A wireless sensor node device for hydrological monitoring based on real-time embedded cps
A wireless sensor and hydrological monitoring technology, applied in measuring devices, open-air water source surveys, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as poor pertinence, low efficiency, and poor versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
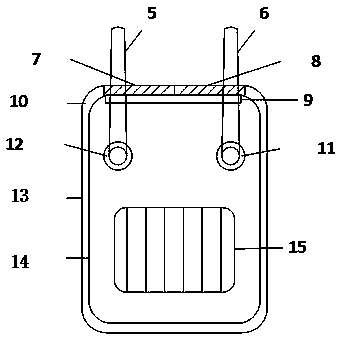
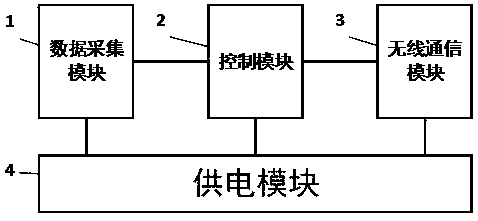
[0038] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-10 As shown, the wireless sensor node device for hydrological monitoring based on real-time embedded CPS includes data acquisition module 1, control module 2, wireless communication module 3, power supply module 4, antenna I5, antenna II6, resin sealant layer I10, resin sealant Layer II11, resin sealing layer III12, polysulfone mold layer I13, polysulfone mold layer II14, solar panel 15; the data acquisition module 1 includes a liquid level sensor 7, a rainfall sensor 8, and a digital temperature and humidity sensor 9; data acquisition Module 1 is connected to control module 2, control module 2 is connected to wireless communication module 3, power supply module 4 is respectively connected to data acquisition module 1, control module 2, and wireless communication module 3; antenna I5 is fixed on the surface layer through resin sealant layer III12 On the polysulfone mold layer I13, the antenna II6 is fixed on the surface polysulfone mold layer ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: as Figure 1-10 As shown, the hydrological monitoring wireless sensor node device based on real-time embedded CPS, this embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, wherein:
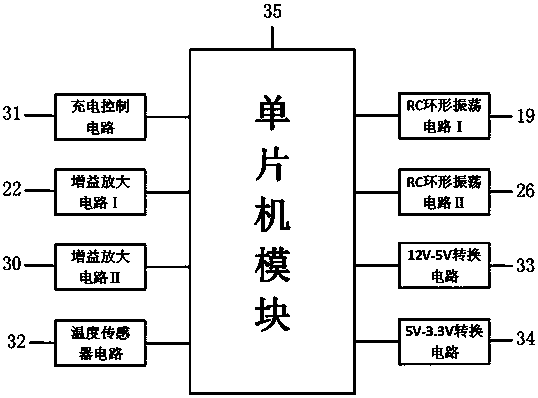
[0043]Preferably, the rain sensor 8 includes an arched glass plate 16, a diffractive optical element I17, a focused infrared beam transmitter 18, an RC ring oscillation circuit I19, a polycarbonate transparent shell 20, an optical receiver 21, and a gain amplifier circuit I22 wherein the straight edge of the arched glass plate 16 is seamlessly connected with the diffractive optical element I17 through polycarbonate and silica gel, the beam sending end of the focused infrared beam transmitter 18 is embedded in the diffractive optical element I17, and the focused infrared beam transmitter 18 is not embedded The other parts of the diffractive optical element I17 are sealed by opaque light-shielding materials to prevent a part of the emitted infrared light beam from being directly received by...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: as Figure 1-10 As shown, the wireless sensor node device for hydrological monitoring based on real-time embedded CPS, this embodiment is the same as Embodiment 2, wherein:
[0045] Preferably, the digital temperature and humidity sensor 9 is an improved intelligent temperature sensor DS18B20, whose maximum resolution can reach 0.0625 degrees Celsius. DS18B20 can directly read the measured temperature value, the temperature measurement range is -55~+125°C, with an increment of 0.5°C, and it uses a wire system to connect with the microcontroller. The unique single-wire interface only needs one port pin for communication, without external devices The external hardware circuit is reduced, and the cost is low and the use is convenient.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com