A Method for Measuring Liquid Viscosity Coefficient Using Spring Ball System
A viscosity coefficient, small ball technology, applied in the field of physical experiments, can solve the problems such as the inability to effectively guarantee the falling angle and posture of the needle drop, the declination in the vertical direction of the needle drop, and the complicated equipment and equipment, so as to achieve a convenient and fast measurement method. Simple instrument and the effect of improving experimental efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and a specific embodiment.
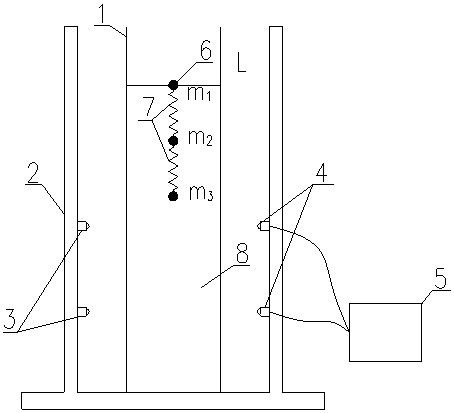
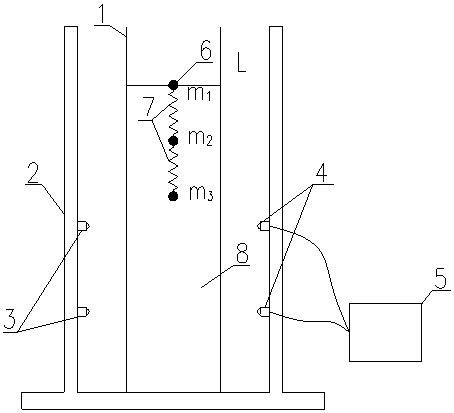
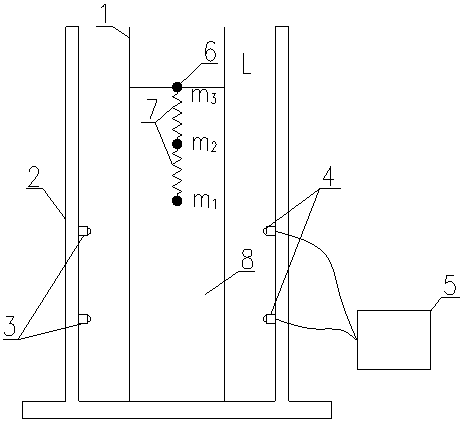
[0045] like figure 1 As shown, the spring ball system that the method for measuring the viscosity coefficient of liquid described in this embodiment relies on consists of three small balls 6
[0046] It is composed of two springs 7 cross-connected. The three small balls 6 have smooth surfaces and similar diameters, and the diameters from top to bottom are d 1 、d 2 、d 3 , with a mass of m 1 、m2 、m 3 , and m 1 2 3 ; The spring 7 is a light and uniform spring, and the lengths of the two springs 7 are close to each other, and the lengths from the top to the bottom are L respectively 1 , L 2 .
[0047] like figure 2 and image 3 As shown, it is the photoelectric falling ball viscometer used in this embodiment. The measuring cylinder 1 is a plexiglass measuring cylinder with an experimental liquid 8 inside. Two lasers 3 are installed on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com