A Low-Complexity Message Passing Decoding Algorithm Based on Factor Graph Evolution in Sparse Code Multiple Access
A sparse code multiple access and low-complexity technology, applied in the field of non-orthogonal multiple access, can solve the problems of increasing decoding complexity, destroying real-time requirements, and increasing access delay, so as to reduce high complexity , Improve performance and reduce decoding delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The implementation of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings and examples.
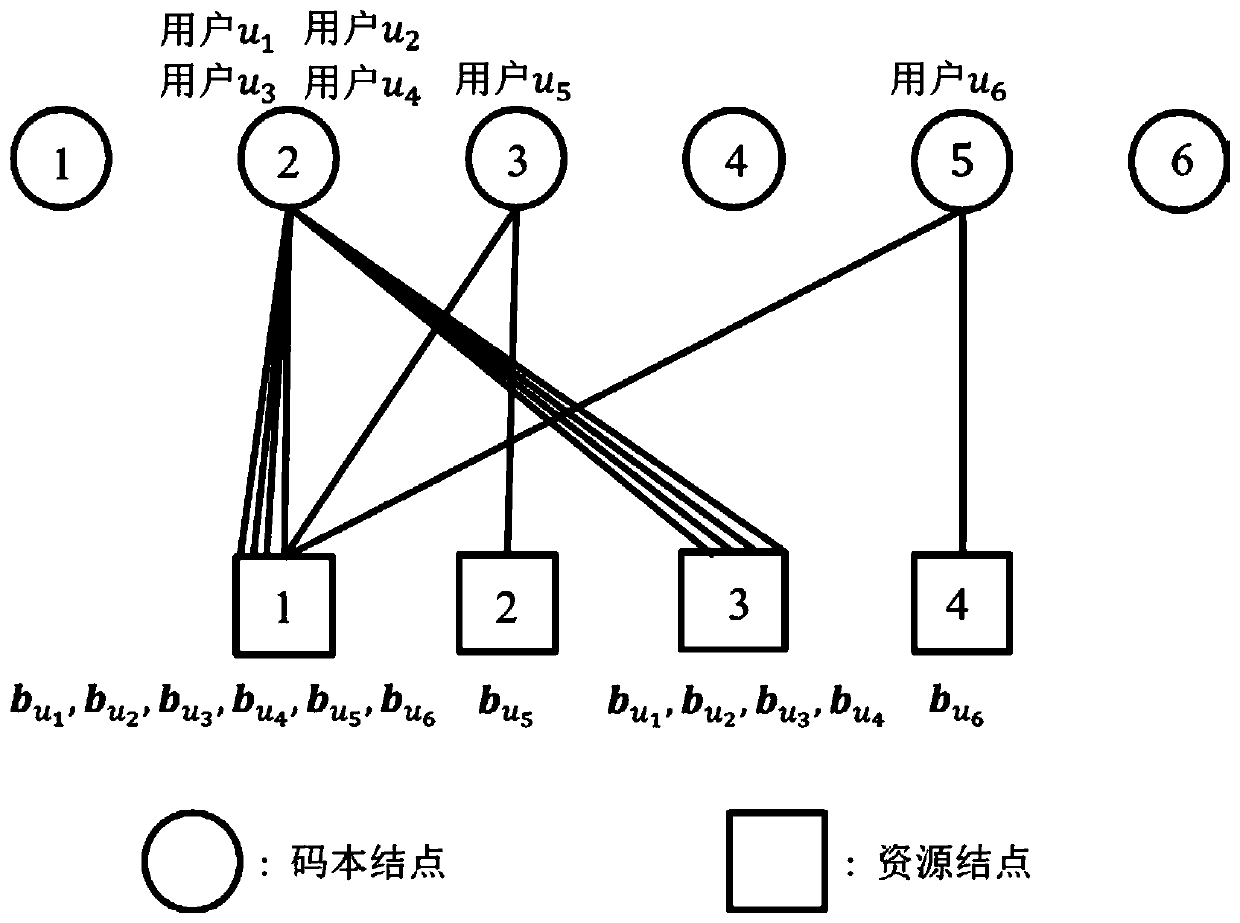
[0024] refer to figure 1 , figure 1 In the case of K=6 codebook nodes and L=4 resource nodes, a codebook collision situation where 6 users access is given, that is, 4 users use codebook 2, and 1 user uses codebook 3 and 1 user uses the codebook 5 .
