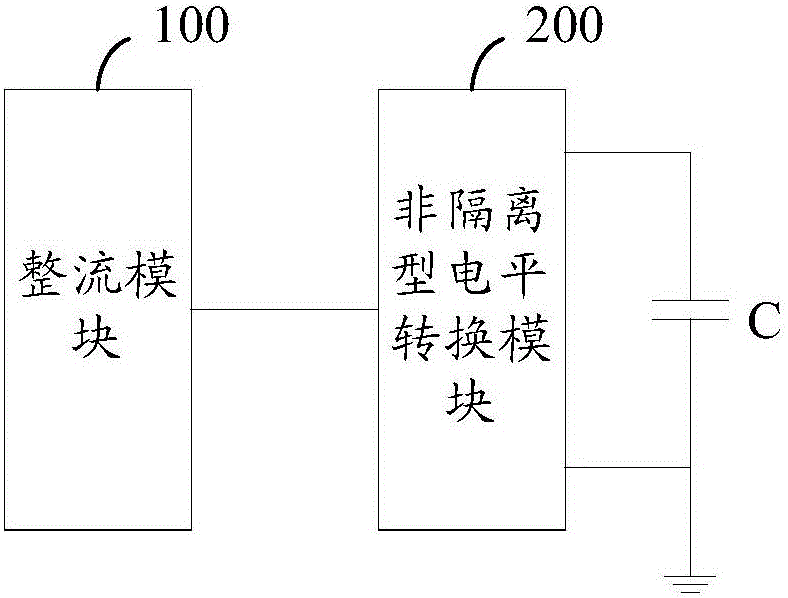
[0057] see Figure 1a and Figure 1b , which is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 1 of the device for suppressing potential-induced decay provided by the present invention.
[0058] The device for suppressing potential-induced attenuation provided in this embodiment is connected between the AC output terminal of the converter in the photovoltaic system and the grid-connected power frequency transformer; the device includes: a rectifier module 100, a non-isolated level conversion module 200 and at least one capacitor C;
[0059] like Figure 1a As shown, the input end of the rectification module 100 is connected to the output end of the converter; the rectification module 100 is used to rectify the alternating current output by the converter into direct current; the non-isolated level conversion A module 200, configured to perform level conversion on the direct current output by the rectification module; the level conversion is step-up conversion or voltage reverse conversion;...
Embodiment 2
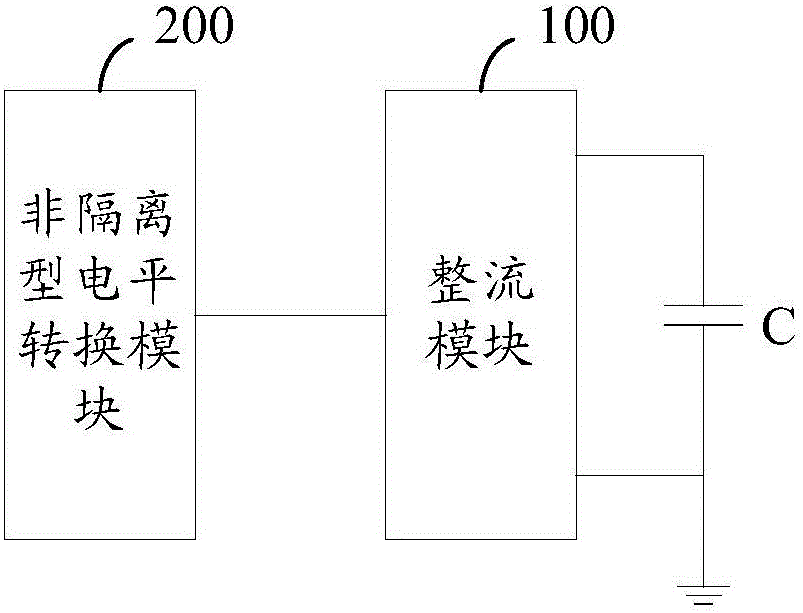
[0067] see Figure 2a and Figure 2b , which is a schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the device provided by the present invention.
[0068] In this embodiment, when the input end of the rectification module 100 is connected to the output end of the converter: the non-isolated level conversion module is specifically any one of the following: Boost circuit, Buck-boost circuit , Cuk circuit, Sepic circuit and Zeta circuit.
[0069] It should be noted that in this embodiment, the rectification module 100 is an uncontrolled rectification bridge as an example for introduction. like Figure 2a As shown, the uncontrolled rectifier bridge is a three-phase full-bridge circuit.
[0070] In this embodiment, the buck-boost circuit 2001 is introduced as the non-isolated level conversion module; the output terminal of the buck-boost circuit 2001 is connected in parallel with the capacitor C;
[0071] When the positive pole of the capacitor C is grounded, the voltage of the ph...
Embodiment 3
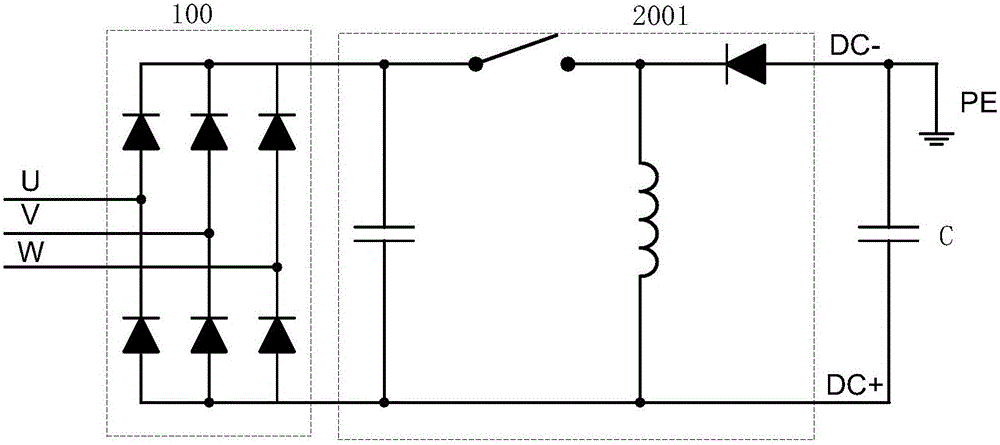
[0079] see Figure 4a and Figure 4b , which is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 3 of the device provided by the present invention.
[0080] In the device provided in this embodiment, when the input end of the rectification module 100 is connected to the output end of the converter: the non-isolated level conversion module is a Boost circuit 2002; the output ends of the Boost circuit 2002 are connected in parallel The capacitance C;
[0081] like Figure 4a As shown, when the negative electrode of the capacitor C is grounded, the voltage of the photovoltaic system to the ground is positive by controlling the output voltage of the non-isolated level conversion module.
[0082] like Figure 4b As shown, when the positive pole of the capacitor C is grounded, the voltage of the photovoltaic system to ground is negative by controlling the output voltage of the non-isolated level conversion module.
[0083] Combine below Figure 5a illustrate Figure 4a The device provided c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com