An Efficient Page Organization and Management Method for Non-Volatile Memory
A technology of non-volatile memory and management method, which is applied in the field of computer memory page management, and can solve the problems of high number of page erases, performance bottlenecks, and failure to consider NVM wear leveling, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
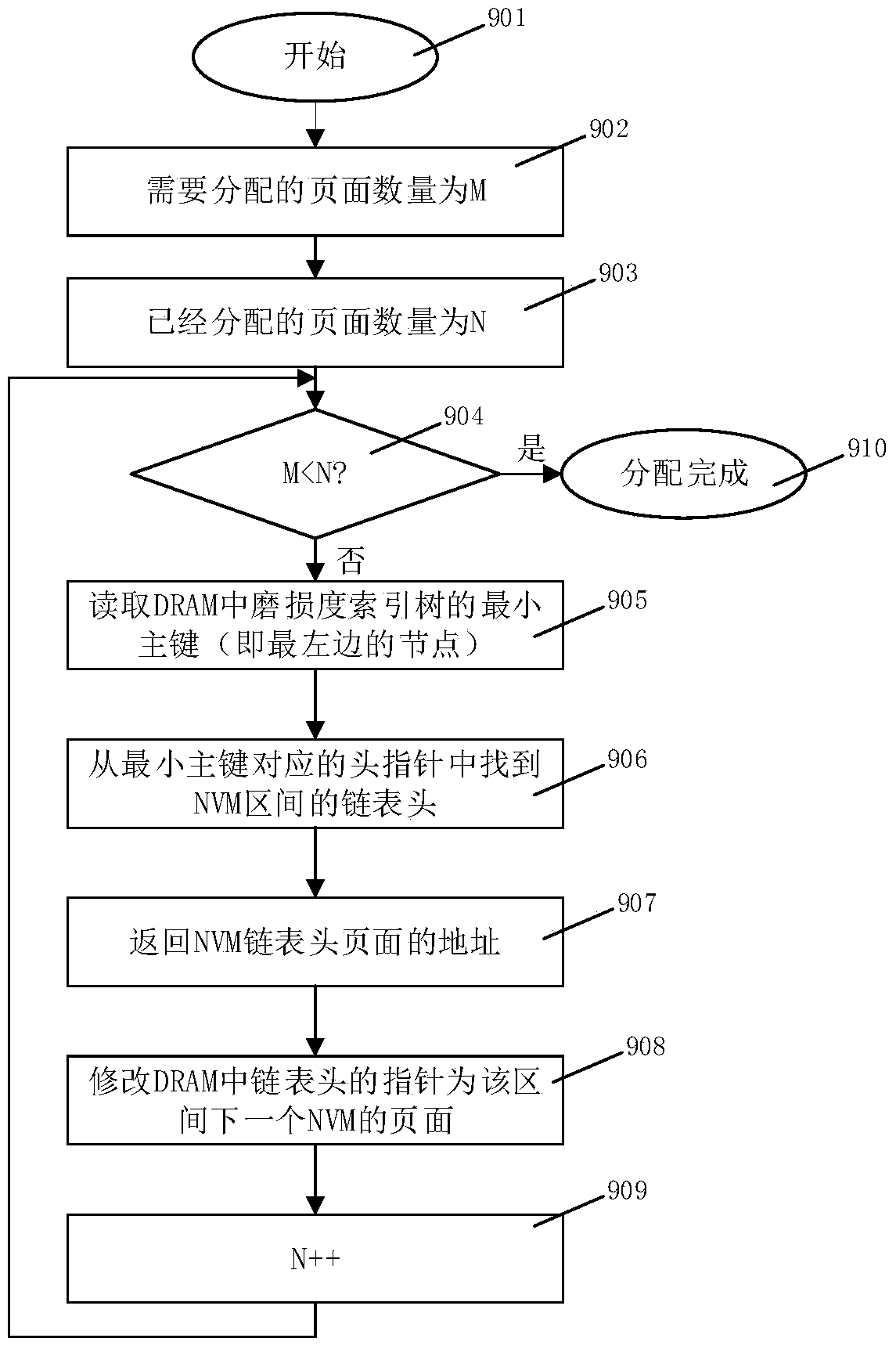
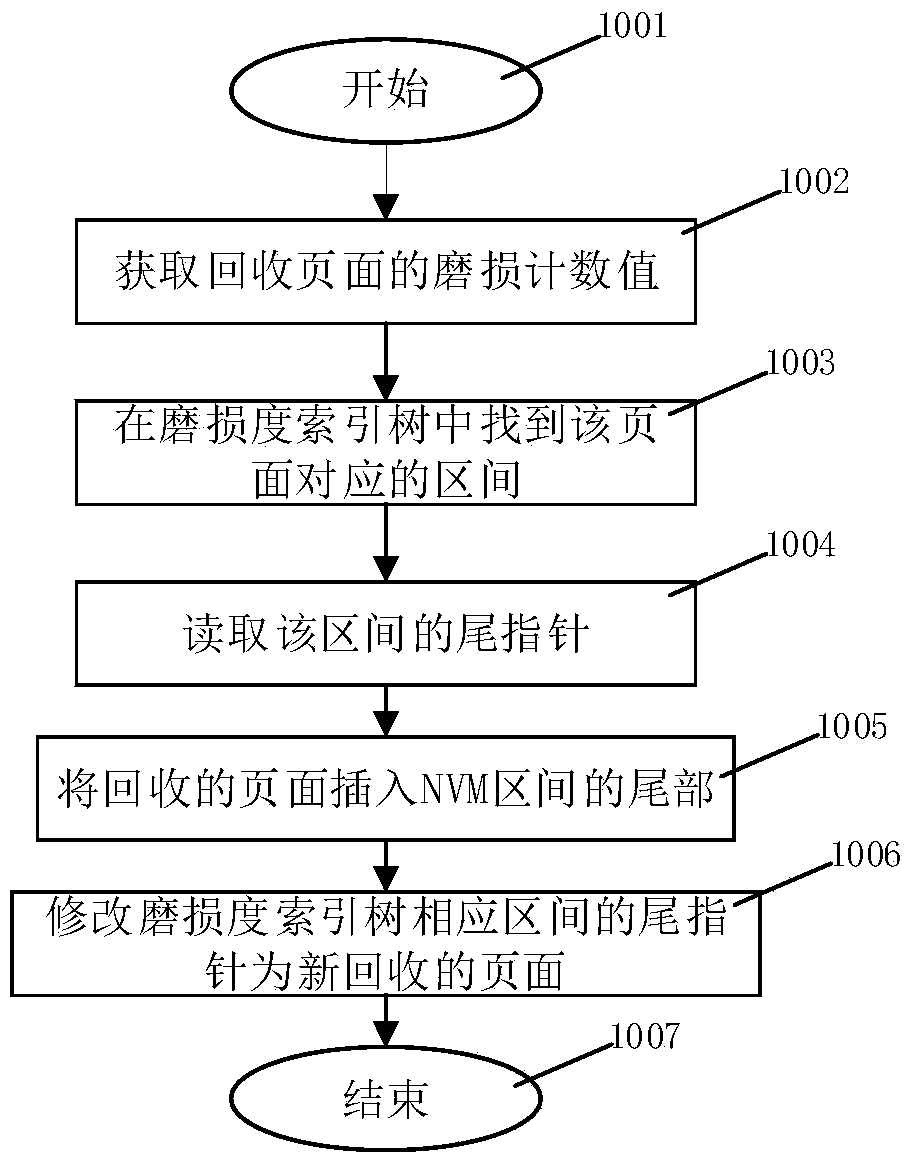
[0067] As shown in the figure, a tree data structure based on the wear counting mechanism provided in this embodiment manages the free space of the NVM, including the following steps:
[0068] Divide the NVM space into fixed-size pages (for example, 4KB, 2MB, or a collection of pages of different sizes), and use a continuous area in the NVM memory to store the "wear count value" of each page. The "wear count value" records The cumulative number of writes per page;
[0069] Each NVM page has two sets of pointer management, one of which is used to link all pages into a "free list", and the other pointer is used to combine all NVM pages into different intervals according to the wear count value;
[0070] When the system is running, the free pages in NVM are organized in a tree structure, which is called "wear index tree". The bottom layer of the wear degree index tree is the free pages in NVM. The free pages are divided into multiple intervals according to the wear count value, ...
