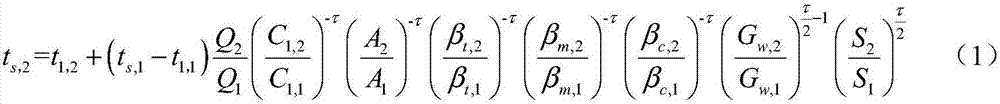Diagnosis method for energy saving at cold end of condensing steam turbine
A technology of energy-saving diagnosis and steam turbine, which is applied in the direction of engine function, mechanical equipment, engine components, etc., and can solve problems such as not considering the cleanliness of the condenser, mutual interference, lack of cleanliness of the condenser in the power plant, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
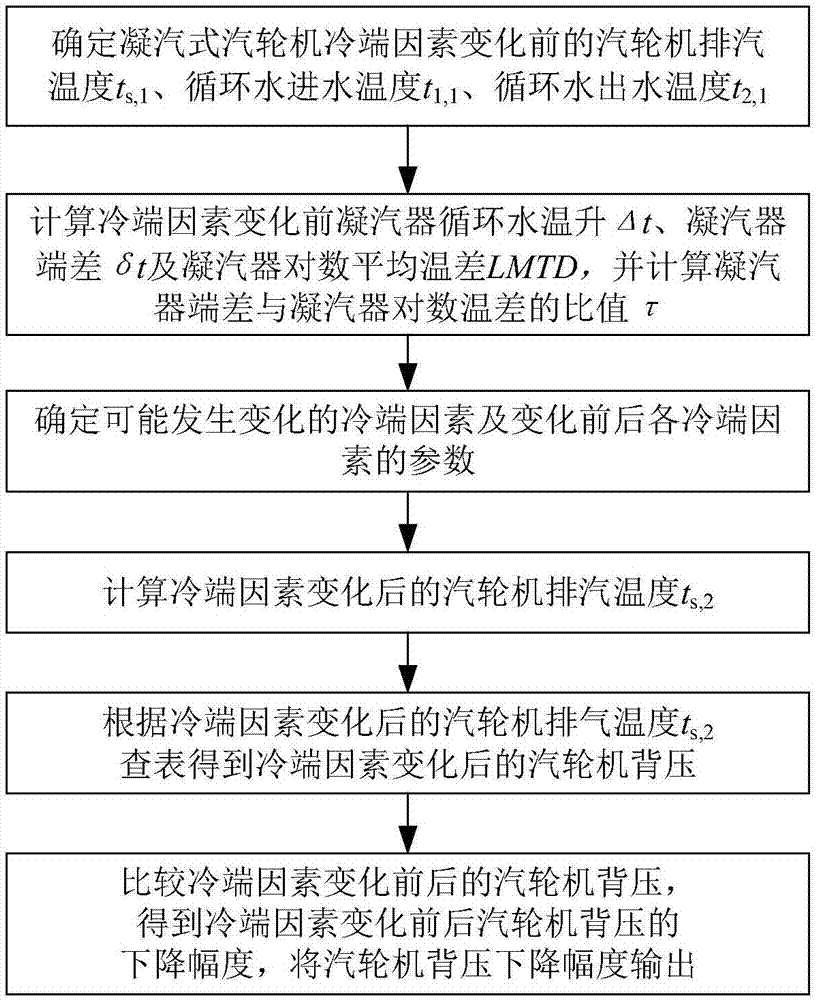
[0048] Such as figure 1 As shown, the implementation steps of the method for diagnosing energy saving at the cold end of a condensing steam turbine in this embodiment include:
[0049] 1) Determine the exhaust steam temperature t of the condensing steam turbine before the energy-saving related cold-end factors change s,1 , circulating water inlet temperature t 1,1 , Circulating water outlet temperature t 2,1 (where the steam turbine exhaust temperature t s,1 It can be measured directly under the condition of ensuring the measurement accuracy, or can be obtained by measuring the back pressure of the steam turbine based on the preset water and steam property table or enthalpy entropy diagram), and calculate the condenser before the cold end factor changes from the above data Circulating water temperature rise Δt, condenser end difference δt and condenser logarithmic mean temperature difference LMTD, and calculate the ratio of condenser end difference to condenser logarithmic ...
Embodiment 2
[0134] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the main difference is: calculate the exhaust steam temperature t of the steam turbine after the cold end factor changes s,2 The formulas are different. In this example, on the basis of formula (1), it is assumed that the characteristics of the condenser remain unchanged, and the cleanliness of the condenser remains unchanged in a short period of time. For example, it is assumed that the circulating water inlet temperature and the heat load of the condenser Also unchanged, formula (1) is simplified to get formula (5), and formula (5) is used to calculate the exhaust steam temperature t of the steam turbine after the cold end factor changes s,2 .
[0135]
[0136] In formula (5), t s,1 and t s,2 respectively represent the exhaust steam temperature of the steam turbine before and after the change of the cold end factor, t 1 Indicates the circulating water inlet temperature, G w,1 and G w,2 Respectively represe...
Embodiment 3
[0138] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the main difference is: this embodiment is for cooling tower transformation, and calculates the exhaust steam temperature t of the steam turbine after the cold end factor changes s,2 The formulas are different. In this embodiment, on the basis of formula (1), it is considered that the characteristics of the condenser remain unchanged, and the cleanliness of the condenser remains unchanged in a short period of time. For example, it is assumed that the circulating water flow rate and the heat load of the condenser , simplify the formula (1) to get the formula (6), and use the formula (6) to calculate the exhaust steam temperature t of the steam turbine after the cold end factor changes s,2 .
[0139]
[0140] In formula (6), t s,1 and t s,2 respectively represent the exhaust steam temperature of the steam turbine before and after the change of the cold end factor, t 1,1 and t 1,2 Respectively represent the circ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com