3D geologic modeling method based on T splines
A modeling method and 3D geological technology, applied in 3D modeling, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult updating of geological models, destroying geometric continuity of splicing, difficult geological data, etc., to achieve the effect of maintaining accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0079] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
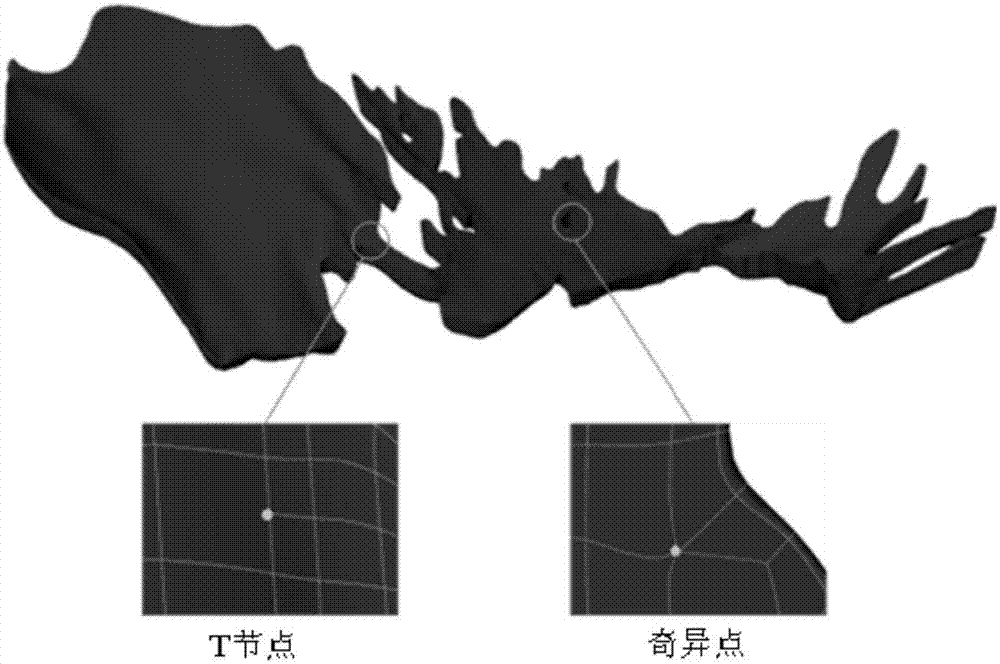
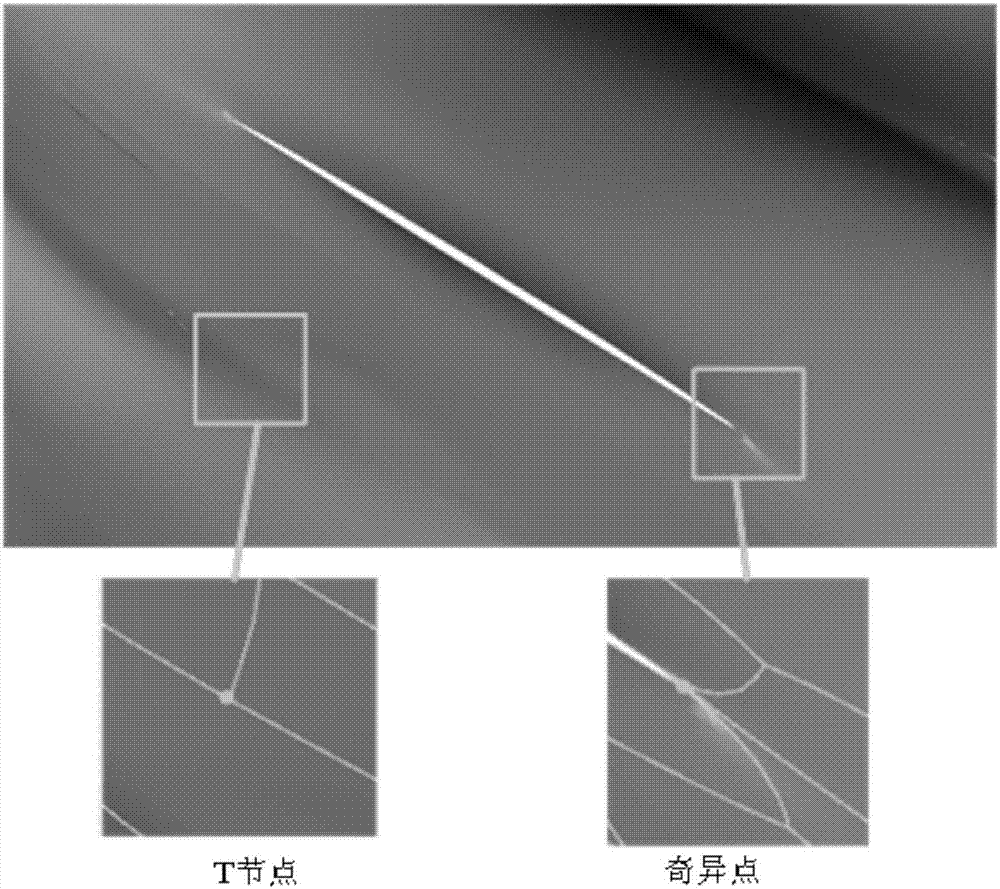
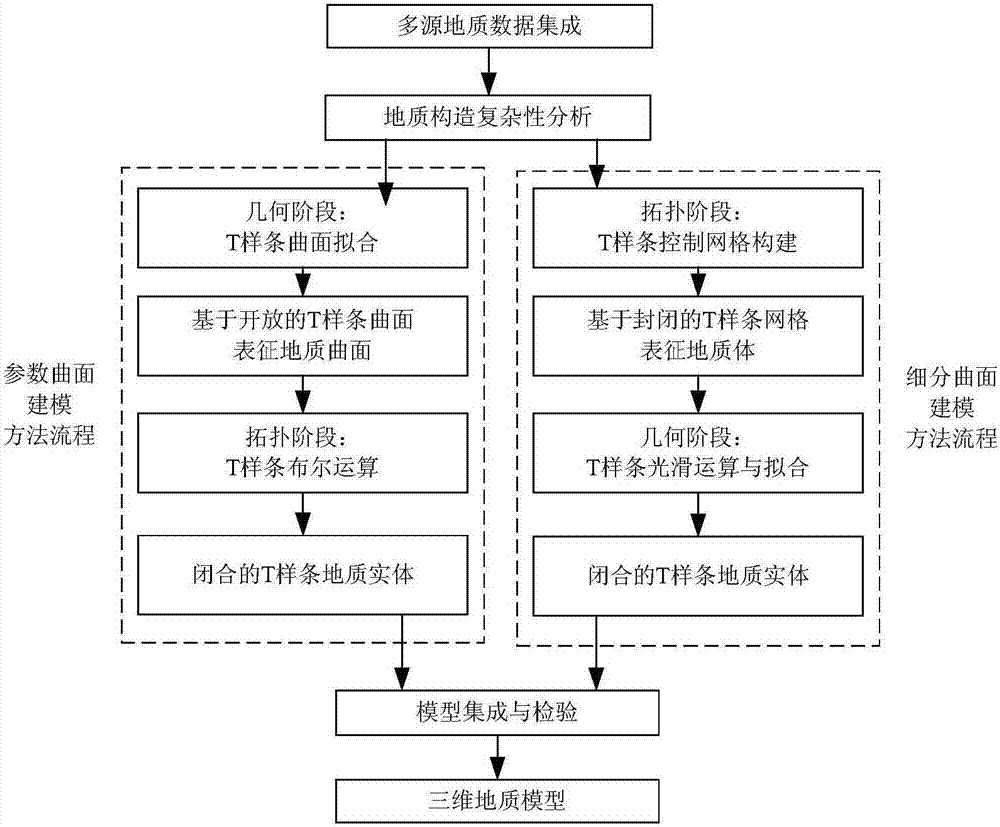
[0080] The present invention proposes a three-dimensional geological modeling method based on T-splines, uses T-splines as the spatial data structure of three-dimensional geological modeling, and conducts three-dimensional fine modeling for the complex shape of geological objects, so as to realize the quantitative description of the complexity of geological structures , the method includes the following steps (see figure 1 ):
[0081] 1. Multi-source geological data integration;
[0082] 2. Structural complexity analysis of geological objects based on geological data. The analysis process includes the following two steps:
[0083] Step 1. Carry out structural complexity analysis on the fractal geometric complexity, arbitrary genus topological complexity and discontinuous complexity of geological objects based on geological data;
[0084] Step 2. On the basis of stru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com