A kind of non-ATP competitive FGFR1 inhibitor and its application
A technology of FGFR1 and inhibitor, applied in the field of pharmacy, can solve the problems of large toxic and side effects, poor targeting selectivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The synthesis of embodiment 1 compound
[0024] Dissolve 1mmol of the corresponding terephthalaldehyde and 2mmol of substituted acetophenone in about 20mL of absolute ethanol, add 10-15 drops of 50% NaOH solution at 5-8°C, react for 5-24h at 5-8°C, and use The progress of the reaction was detected by TLC. After the reaction, add 1-2 times the volume of the reaction solution in water to precipitate precipitates, filter, and vacuum dry overnight to obtain a powder product, which is purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain compounds with a purity greater than 98%. Among the multiple compounds synthesized, the pharmacological activities vary greatly, and the representative compounds and their physicochemical properties are as follows:
[0025] Effective compound (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(2-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one)(L16H50)Yellow powder,90.2%yield ,mp144.4~147.1℃.ESI-MS m / z:407.0(M+1) + calcd for C 24 h 16 Cl 2 o 2 :407.29. 1 H-NMR (DMS O)...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The inhibitory activity of embodiment 2 compound to FGFR1 kinase
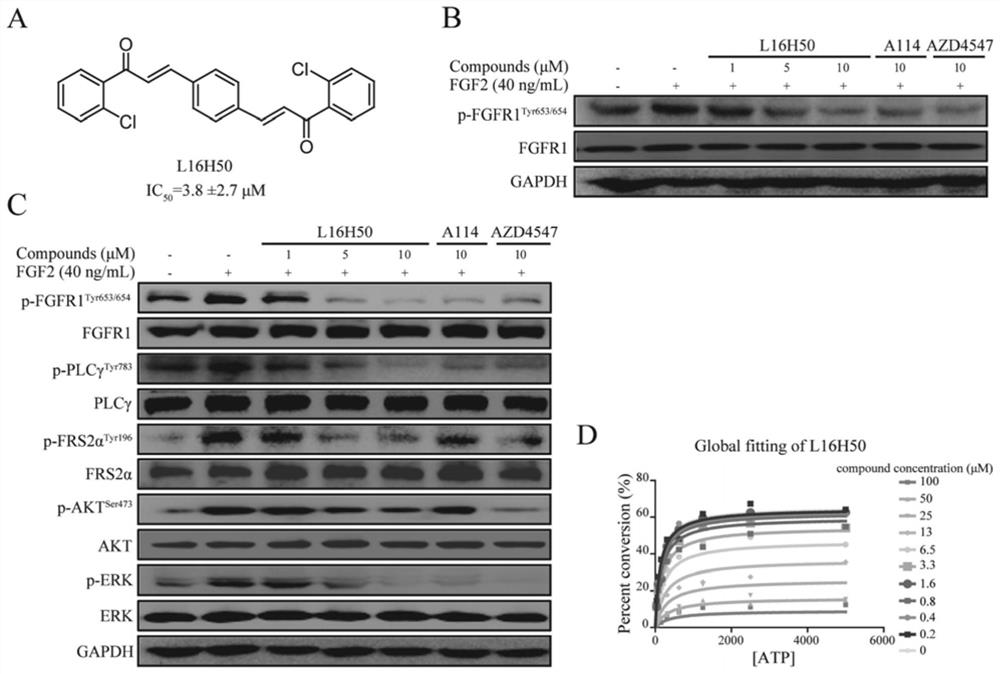
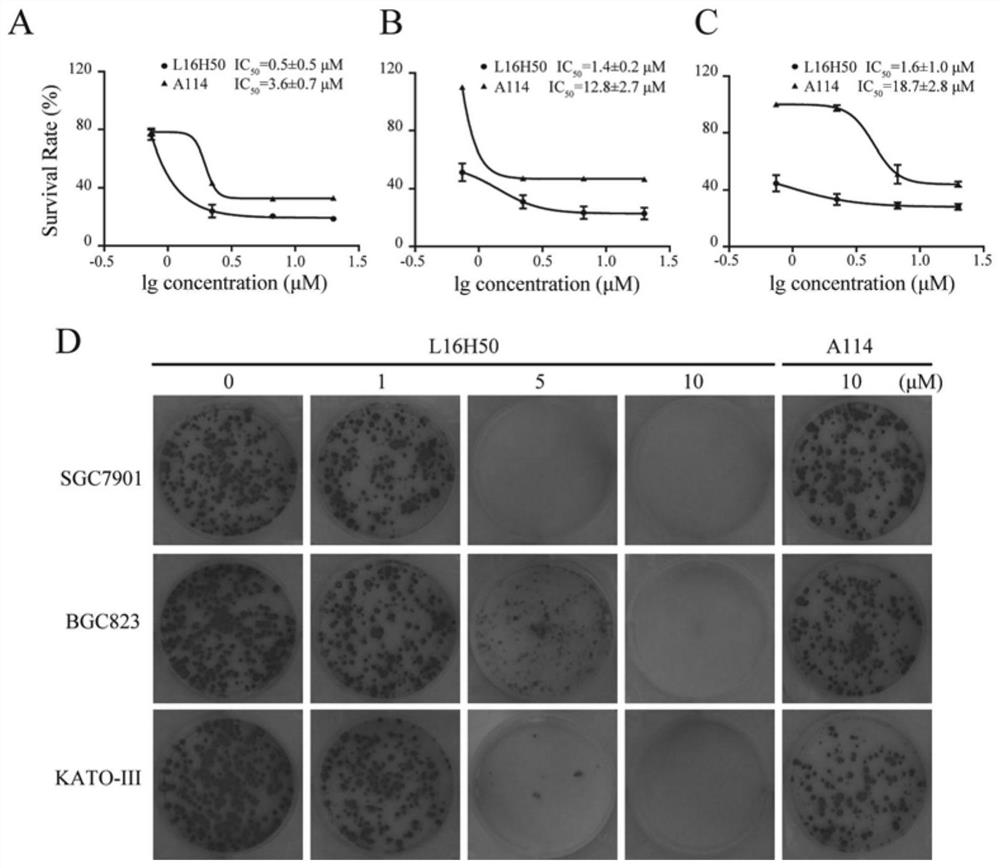
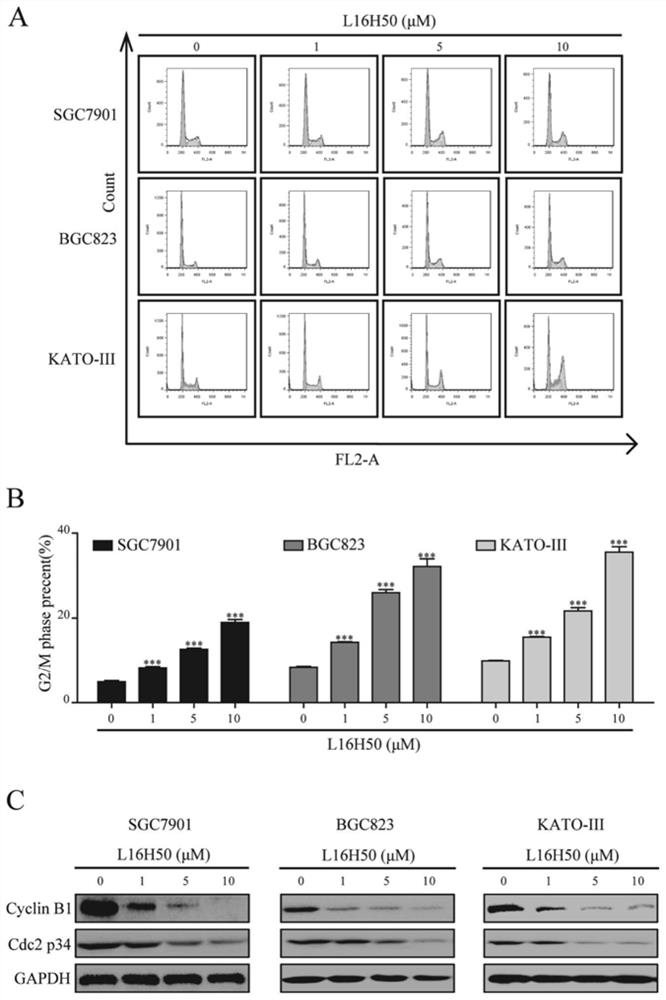
