Global Navigation Satellite System (gnss) Spoofing Detection With Carrier Phase And Inertial Sensors
A global navigation satellite and carrier phase technology, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning systems, radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as not an ideal solution, increased installation costs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
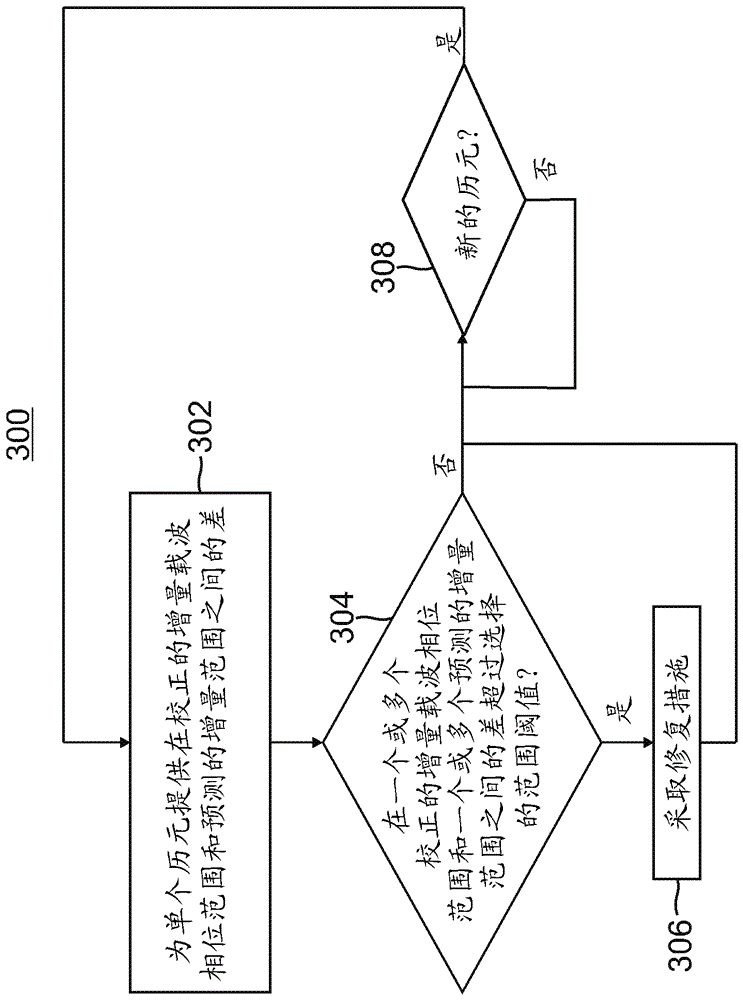
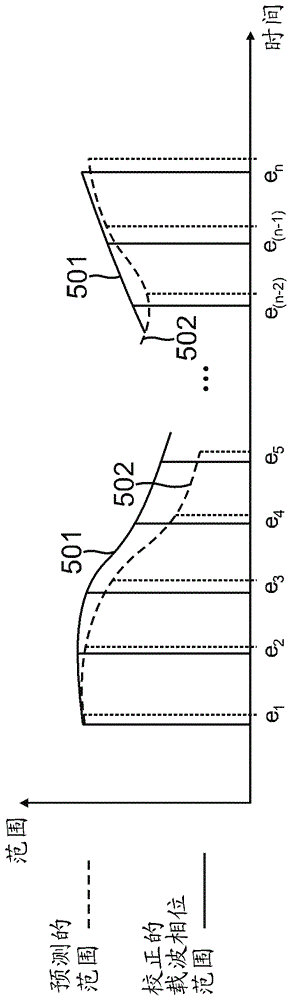
[0078] Example 1 includes a system for detecting spoofing attacks, the system comprising: a satellite motion and receiver clock correction module communicatively coupled to periodically input from a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver for multiple signals in the field of view of the GNSS receiver The carrier phase range of satellites, the satellite motion and the receiver clock correction module are communicatively coupled to output a corrected delta carrier phase range for the current epoch to a first input of the subtractor; compute the predicted range and the delta range module communicatively coupled to output to a second input of the subtractor a predicted delta range based on the inertial measurements observed for the current epoch; the subtracter to output to the delta range difference detection logic for the current epoch the difference between the corrected delta carrier phase range and the predicted delta range for the epoch; and delta range difference ...
