Preparation method of N2,9-diacetylguanine
A technology of diacetylguanine and guanine, which is applied in the chemical field, can solve the problem that the reaction conversion rate only reaches 60%, and achieve the effects of good particle size, reduced energy consumption, and reduced dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
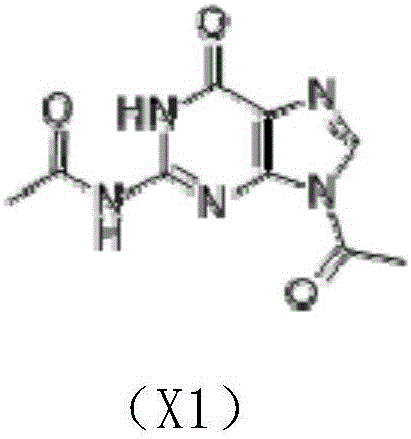
[0027] In a 500ml three-necked flask, add 240g of pyridine, 20g of guanine, and 1g of DMAP (4-dimethylaminopyridine) in sequence, stir to dissolve, and cool to -5°C in an ice bath. Add 42g of acetyl chloride into the separatory funnel, and slowly add it dropwise while stirring. Control the dropping process for 25-35min, and the temperature is lower than 10°C. After the dropwise addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2.5 h to obtain the X1 reaction solution.
[0028] Distill the reaction solution X1 under reduced pressure to control the pressure to -0.09Mpa. When the temperature rises to 51°C, pass the effluent acetyl chloride into water. When the temperature rises to 92°C, collect the effluent pyridine and recover it for use. A solid containing X1 precipitated out.
[0029] Add the obtained X1 solid into a flask containing 140 g of distilled water, stir for 40 min, and suction filter at room temperature to obtain a solid containing X1.
[0030] Add the s...
Embodiment 2
[0033] In a 500ml three-necked flask, add 240g of pyridine, 20g of guanine, and 1g of DMAP (4-dimethylaminopyridine) in sequence, stir to dissolve, and cool to -5°C in an ice bath. Add 42g of acetyl chloride into the separatory funnel, and slowly add it dropwise while stirring. Control the dropping process for 25-35min, and the temperature is lower than 10°C. After the dropwise addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2.5 h to obtain the X1 reaction solution.
[0034] Distill the reaction solution X1 under reduced pressure to control the pressure to -0.09Mpa. When the temperature rises to 51°C, pass the effluent acetyl chloride into water. When the temperature rises to 92°C, collect the effluent pyridine and recover it for use. A solid containing X1 precipitated out.
[0035] Add the obtained X1 solid into a flask containing 140 g of distilled water, stir for 40 min, and suction filter at room temperature to obtain a solid containing X1.
[0036] Add the s...
Embodiment 3
[0039] In a 500ml three-necked flask, add 240g of pyridine, 20g of guanine, and 1g of DMAP (4-dimethylaminopyridine) in sequence, stir to dissolve, and cool to -5°C in an ice bath. Add 42g of acetyl chloride into the separatory funnel, and slowly add it dropwise while stirring. Control the dropping process for 25-35min, and the temperature is lower than 10°C. After the dropwise addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2.5 h to obtain the X1 reaction solution.
[0040] Distill the reaction solution X1 under reduced pressure to control the pressure to -0.09Mpa. When the temperature rises to 51°C, pass the effluent acetyl chloride into water. When the temperature rises to 92°C, collect the effluent pyridine and recover it for use. A solid containing X1 precipitated out.
[0041] Add the obtained X1 solid into a flask containing 140 g of distilled water, stir for 40 min, and suction filter at room temperature to obtain a solid containing X1.
[0042] Add the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com