Cognitive radio network power distribution method with multichannel cooperative communication
A cognitive wireless network and cooperative communication technology, applied in the field of cognitive wireless network power allocation of multi-channel cooperative communication, can solve the problem of not considering the total power constraint of the same cooperative relay terminal, not considering the selfish behavior of users, and not considering the secondary user. Issues such as multiple channel power allocation criteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
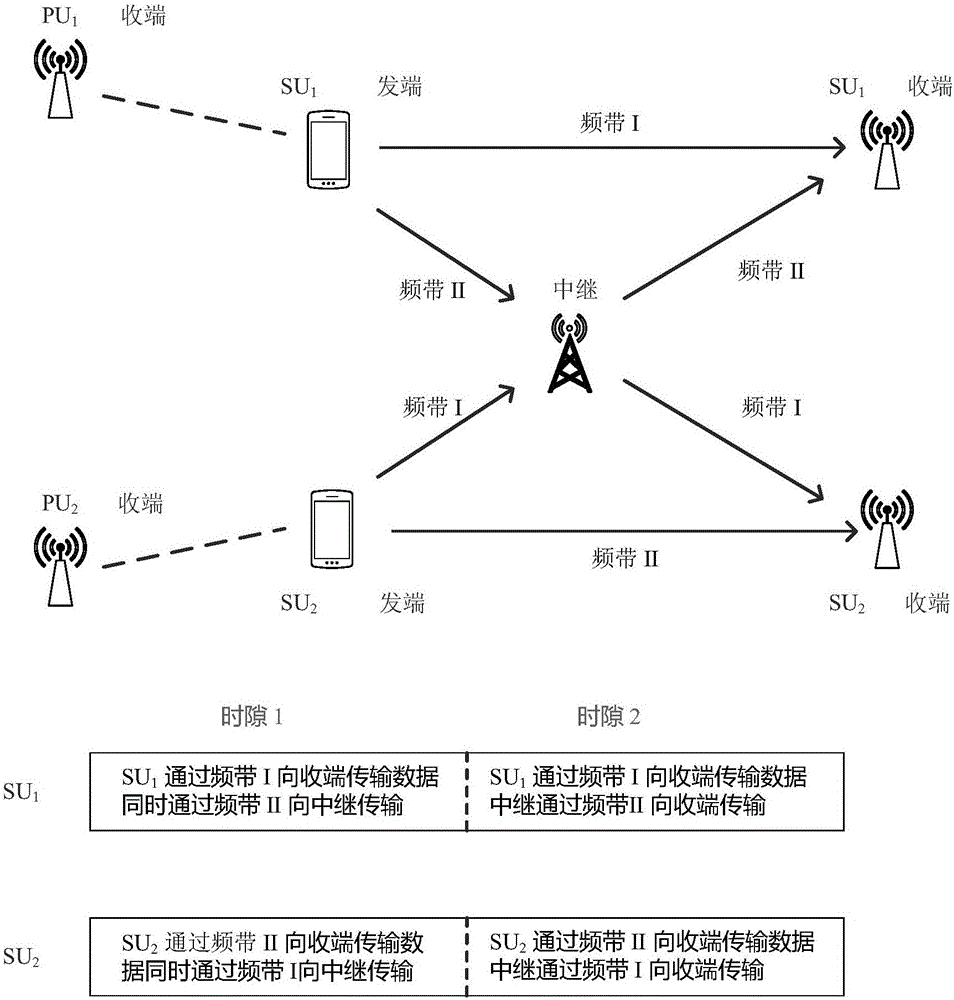
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a cognitive wireless network power allocation method for multi-channel coordinated communication. The cognitive wireless network includes at least a first primary user originating end, a first primary user receiving end, a second primary user originating end, The second main user receiving end, the first user sending end, the first user receiving end, the second user sending end, the second user receiving end, the relay device sending end, the relay device receiving end, the first channel and the second user receiving end channel, which divides the transmission time into two slots:
[0064] In the first time slot, the first primary user transmitting end and the first primary user receiving end transmit data through a first channel, and the second primary user transmitting end and the second primary user receiving end transmit data through a second channel; the The first user sending end and the first user receiving en...
Embodiment 2
[0105] The cognitive wireless network power allocation method provided in this embodiment considers a cognitive wireless network based on padding spectrum sharing, which includes at least two secondary users (transmitting and receiving pairs) and a half-duplex relay device. Two channels are used by secondary users, and if secondary user transmissions do not interfere with primary user transmissions, they can access both channels. It is assumed that each channel is occupied by a primary user, and both the secondary user and the relay device have the ability to transmit and receive on multiple channels at the same time. Record the two secondary users as SU1 and SU2 respectively, record the two channels as channel I and channel II respectively, and the primary users occupying channel I and channel II as PU1 and PU2 respectively. Without loss of generality, it is assumed that both channels are of unit bandwidth. The total transmission power owned by SU1 and SU2 is limited to P1 a...
