A method for graphene to remove valence electrons
A technology of valence electrons and graphene, applied in the field of graphene devalence electrons, can solve the problems of undisclosed graphene devalence electron technology, high chemical stability of graphene, difficult application of graphene, etc., so as to change the characteristics of mutual attraction , the effect of easy industrial scale-up and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
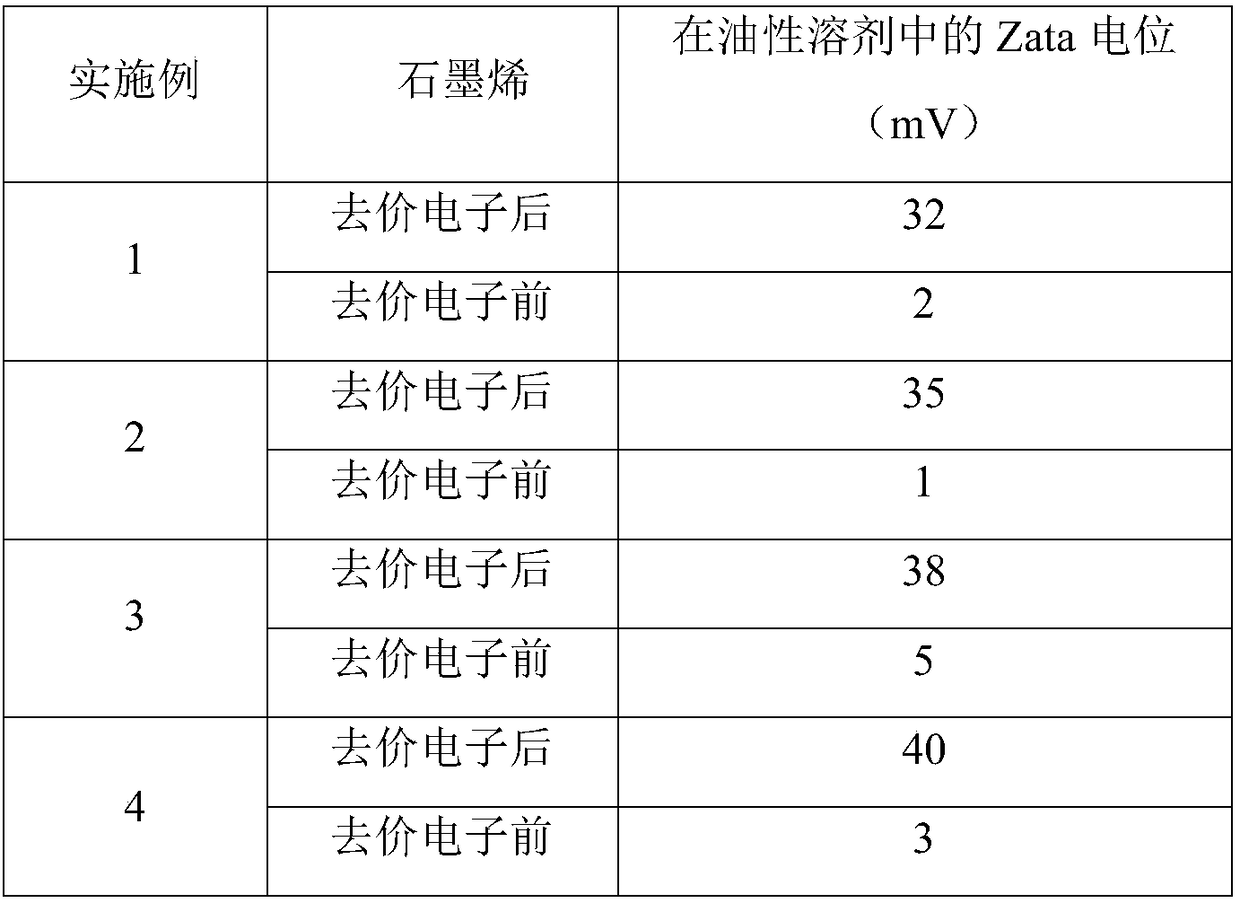
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Add graphene oxide, PEG, urea, and sodium sulfide to the ether solvent (graphene oxide: PEG: urea: sodium sulfide: ether = 100g: 4g: 5g: 3g: 2L), sonicate for 2 hours, and place the mixed solution in In the fume hood, the graphene / valence electron remover mixture is obtained after the solvent is volatilized. Place the obtained graphene / valence electron remover mixture in a carbon dioxide / water vapor (flow 200ml / min) / argon (flow 200ml / min) atmosphere, activate it at 800℃ for 100min, stop heating, The gas flow was switched to diborane, and the reaction was carried out at 200°C for 15 hours. Finally, the temperature was naturally reduced to room temperature in a mixed atmosphere of argon (flow rate of 200ml / min) to obtain devalence electron graphene.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Dissolve graphene oxide, potassium 12-tungstophosphate and phosphoric acid in deionized water (graphene oxide: potassium 12-tungstophosphate: phosphoric acid: water = 100g: 3g: 5g: 2L), ultrasonically stir for 1 hour, and centrifuge to obtain The graphene / valence electron remover mixture is placed in a carbon dioxide / water vapor (flow 200ml / min) / argon (flow 200ml / min) atmosphere, activated at a temperature of 500°C for 120 minutes, stop heating, and switch the gas flow It is borane, reacted at 180°C for 12 hours, and finally the temperature is naturally lowered to room temperature under an argon (flow rate of 200ml / min) mixed atmosphere to obtain devalent electron graphene.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Dissolve graphene oxide and polymethyl methacrylate, siloxane, sodium hydrosulfide, and triphenylphosphine in a mixed solution of cyclohexane and methylpyrrolidone (graphene: polymethyl methacrylate: silicone Alkane: sodium hydrosulfide: triphenylphosphine: cyclohexane and methylpyrrolidone mixed solution = 100g: 4g: 5g: 3g: 2g: 2L), ultrasonically stirred for 1.5 hours, remove the solvent, the obtained graphene / valence The electron remover mixture is placed in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide / water vapor (flow 200ml / min) / argon (flow 200ml / min) and activated at a temperature of 750°C for 120 minutes, then stop heating and switch the gas flow to propborane. The reaction was carried out at 150° C. for 24 hours, and finally the temperature was naturally reduced to room temperature in a mixed atmosphere of argon (flow rate of 200 ml / min) to obtain devalent electron graphene.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com