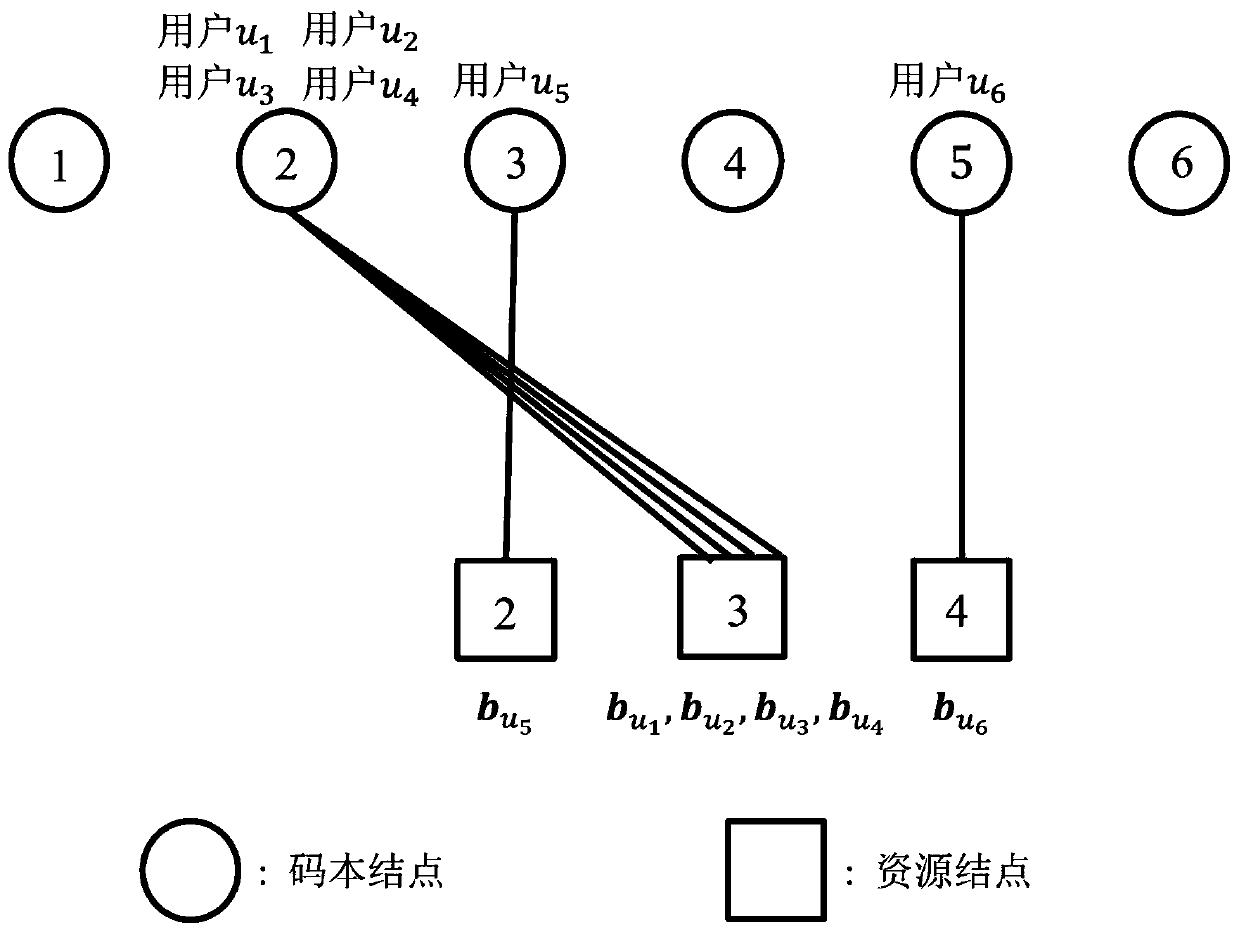
[0025] refer to figure 2 , figure 2 The present invention is given in figure 1 A specific embodiment in the case of codebook collision is shown, that is, when the factor graph update step δ is equal to the update final value, the factor graph only evolves in one step, and the simplest factor graph in which all access user information is preserved is obtained directly.
