A cut sequence set-based dynamic fault tree Monte-Carlo simulation quantitative calculation method
A dynamic fault tree, quantitative calculation technology, applied in the direction of calculation, design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as combinatorial explosion, not suitable for large system analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
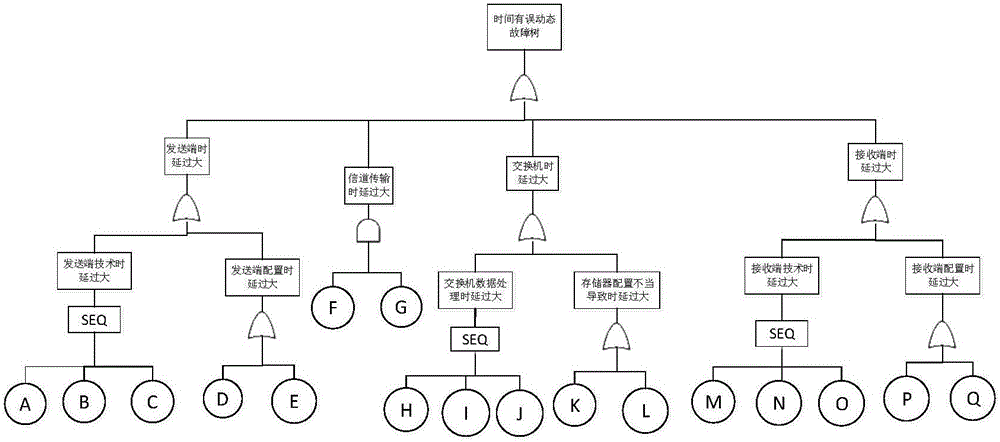
[0067]The standard and definition of transmission delay are given in the specification of AVINC 664 full-duplex switched Ethernet (AFDX) for avionics. The total delay of the set end system includes technical delay and configuration delay, where the technical delay is independent of the traffic load, and the technical delay is defined as the end system receives and processes application data when there is no other task processing, and starts The time required for sending, and the configuration delay depends on the configuration and traffic load of the sending end, and there will be delays such as jitter due to different configurations and traffic loads, and the jitter will vary depending on the specific situation.
[0068] In the AFDX network, the data transmission process needs to go through the stages of sending end ES, channel transmission, switch store and forward, and receiving end ES. Therefore, the data delay problem is analyzed from these stages, and the events that caus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com