Sanitary ceramic slip ball-milling process
A technology for sanitary ceramics and mud, applied in the field of sanitary ceramics, can solve the problems of reducing the processing efficiency of the grinding process of hard materials, reducing the qualified rate of semi-finished products and finished products, reducing the qualified rate of semi-finished products and finished products, etc. The effect of improving strength and improving yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
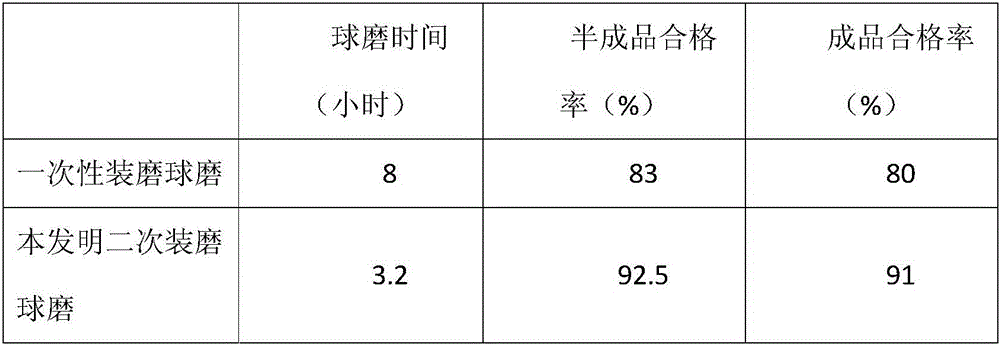
[0033] Firstly, the raw materials were weighed: 6750kg of hard materials, including 2700kg of potassium feldspar, 1800kg of pyrophyllite, and 2250kg of sericite; 6450kg of soft materials, including 1800kg of clay, 1500kg of washed china clay, 750kg of washed kaolin, 1275kg of jiefu clay, 1125kg of washed black mud, Alkali noodles 22.5kg, water glass 187.5kg, water 4050kg.
[0034] The above-mentioned weighed raw materials are sorted into primary abrasives and secondary abrasives, wherein:
[0035] Abrasive materials in one charge include 2700kg of potassium feldspar, 1800kg of pyrophyllite, 2250kg of sericite, 1800kg of clay, 22.5kg of alkali surface, 112.5kg of water glass, and 2700kg of water, totaling 11385kg;
[0036] The secondary abrasive is the part of the weighed raw materials except the secondary abrasive, including 1500kg of washed china clay, 750kg of washed kaolin, 1275kg of jiefu clay, 1125kg of washed black mud, 75kg of water glass, and 1350kg of water, totaling ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com