SAR moving target detection method based on adaptive Chirp decomposition
A moving target detection and self-adaptive technology, applied in measurement devices, radio wave measurement systems, radio wave reflection/re-radiation and other directions, can solve the problem of inaccurate multi-target parameter estimation, achieve fast convergence speed and easy hardware implementation , Detect the effect of stable valuation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: The specific process of a SAR moving target detection method based on adaptive Chirp decomposition in this embodiment is as follows:
[0020] Step 1. Preprocessing the SAR echo to obtain a preprocessing result;
[0021] Step 2, performing adaptive chirp decomposition on the preprocessing result to obtain the decomposition result;
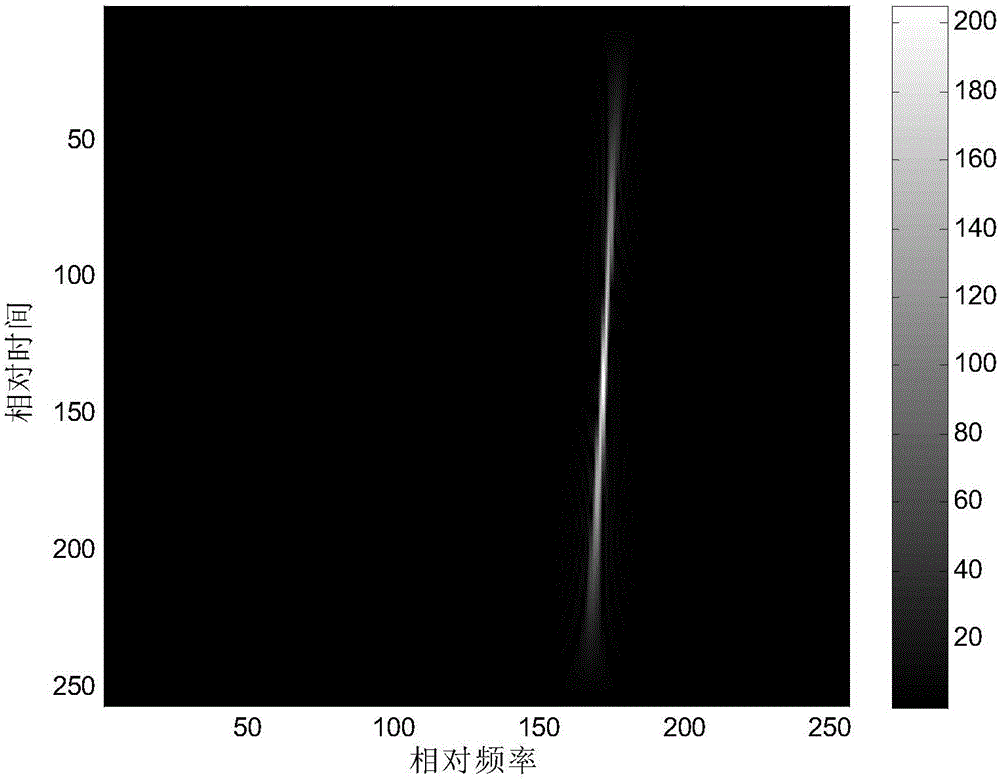
[0022] Step 3, perform time-frequency reconstruction according to the decomposition result, and obtain the time-frequency reconstruction result;
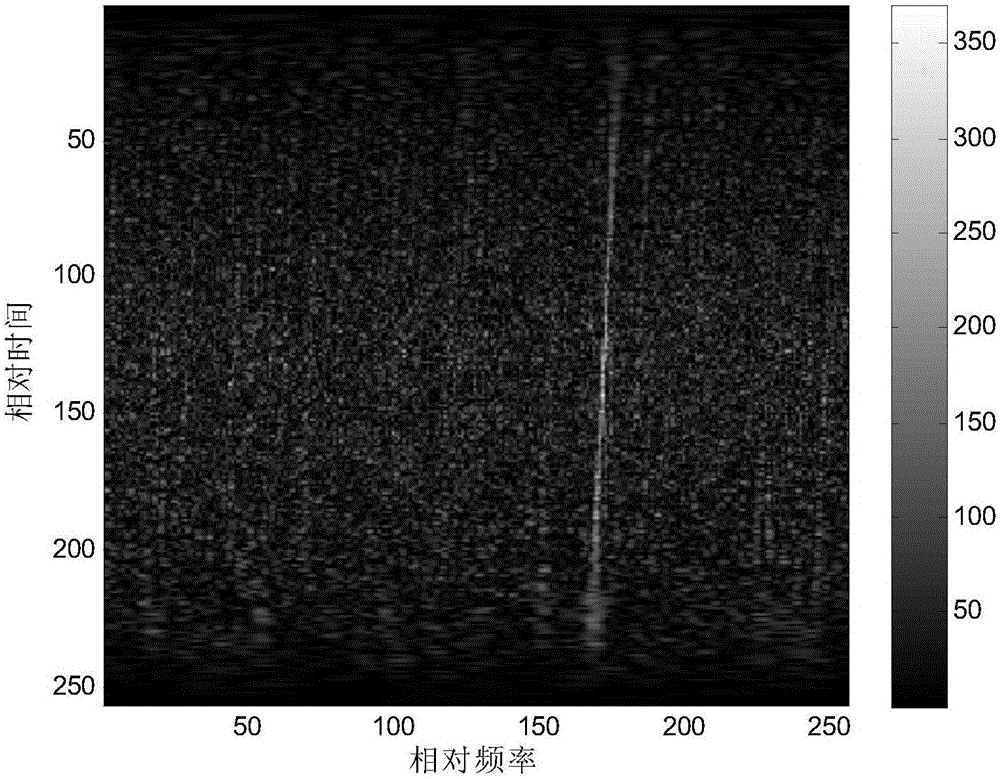
[0023] Step 4: Detect the target according to the reconstruction result, and obtain the detection target result;
[0024] As mentioned above, SAR is a synthetic aperture radar, and chirp is a chirp signal.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0025] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the SAR echo is preprocessed in the step one, and the preprocessing result is obtained; the specific process is:
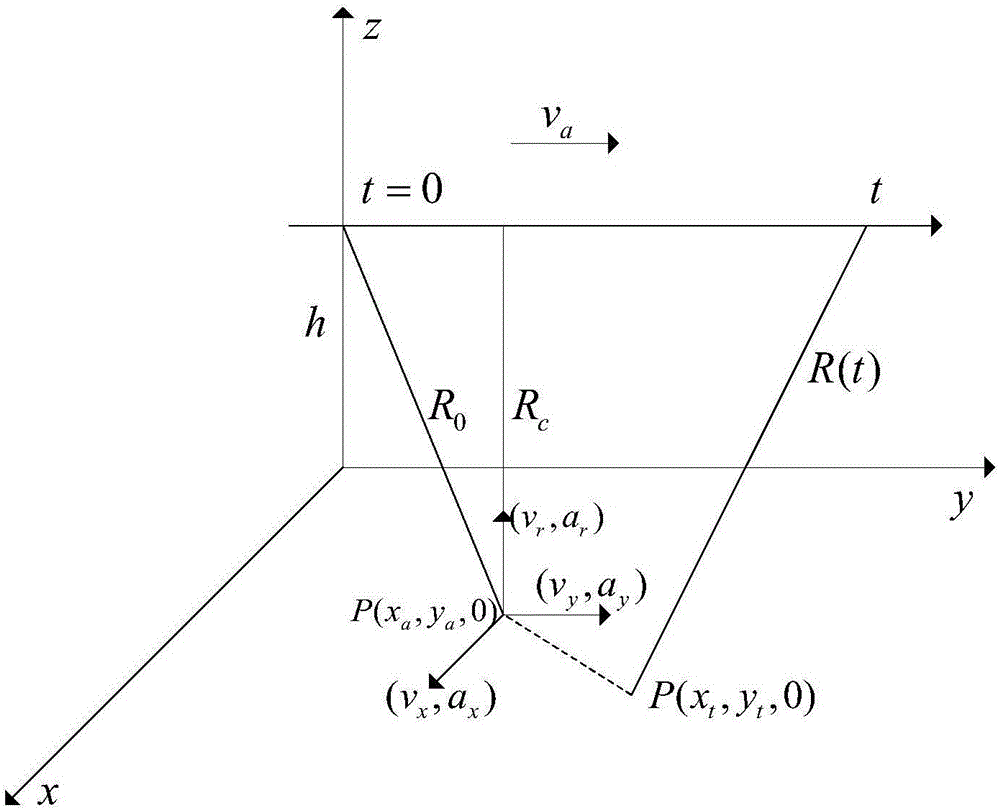
[0026] Taking the ground coordinate system (x-y-z) as the reference coordinate system, without considering the rotation of the earth, figure 1 The SAR geometric characteristics of moving targets are drawn.
[0027] Assume that the radar is in the working state of looking sideways, and the flying speed of the carrier aircraft is v a , at time t=0, the carrier coordinates are (0,0,h), and the ground moving target P is located at (x 0 ,y 0 ,0), let the position of the ground moving target P at time t=0 be its true position; the distance from point P of the ground moving target to the flight route of the carrier aircraft is R c , The slant distance from the ground moving target P to the carrier aircraft is R 0 , The speed and acceleration of the ground moving...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in the step 2, adaptive chirp decomposition is performed on the preprocessing result to obtain the decomposition result; the specific process is:
[0043] Treat the preprocessing result s(t) obtained in step 1 as n chirp wavelet bases g i (t) linear superposition, namely:
[0044]
[0045]
[0046] Among them, σ i , t i , ω i , β i represent the width, time center, initial frequency and modulation frequency of the i-th chirp wavelet base respectively, and n is the chirp wavelet base g i The number of (t), the value is a positive integer; c i is the coefficient of the i-th chirp wavelet base;
[0047] g i The WVD distribution of (t) is expressed as: WVD is a Wigner-Willi distribution;
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] Get the chirp wavelet base g i The WVD distribution of (t) is concentrated on a straight line, so that ω is the initial frequency of the chirp wavelet base; th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com