GhLMM gene capable of substantially improving disease resistance of cotton and application thereof
A technology of disease resistance and genetics, applied in the field of biotechnology applications, can solve the problems of function loss and other problems, and achieve the effect of enhancing the disease resistance of cotton
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
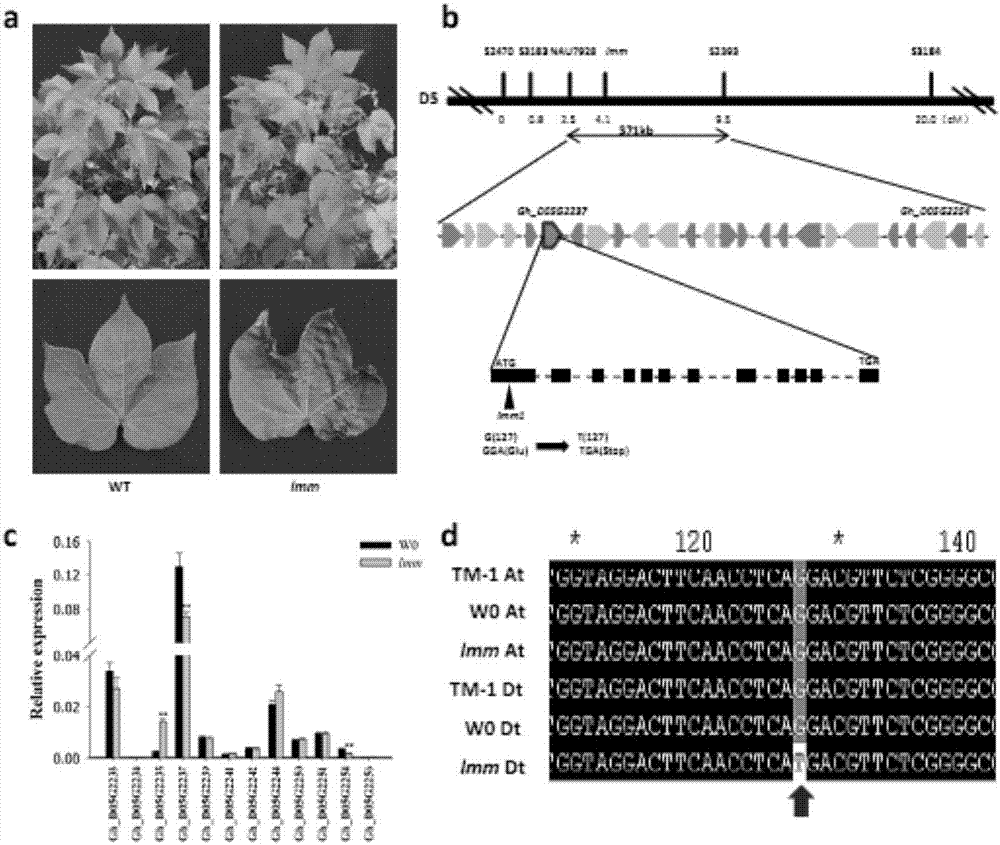
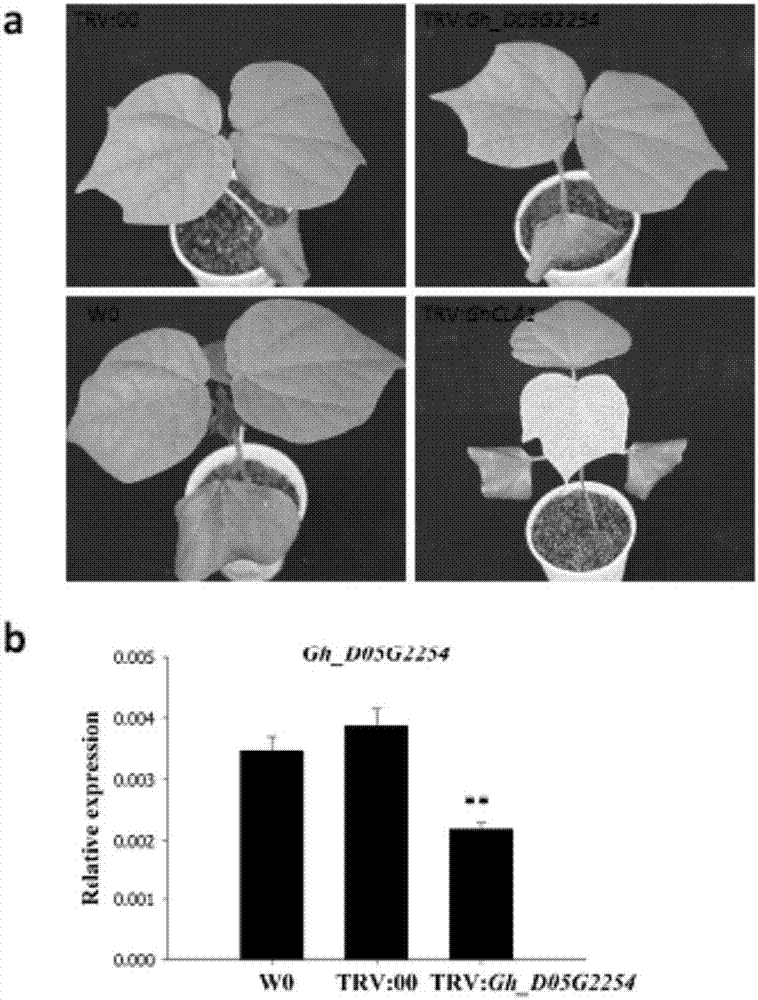
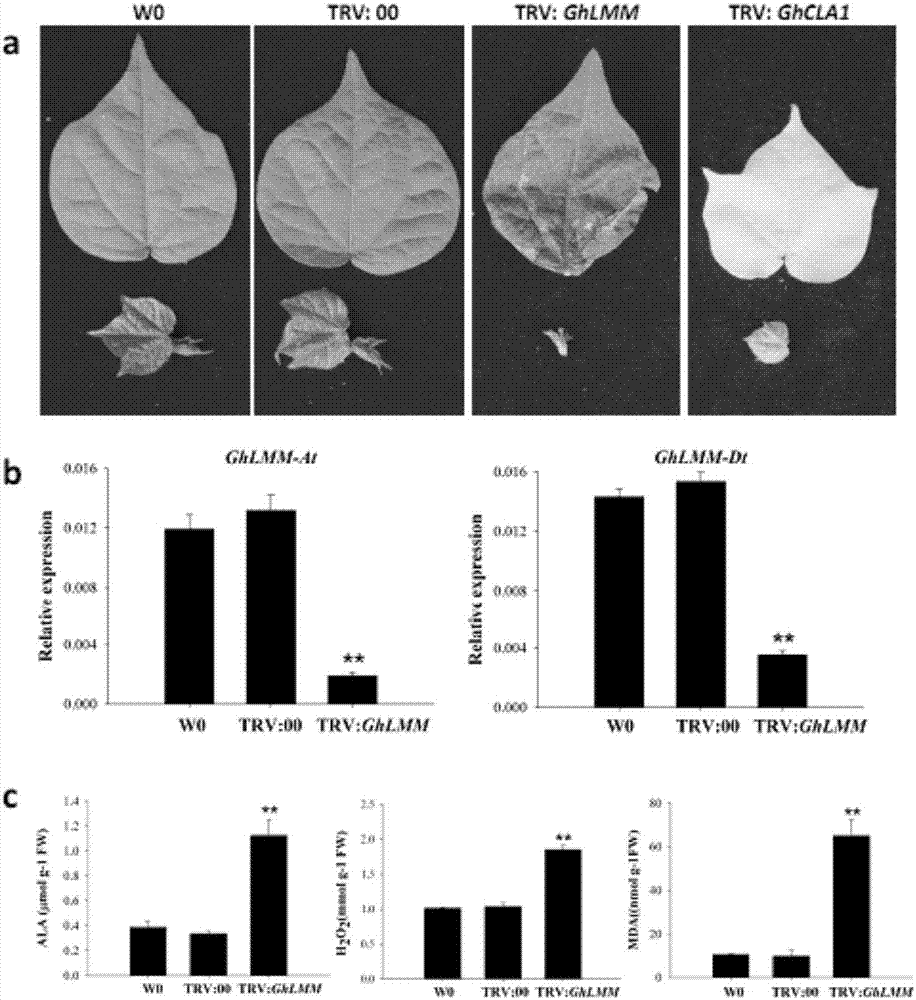
[0068] (1) Discovery, fine mapping and map-based cloning of cotton-like lesion mutant Ghlmm
[0069] We found a Lesionmimic mutant in the tissue culture regeneration seedlings of upland cotton variety W0. In the absence of any biotic and abiotic stress, the mutant spontaneously formed lesions on the leaves. We named it the upland cotton disease mutant Ghlmm. The Ghlmm mutant can complete the normal growth cycle. Compared with the control W0, its fiber quality and seed yield are basically unaffected (Table 1).
[0070] Cross the upland cotton disease mutant Ghlmm with the genetic standard line TM-1, F 1 The plant leaves have no disease spots and the phenotype is wild type. F 1 Selfing produces 763 strains of F 2 Separated groups. In F 2 The leaf phenotypic traits were investigated in the three growth and development stages of the population at the seedling stage, bud stage, and flower and boll stage to determine the phenotype of individual plants. The results show that in F 2 In...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com