example 2
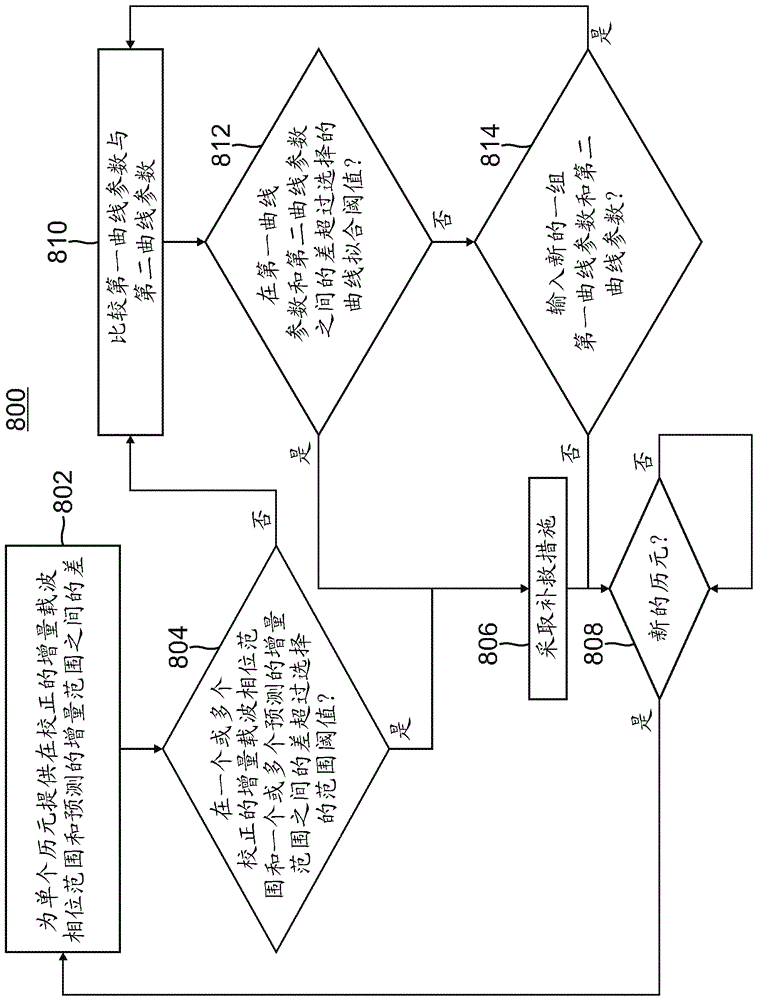
[0079] Example 2 includes the system of Example 1, further comprising: a first curve fitting module configured to: input from the satellite motion and receiver clock correction module the plurality of corrected carrier phase ranges obtained continuously during the respective plurality of epochs ; fitting a plurality of corrected carrier-phase ranges obtained in succession to a first curve in an appropriate order of selection; and outputting information indicating first curve parameters associated with the first curve to the curve fit detection logic; the second curve a fitting module configured to: input a plurality of predicted ranges obtained continuously during respective plurality of epochs from the calculate predicted range and incremental range module; fit the continuously obtained plurality of predicted ranges to the selected a second curve in an appropriate order; and outputting to the curve-fit detection logic information indicative of a second curve parameter associat...
example 3
[0080] Example 3 includes the system of Example 2, further comprising: a processor configured to execute at the satellite motion and receiver clock correction module, the calculate predicted range and delta range module, the first curve fitting module, and the second first curve fitting module. An algorithm in the Curve Fitting module.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com