Space radiation effect bioequivalence evaluation method of aliphatic polymer insulation materials for space navigation
A technology of insulating materials and radiation effects, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large evaluation errors and achieve high accuracy and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
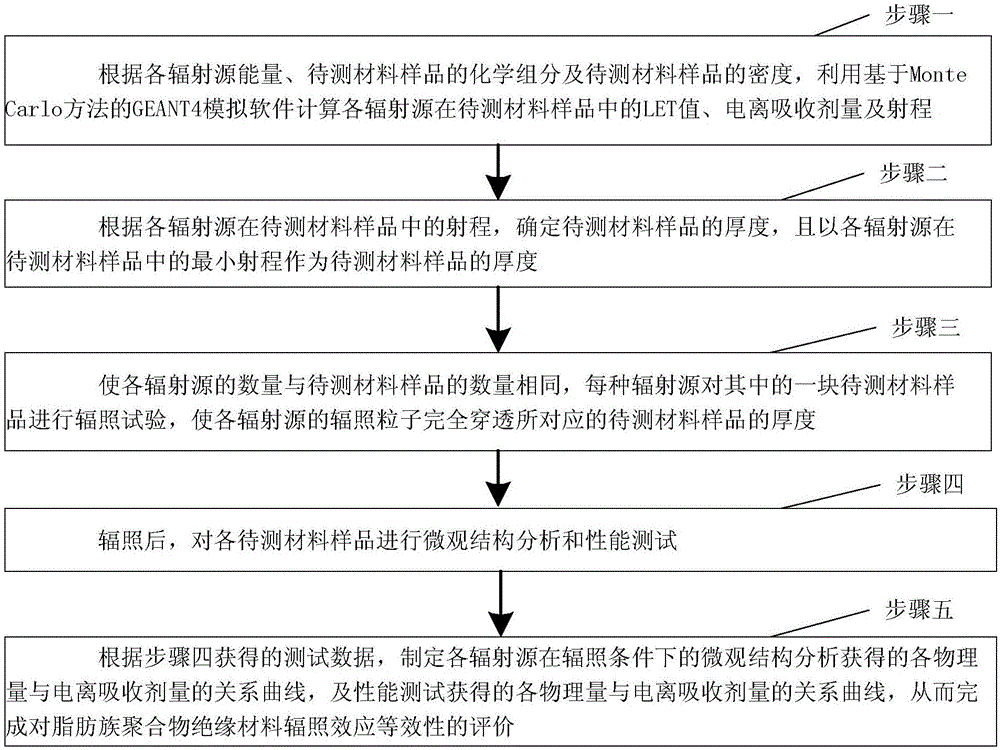
[0033] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the method for evaluating the equivalence of space irradiation effect of aliphatic polymer insulation materials for aerospace described in this embodiment, the method includes the following steps:
[0034] Step 1. Calculate the LET value, Ionization absorbed dose and range;
[0035] The material sample to be tested is an aliphatic polymer insulating material;
[0036] Each of the radiation sources described includes a Co source, electrons, protons and heavy ions;
[0037] Step 2. Determine the thickness of the material sample to be tested according to the range of each radiation source in the material sample to be tested, and use the minimum range of each radiation source in the material sample to be tested as the thickness of the material sample to be tested;
[0038] Step 3. Take four samples of the material to be tested, and the thickness of each sample of the material to be tested is the sam...
