Timing Synchronization Method in Physical Layer
A timing synchronization, physical layer technology, applied in the field of broadcasting and communication, can solve the problems of inability to store the whole frame of data, low signal-to-noise ratio, carrier frequency offset effect, etc., to achieve the effect of complexity and low signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
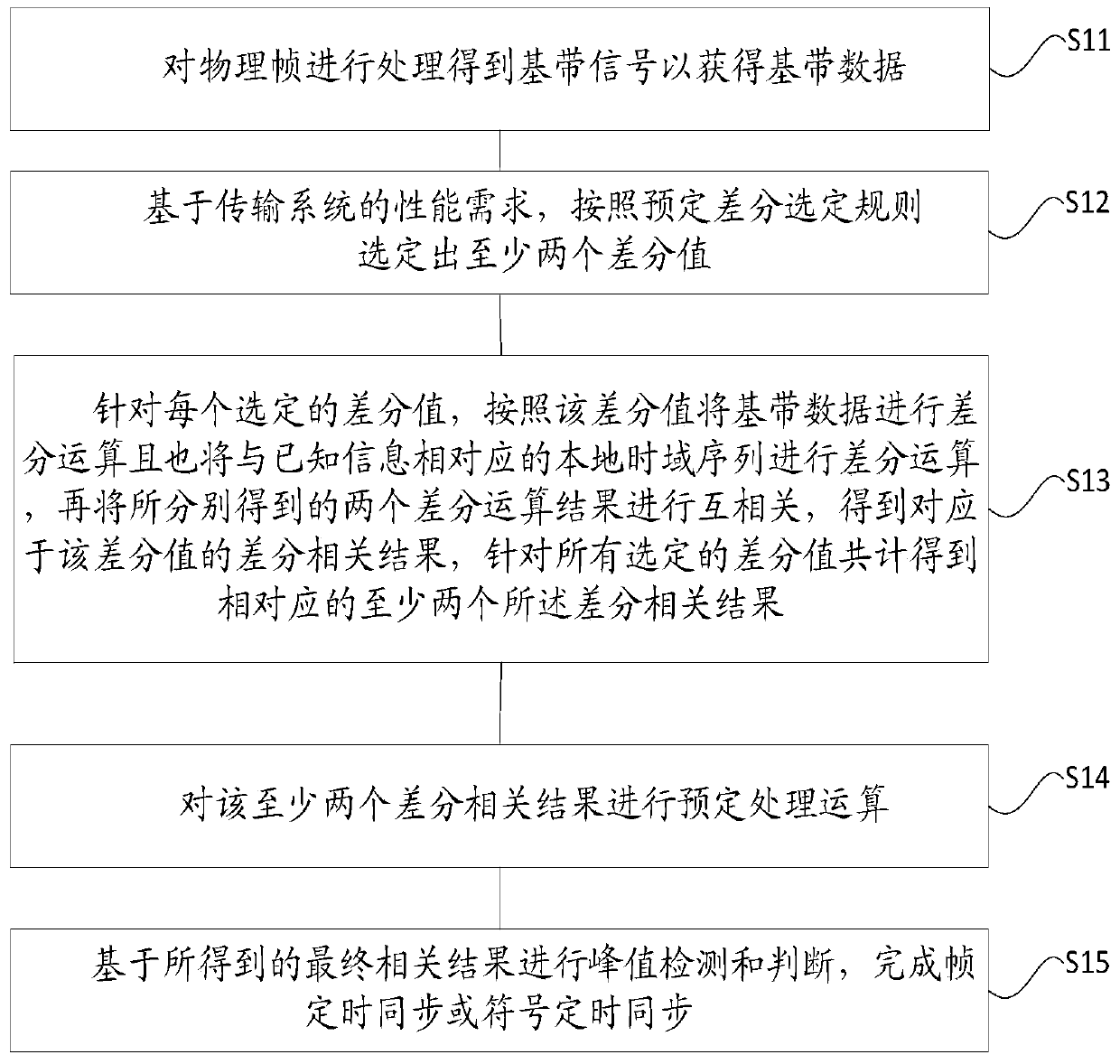
[0027] An embodiment of the present invention provides a timing synchronization method in a physical layer. Such as figure 1 What is shown is a schematic flowchart of the timing synchronization method in the specific implementation manner of the present invention.
[0028] refer to figure 1 , in this embodiment, the timing synchronization method is suitable for a transmission system that utilizes known information for transmission. The transmission system is a broadcasting system or a communication system.