Embodiment 2
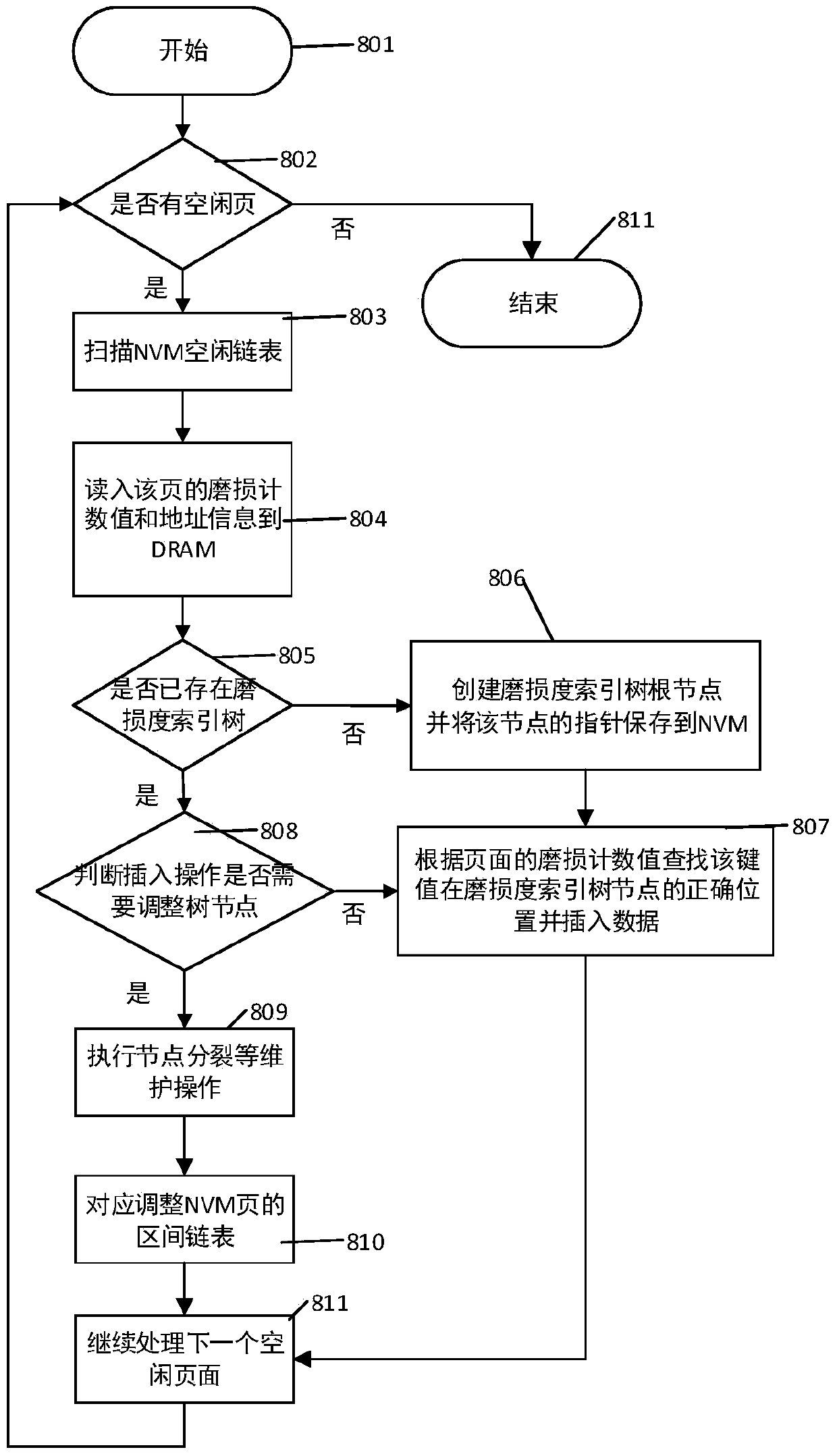
[0081] The index initialization or reconstruction process provided by this embodiment, such as figure 1 Shown:
[0082] The process starts at step 801 and proceeds as follows:
[0083] In step 802, it is judged whether there is a free page in the NVM, if not, then the process ends in step 811; if there is, in step 803, the free linked list of the NVM page is scanned;
[0084] In step 804, read the address and wear count information of each scanned page into DRAM;
[0085] In step 805, it is judged whether there is already a wear degree index tree in the DRAM. If not, go to step 806; otherwise go to step 807.
[0086] In step 806, create a new wear degree index tree root node, and save the pointer of this node to NVM;
[0087] In step 807, find the correct position of the page from the wear degree index tree, and insert the data, that is, it is necessary to ensure that the primary keys of the nodes in the DRAM are arranged in an orderly manner;
[0088] In step 808, it is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com