Lower jaw masticatory robot based on pneumatic artificial muscle
A technology of pneumatic artificial muscles and chewing robots, applied in the field of bionic robots, can solve the problems of poor bionicity and complex structure, and achieve the effects of weight reduction, bionicity improvement, and light weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
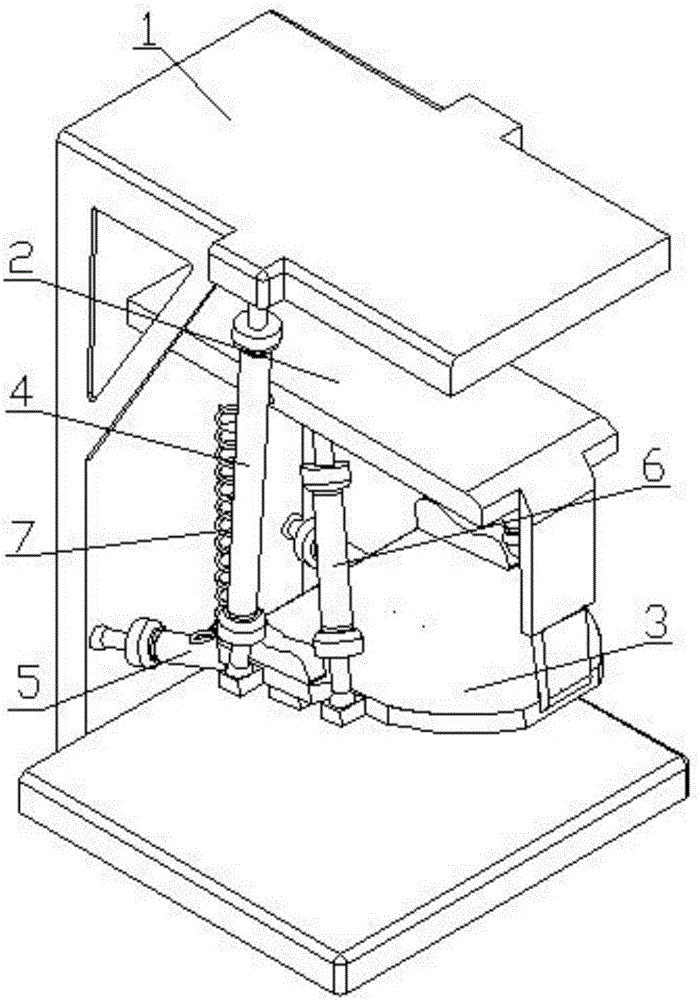
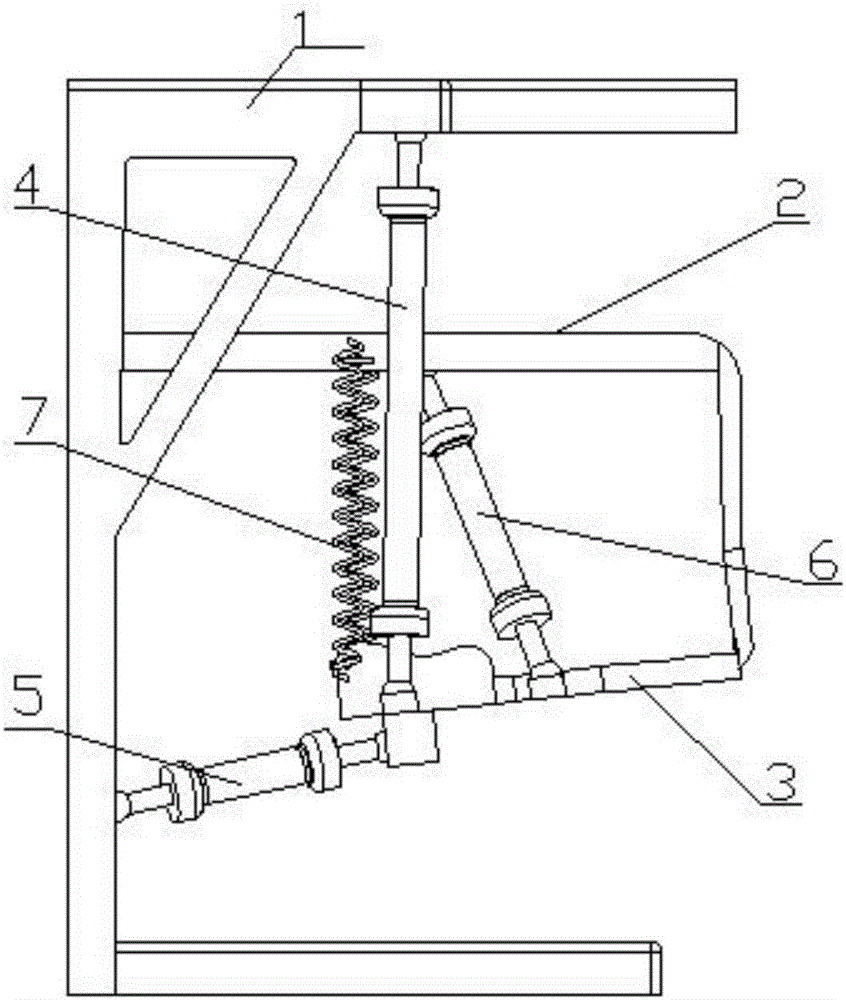
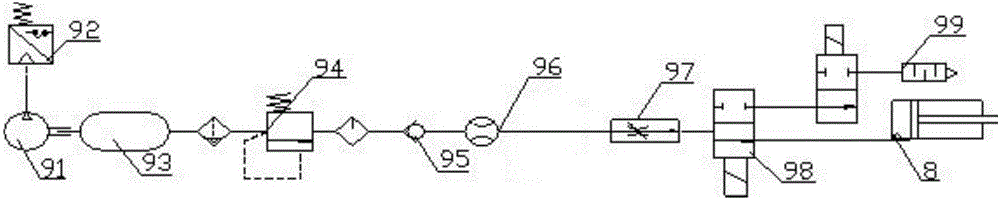
[0029] An artificial muscle chewing robot based on human bionics, which uses pneumatic muscles 8 to replace the three main types of chewing muscles in the human body. The mandible cooperates with each pneumatic muscle 8 as a moving platform. The robot was built on a biomechanical model of the mandible structure and masticatory muscles. The chewing process is divided into two major processes: opening and closing. Since the opening process has the effect of gravity, and it is a preparation for closed chewing, no useful work is done. Therefore, we will focus on the closing muscles (masserus, temporalis, and pterygium). ) and temporomandibular joint ligament for bionic design. The main closed mouth muscles to consider include the masseter, pterygoid, and temporal muscles. The chewing robot is driven by a linear actuator—pneumatic muscle 8. The connection between muscles is modeled as a ball hinge connection, which improves the degree of freedom of each joint. According to human...
Embodiment 2
[0033] An artificial muscle chewing robot based on human bionics, which uses pneumatic muscles 8 to replace the three main types of chewing muscles in the human body. The mandible cooperates with each pneumatic muscle 8 as a moving platform. A spring is used to replace the