[0029] If the transmission system is a multi-carrier system, its preamble symbols contain known information. For example, the preamble symbol is generated based on the OFDM symbol, and pilots are inserted into certain subcarriers in the OFDM symbol, then the preamble symbol contains known information. Alternatively, the preamble symbol is based on the superposition of two time domain signals in the time domain, one is a time domain signal for signaling and the other is...
Embodiment 2
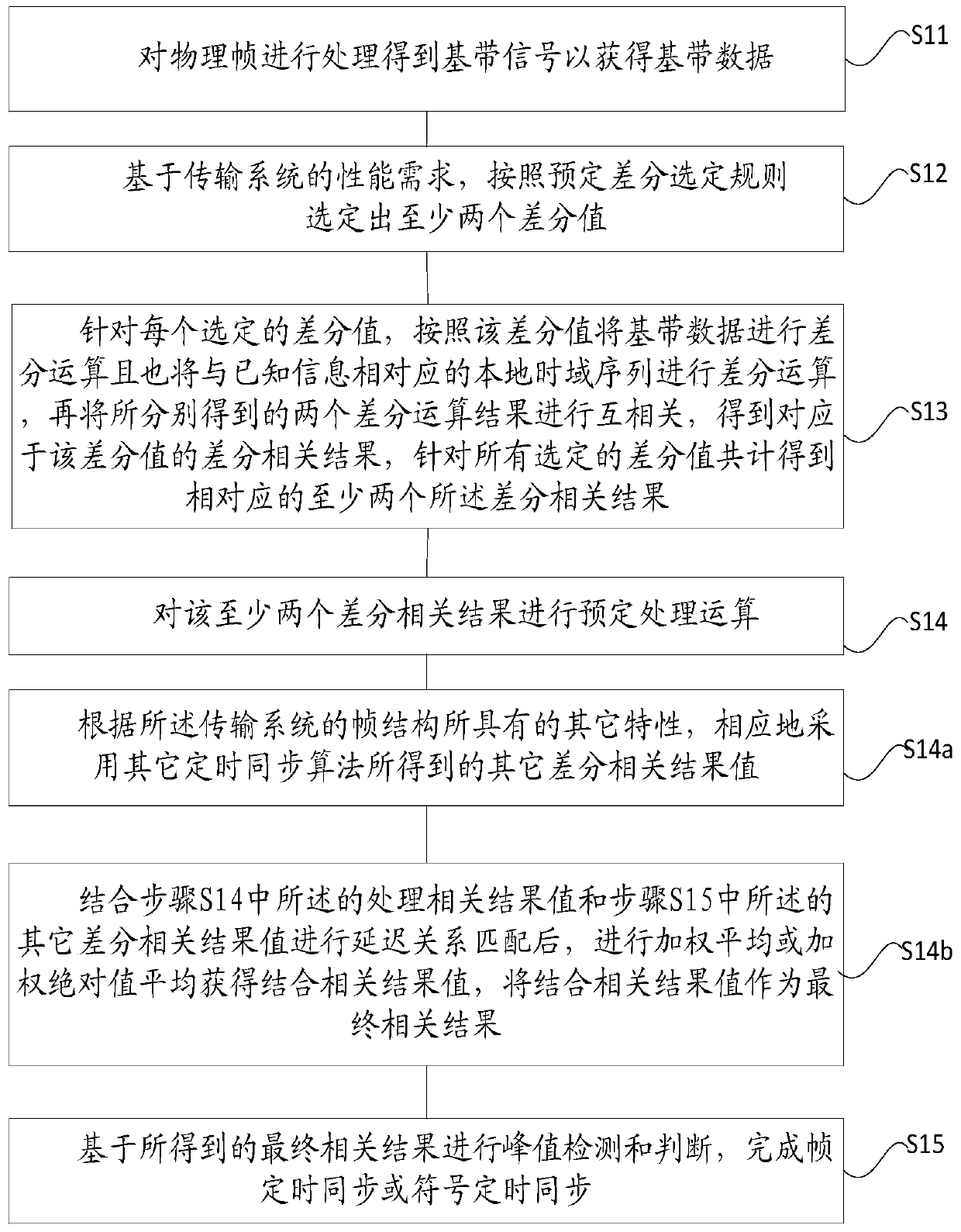
[0089] In addition to the technical solution of using at least two differential values for positioning synchronization in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, the inventors also found that the process of using a single differential value for positioning synchronization in the prior art can also be compared with other timing synchronization Other differential correlation results obtained by the algorithm R other,m Combined, it is used to solve the problems caused by positioning synchronization with a single difference value, such as only generating a set of difference correlation results, which cannot obtain very robust performance.