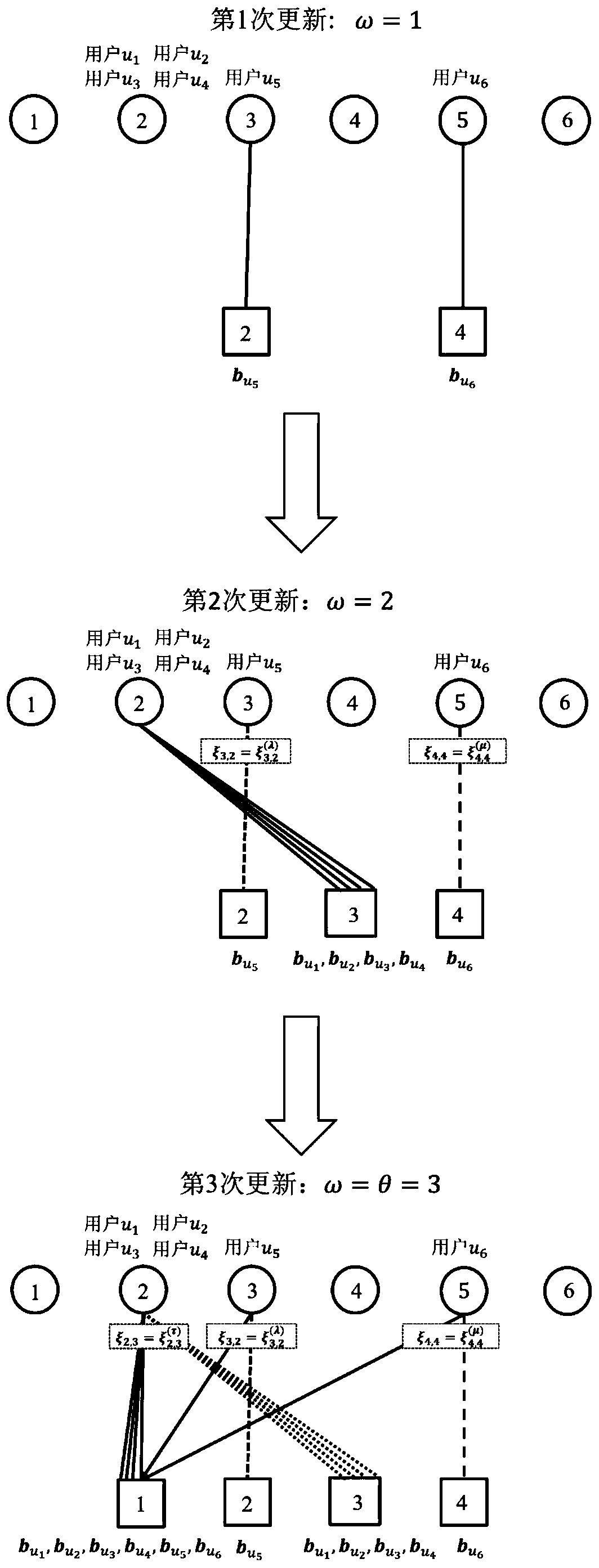
[0026] refer to image 3 , image 3 The present invention is given in figure 1 Another specific embodiment in the case of codebook collision shown is the case where the factor graph update step size δ=1, and the update fina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com