Protective rubber for later machining of machining equipment surface
A machining and rubber technology, applied in metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, used abrasive processing devices, etc., can solve the problems of aging of the protective cover, affecting the service life of the protective cover, time-consuming and laborious, etc. The effect of work efficiency and protection quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0010] The specific implementation, structure, features and effects provided by the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and preferred embodiments.
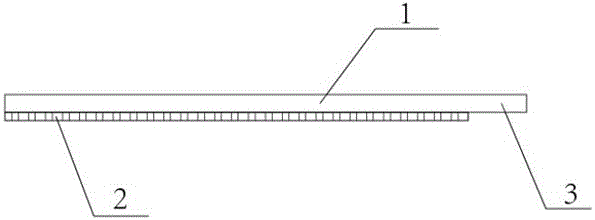
[0011] A protective rubber for post-processing of the machined surface of equipment, comprising: a protective rubber 1 and a rubber layer 2, wherein: the protective rubber 1 is made of EPDM rubber, and the shape of the protective rubber 1 is consistent with the surface of the machined equipment to be protected The shape is consistent; one end of the protective rubber 1 is provided with an easy-to-open area 3, the adhesive layer 2 is arranged on the bottom surface of the protective rubber 1, and no adhesive layer 2 is provided on the bottom surface of the easy-to-uncover area 3 of the protective rubber 1.
[0012] Further, the thickness of the protective rubber 1 is 2MM.
[0013] Further, the adhesive layer 2 is double-sided adhesive.
[0014] Compared with the prior ar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com