A method for cultivating rice varieties resistant to rice blast
A technology for resistance to rice blast and rice blast, applied in the field of breeding, can solve problems such as the contradiction between strong resistance and high yield, and achieve the effects of improving the level of resistance spectrum and lasting resistance, broadening the genetic distance, and prolonging the service life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Development of a functional marker of the panicle blast resistance gene Pb1
[0047] 1. Primer design
[0048] Pb1 gene: genebank accession number AB570371.1; P5 gene: genebank accession number AB570370.1.
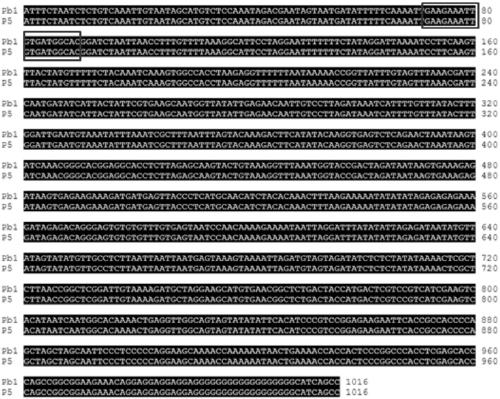
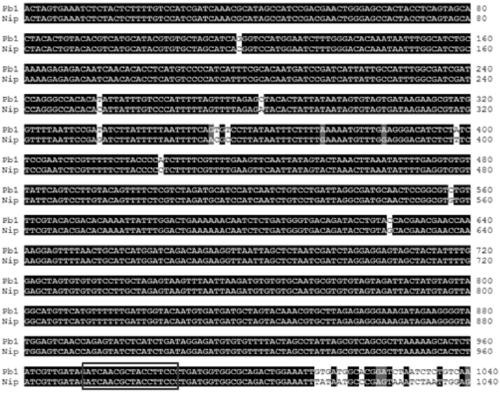
[0049] Pb1 is located in a tandem repeat of 60 kb, and Pb1 is located in the second repeat, corresponding to P5 in the first repeat. The protein encoded by P5 has only one more glutamic acid than Pb1. Both Pb1 and P5 have panicle blast resistance, but Pb1 has significantly higher panicle blast resistance than P5. The difference in the panicle resistance of the two genes is not due to this glutamic acid. The difference was caused by the gene expression level of Pb1 was significantly higher than that of P5. By comparing the upstream promoter region of the Pb1 and P5 gene coding regions, it was found that the promoter sequence of the upstream 1016bp of the gene coding region was completely matched ( figure 1 ), and the susceptible varieties (Nip is Nipponb...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 Pita, Piz-t functional markers and primers
[0077]The Pita and Piz-t functional markers and primers all used molecular markers and primer sequences already published in the prior art (Table 1). A 1042bp fragment was detected by using Pita primers, while Npita primers could not amplify the target fragment. Such a material contains the Pita gene; when using Piz-t functional marker primers to amplify two different types of materials, there is a 160bp target band Only A base type (including Piz-t gene), containing a 221bp target band only G base type (excluding Piz-t gene), 331bp target band is A base type (containing Piz-t gene ) and G base type (excluding Piz-t gene) shared bands.
[0078] The experimental procedure for the detection of the disease resistance gene Pita was based on reference [1], with slight modifications: ①In the amplification program, 72°C extension was used for 1 min; ②Electrophoresis was performed using 4% polyacrylamide gel.
[0079] The...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3 Evaluation of resistance gene polygenic aggregation mode "Pita+Pb1+Piz-t".
[0087] Using the molecular markers in Example 1, 227 pre-test materials in Jiangsu Province in 2015 were genotyped for disease resistance genes Pita, Pb1 and Piz-t. The results showed that: among 15 lines (including Pita+Pb1+Piz-t), 7 materials had a comprehensive disease index lower than 4.0 (above medium resistance), and the combination probability of medium resistance to rice blast was 46.47%; 51 lines (excluding Pita+Piz-t) Pb1+Piz-t), only 7 materials had a comprehensive disease index lower than 4.0 (above moderate resistance), and the combined probability of moderate resistance to rice blast was 13.73%; the success probability of moderate resistance to rice blast increased by 32.74 percentage points.
[0088] Table 2 Comparison of the mean value of rice blast correlation index of different taxa in the aggregation pattern "Pita+Pb1+Piz-t"
[0089]
[0090] Remarks: Above medi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com