A kind of breeding method of cytoplasmic male sterile early-maturing Chinese cabbage germplasm material
A technology of male sterility and Chinese cabbage, which is applied in the field of breeding germplasm materials of cytoplasmic male sterility and early-maturing Chinese cabbage, can solve the problems of difficult seed production technology, high cost of parental seeds, and difficulty in obtaining hybrids, and achieve functional Normal, short duration, strong resistance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
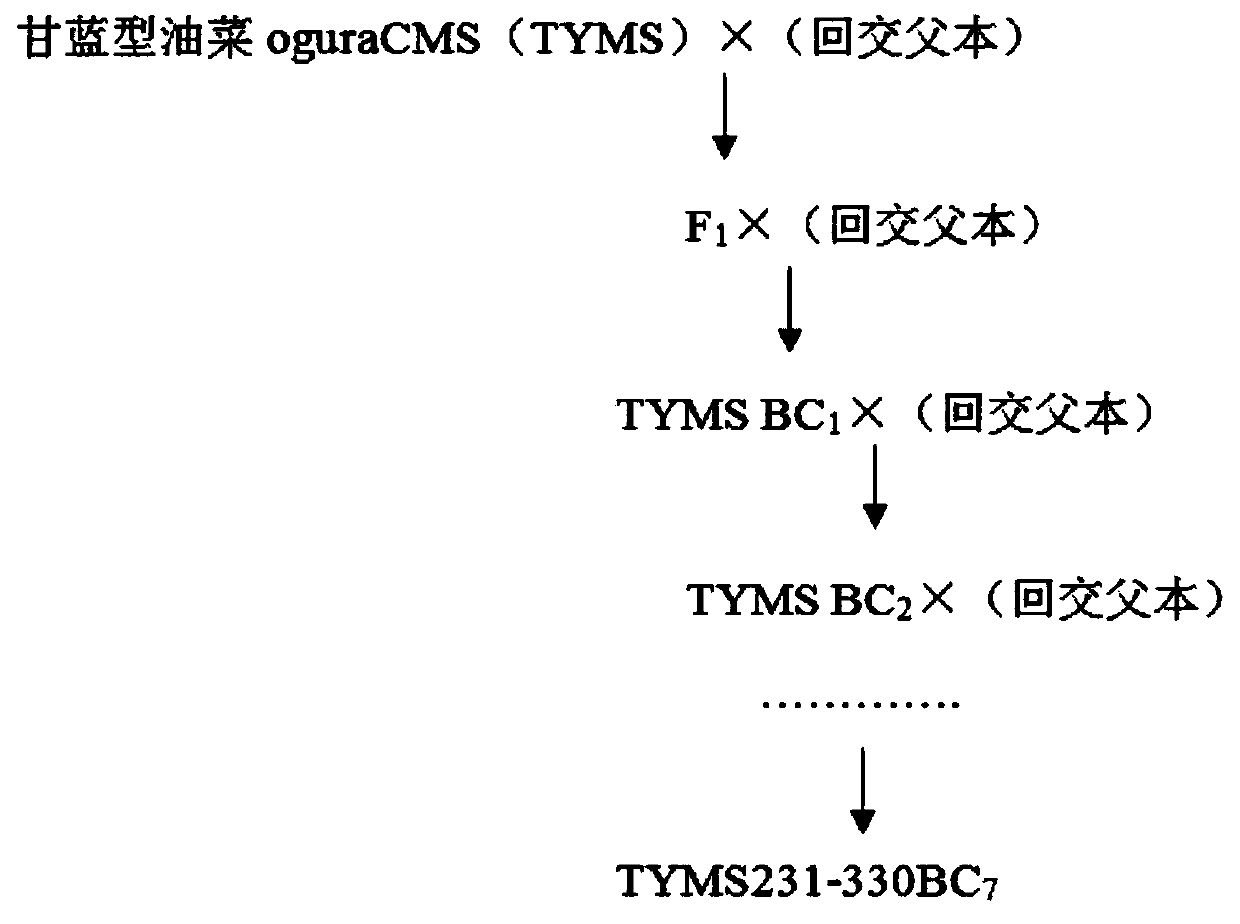
[0035] One of the breeding methods of a cytoplasmic male sterile early-maturing Chinese cabbage germplasm material, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) The backcross male parent Y231-330 (genotype AA) of the precocious self-incompatible line was obtained by using the free microspore culture method (preserved in the mid-term seed resource bank of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, preservation number: S01A0057);
[0037] (2) Using the cytoplasmic male sterile material oguraCMS (its genotype is AACC) of Brassica napus as the female parent, and the Chinese cabbage precocious self-incompatible line Y231-330 obtained in step (1) as the male parent Ben, the first-generation seed F was obtained through interspecific hybridization 1 (genotype AAC);
[0038] (3) the first generation seed F obtained in field sowing step (2) 1 , select the excellent sterile individual plant whose performance traits in the field are consistent with the backcross male parent described in st...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A second method of breeding cytoplasmic male sterile early-maturing Chinese cabbage germplasm materials, comprising the following steps:
[0052] (1) The precocious self-incompatible line backcross male parent Y66-9 (preserved in the mid-term seed resource bank of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, preservation number S01A0061) (its genotype AA) was obtained by adopting the free microspore culture method;
[0053] (2) The cytoplasmic male sterile material oguraCMS (its genotype AACC) of Brassica napus was used as the female parent, and the male parent of the early-maturing self-incompatible line Y66-9 of Chinese cabbage obtained in step (1) was used as the male parent , through interspecific hybridization to obtain the first-generation seed F 1 (genotype AA);
[0054] (3) the first generation seed F obtained in field sowing step (2) 1 , select an excellent sterile individual plant with the same field performance traits as the backcross male parent Y66-9 (all ster...
Embodiment 3
[0067] A method for breeding cytoplasmic male sterile early-maturing Chinese cabbage germplasm materials, comprising the following steps:
[0068] (1) Obtain the precocious self-incompatibility backcross male parent ZY15 (preserved in the medium-term seed resource bank of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, preservation number S01A0060) (genotype AA) by adopting the free microspore culture method;
[0069] (2) Taking the cytoplasmic male sterile material oguraCMS (genotype AACC) of Brassica napus as the female parent, and the Chinese cabbage precocious self-incompatible line ZY15 obtained in step (1) as the male parent, through breeding F 1 (genotype AA);
[0070] (3) the first generation seed F obtained in field sowing step (2) 1 , select an excellent sterile individual plant with the same field performance traits as the backcross male parent ZY15 as the next round of backcross female parent;
[0071] (4) Using the backcross female parent selected in step (3) and the b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com