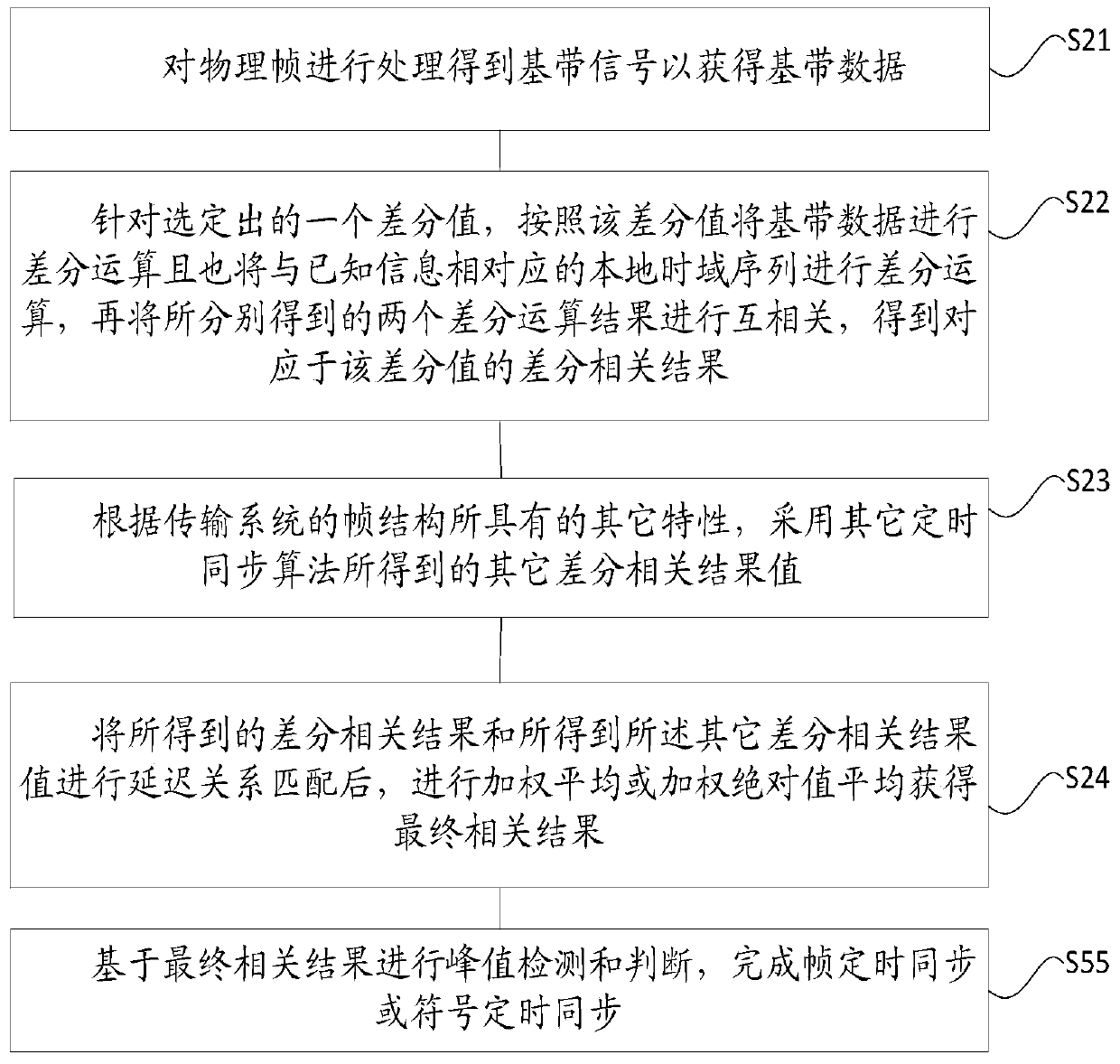
[0090] The present invention also proposes a timing synchronization method in the physical layer, image 3 It is a schematic flowchart of the timing synchronization method in Embodiment 2 of the specific implementation manner of the present invention.
[0091] refer to image 3 , the timing synchronization method in Embodiment 2, which is used in a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com