specific Embodiment approach 2
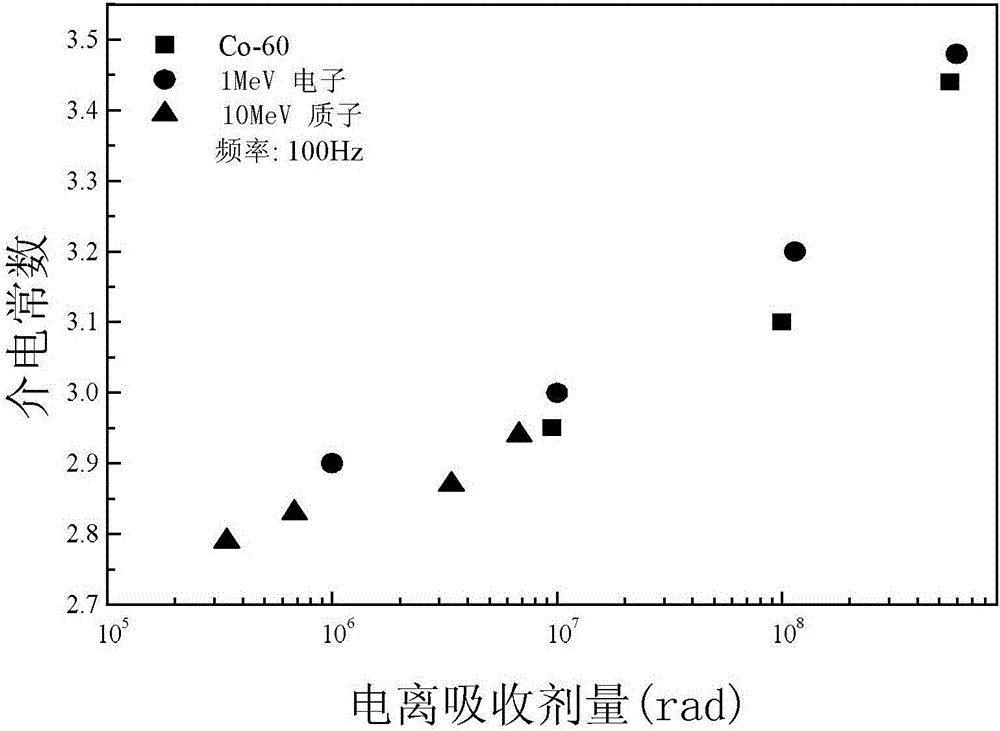
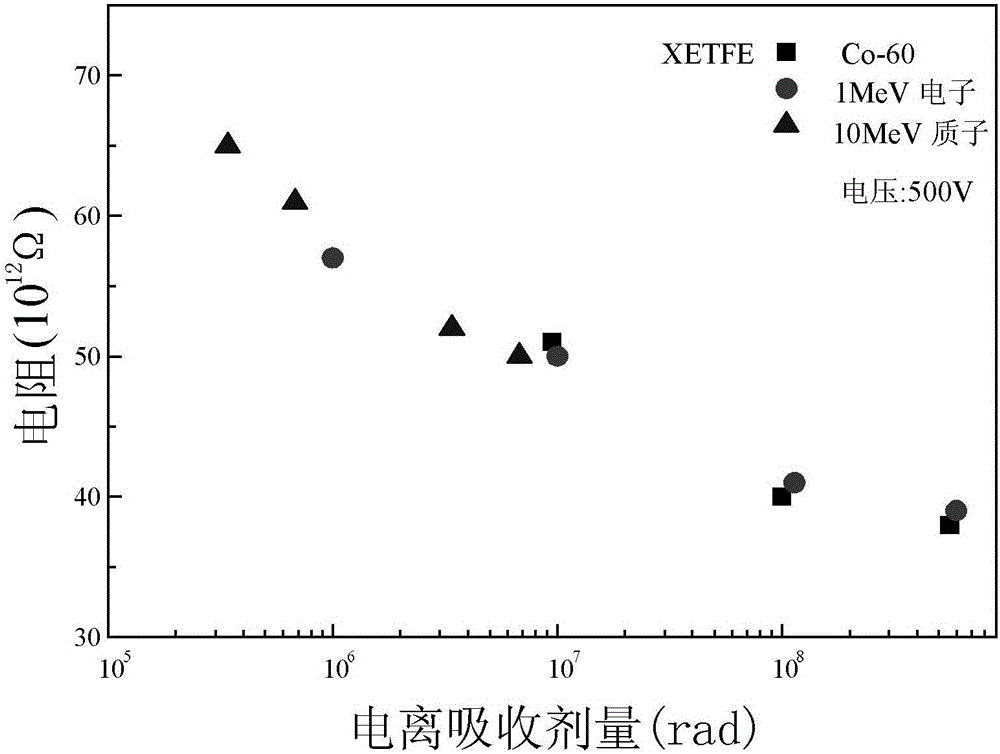
[0047] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the method for evaluating the equivalence of space irradiation effects of aliphatic polymer insulating materials for aerospace as described in Embodiment 1 is that the analysis content of the microstructure analysis includes free radicals , group and chemical composition; the test content of the performance test includes mechanical properties, dielectric properties, insulation properties and optical properties.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0048] Specific embodiment three: The difference between this embodiment and the space irradiation effect equivalence evaluation method of aliphatic polymer insulating materials for aerospace as described in specific embodiment two is that in step five, each physical quantity obtained by microstructure analysis is related to The relationship curve of ionized absorbed dose includes the relationship curve of free radicals and ionized absorbed dose, the relationship curve of group and ionized absorbed dose, and the relationship curve of chemical composition and ionized absorbed dose;
[0049] The relationship curves between various physical quantities and ionized absorbed dose obtained from the performance test include the relationship curve between mechanical properties and ionized absorbed dose, the relationship curve between dielectric properties and ionized absorbed dose, the relationship curve between insulating properties and ionized absorbed dose, and the relationship betwee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com