[0029] The Caliper EZ reader drug screening platform was used to detect the kinase activity of the compound on FGFR1. Set the concentration of ATP at the Km value of FGFR1, which is 262 μmol / mL. In order to detect the IC of the compound against the kinase inhibitory activity 50 , the compound was diluted into 10 concentration gradients from 5 nmol / mL to 100 μmol / mL. During mobility detection, the accumulated amount of product is represented by conversion rate=A / (A+B), where A represents the peak height of the product, and B represents the peak height of the substrate. IC of L16H50 for kinase inhibitory activity 50 For: 3.8±2.7μM; while the inhibition rates of the control compounds L15H50 and L20H50 at the concentration of 100μmol / mL to FGFR1 kinase were 19.5% and 15.8%, respectively, it can be considered that both are not FGFR1 kinase inhibitors.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 L16H50 inhibits FGFR1 kinase activity in a non-ATP competitive manner
[0031] L16H50 is a new type of FGFR1 kinase inhibitor. In order to explore its inhibitory mode on FGFR1 kinase, its competitive relationship with ATP was determined. Specific method: first fix the concentration of the substrate (a sufficient concentration relative to the kinase), then add a certain amount of kinase, and then add different concentrations of ATP (5000, 2500, 1250, 625, 312.5, 156.25, 78.125 and 39.0625μmol / mL) and compounds (L16H50: 100, 50, 25, 13, 6.5, 3.3, 1.6, 0.8, 0.4 and 0.2μmol / mL), and then determine the kinase to substrate under different concentrations of ATP and compound conditions Conversion rate, according to the formula conversion rate = (Vmax*X) / {km*[(1+I / Ki) n ]+X}. X represents the concentration of ATP, and n represents the Hill coefficient. See the experimental results figure 1 D, the results show that at a fixed L16H50 concentration, the substrate conv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com