Position difference-based high-precision nearest neighbor search algorithm
A search algorithm and high-precision technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as time complexity deterioration, calculation complexity reduction, and loss of stability, and achieve the effects of improving accuracy, reasonable conception, and reducing accuracy errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0049] Example 1: On the premise that the number of neighbor points is set to 3, the running time of the three algorithms is shown in Table 2. As can be seen from Table 2, the present invention is based on the high-precision nearest neighbor search algorithm (being called for short HPLDBA algorithm) time of position difference far less than the nearest neighbor search algorithm (being called for short LDMDBA algorithm) and full search algorithm (abbreviating FSA algorithm) of high-dimensional distance position difference ), indicating that the high-precision nearest neighbor search algorithm based on position difference (HPLDBA algorithm for short) of the present invention has certain advantages in terms of efficiency.
[0050] Table 2 Comparison of the running time of the three algorithms on the public dataset (in ms)
[0051]
example 2
[0052] Example 2: The data set is from markov, its dimension is 10, and the value is between 0 and 1. The number of data points varies from 100 to 12800. Among them, the markov sequence {y i} is generated by the following formula:
[0053] the y i+1 +1=ay i + u
[0054] u is a random vector, each component value is between 0 and 1, and set y 0 =0, a=0.9. Experimental results such as Figure 4 shown. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the HPLDBA algorithm is very close to the LDMDBA algorithm, and far smaller than the FSA algorithm.
[0055] in conclusion
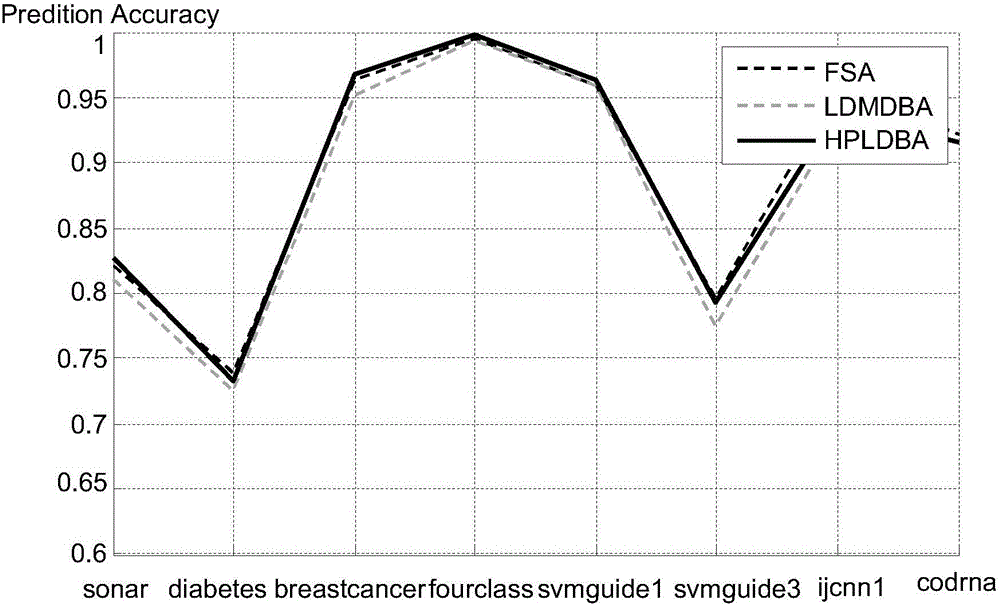
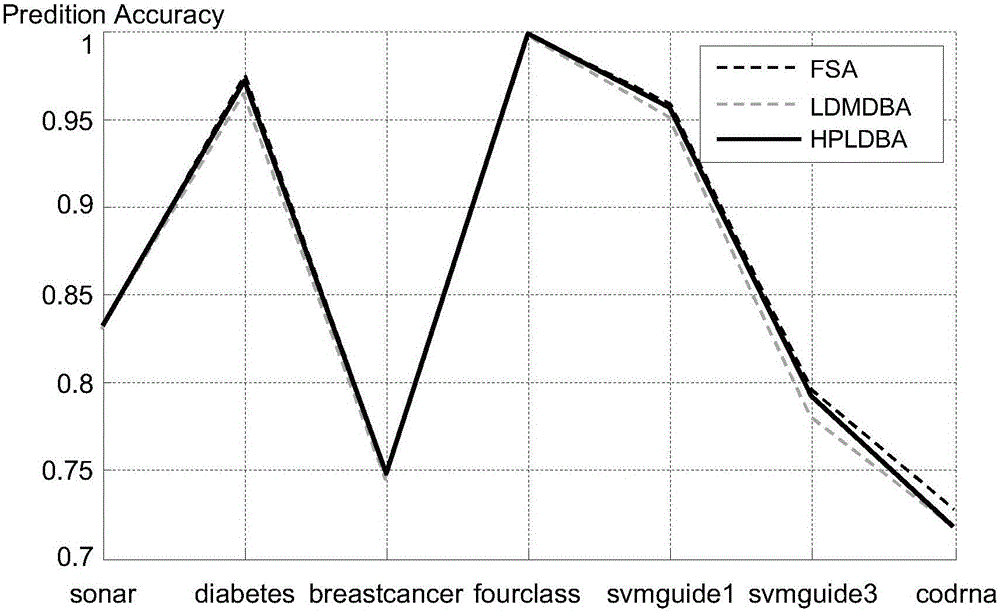
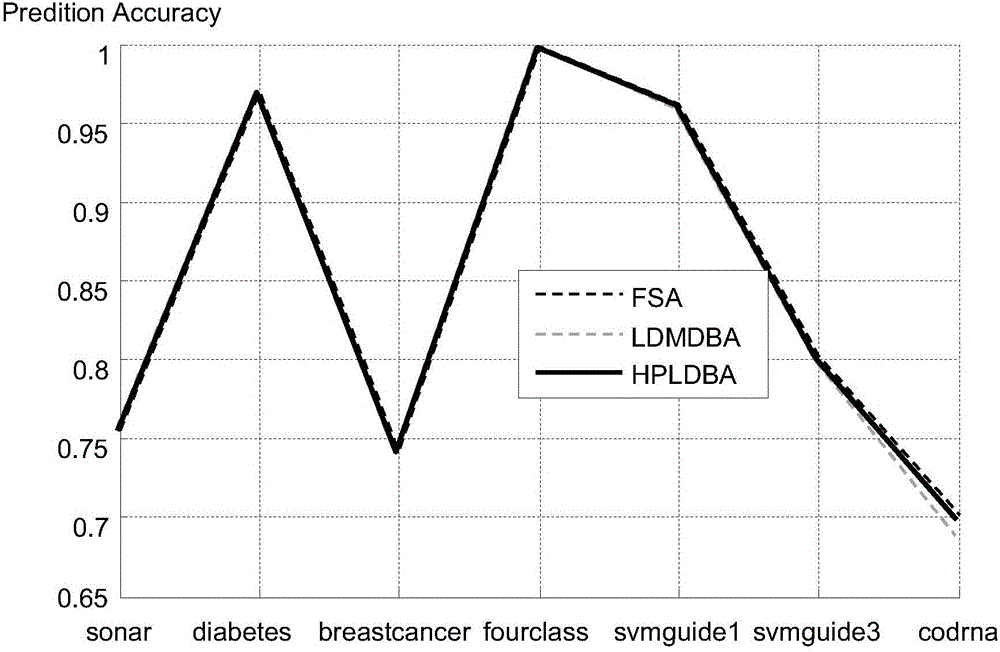
[0056] On the basis of increasing the number of reference points, the present invention proposes a high-precision neighbor search algorithm based on position difference (HPLDBA algorithm for short). Compared with other similar algorithms, the prediction accuracy of this algorithm has obvious advantages, and the time complexity does not increase.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com