damping action of the ligaments of the temporomandibular joint. The robot was built on a biomechanical model of the mandible structure and masticatory muscles. The chewing process is divided into two major processes: opening and closing. Since the opening process has the effect of gravity, and it is a preparation for closed chewing, no useful work is done. Therefore, we will focus on the closing muscles (masserus, temporalis, and pterygium). ) and temporomandibular joint ligament for bionic design. The main closed mouth muscles to consider include the masseter, pterygoid, and temporal muscles. The chewing robot is driven by a linear actuator—pneumatic muscle 8. The connection between muscles is modeled a...
Embodiment 3
[0037] An artificial muscle chewing robot based on human bionics, which uses pneumatic muscles 8 to replace the three main types of chewing muscles in the human body. The mandible cooperates with each pneumatic muscle 8 as a moving platform. A spring is used to replace the damping action of the ligaments of the temporomandibular joint. The robot was built on a biomechanical model of the mandible structure and masticatory muscles. The chewing process is divided into two major processes: opening and closing. Since the opening process has the effect of gravity, and it is a preparation for closed chewing, no useful work is done. Therefore, we will focus on the closing muscles (masserus, temporalis, and pterygium). ) and temporomandibular joint ligament for bionic design. The main closed mouth muscles to consider include the masseter, pterygoid, and temporal muscles. The chewing robot is driven by a linear actuator—pneumatic muscle 8. The connection between muscles is modeled a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com