Embodiment 3
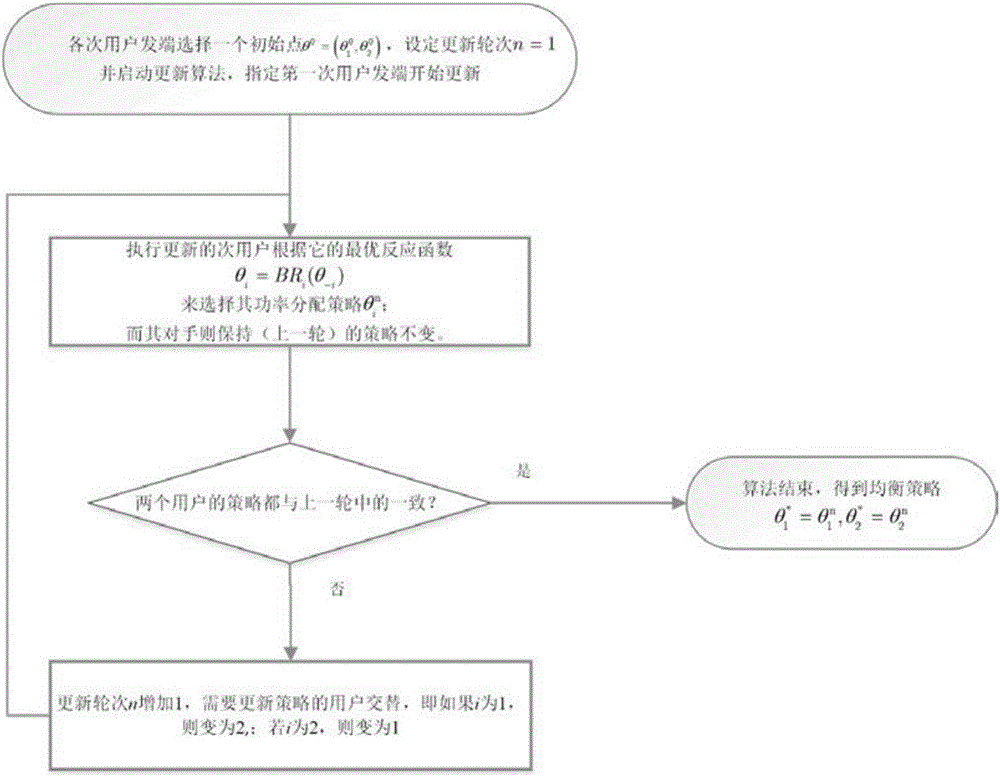
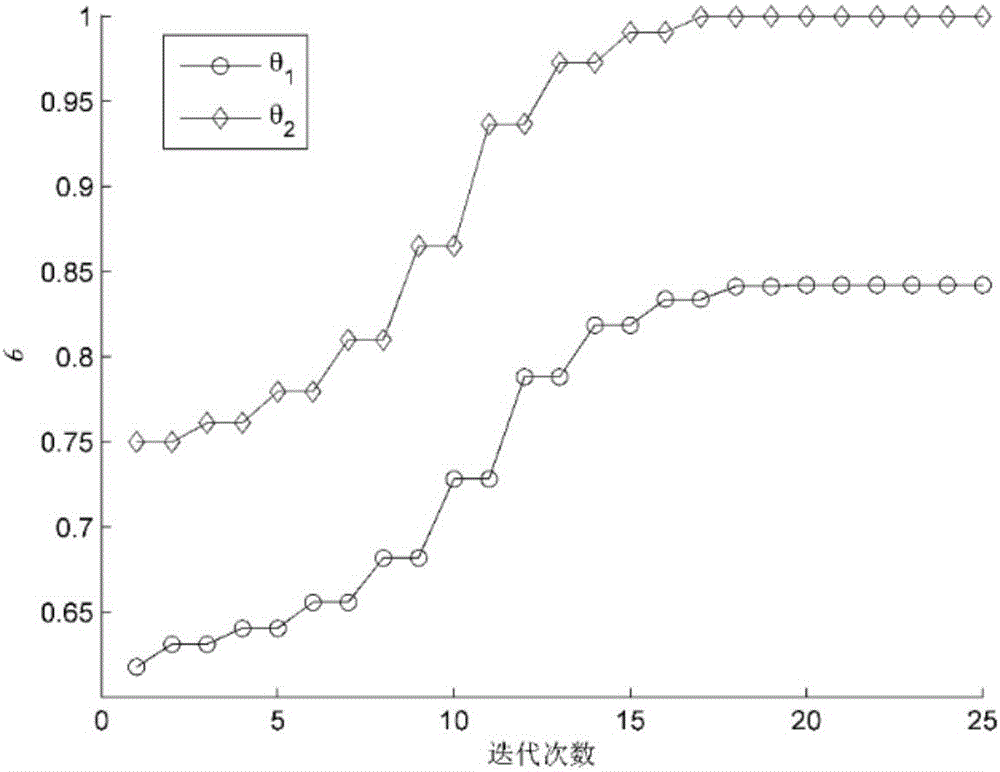
[0160] In the cognitive wireless network power allocation method provided in this embodiment, its network structure and transmission mechanism are as follows: figure 1 shown. In order to analyze the selfish behavior of two secondary users, it is modeled as a non-cooperative game. First examine the capacity of the transport mechanism. Consider SU1 first, remember SU i Send to SU j The channel gain at the receiving end is h ij , SU i The channel gain from the sending end to the receiving end of the relay device is h ir , the relay device sends to the SU i The channel gain at the receiving end is h ri , SU i Send to PU j The channel gain at the receiving end is h ipj , the relay device sends to the PU j The channel gain at the receiving end is h rpj. The total capacity consists of three parts: the direct transmission capacity of the first time slot, the direct transmission capacity of the second time slot, and the relay transmission capacity. The half-duplex relay...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com