Double-layer turn-back driving finger mechanism
A finger and double-layer technology, which is applied in the field of finger mechanisms driven by double-layer foldbacks, can solve the problems of large impact on joints and large space occupation, and achieve the effect of simplifying the structure of the manipulator and saving space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
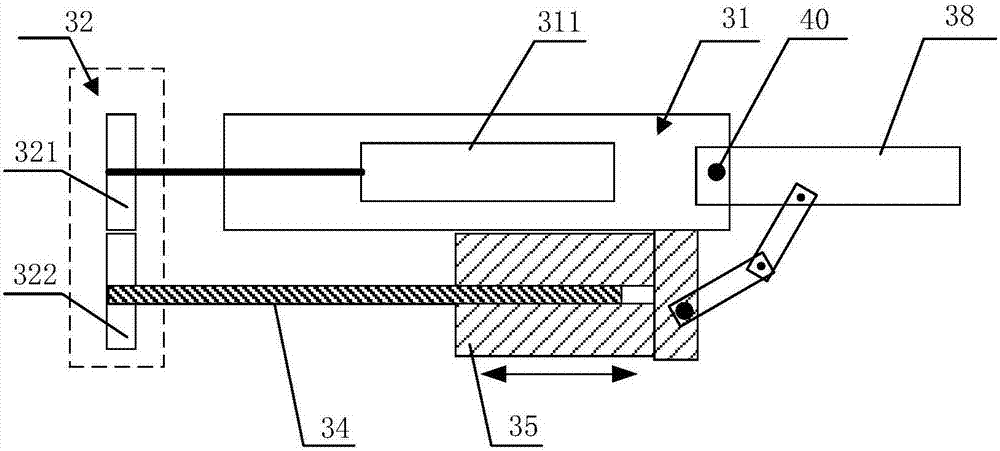
[0038] like Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown in the figure, it is a schematic diagram of the principle of the double-layer folding back-driven finger mechanism according to the embodiment of the present invention. The double-layer folding-back driving finger mechanism according to the embodiment of the present invention includes a finger frame, a gear transmission group, a motor, a screw rod, and a screw matched with the screw rod. Nut and finger body. The gear transmission group includes a first gear and a second gear that mesh with each other, and the finger body and the finger frame are rotatably connected through a first rotating shaft.
[0039] The motor 311 is fixed in the finger frame 31 and is connected with the first gear 321 of the gear transmission group 32 through the output shaft. In practical applications, since the rotational speed output by the motor 311 may be different from the actual required rotational speed, a deceleration component may also be included to ...
Embodiment 2
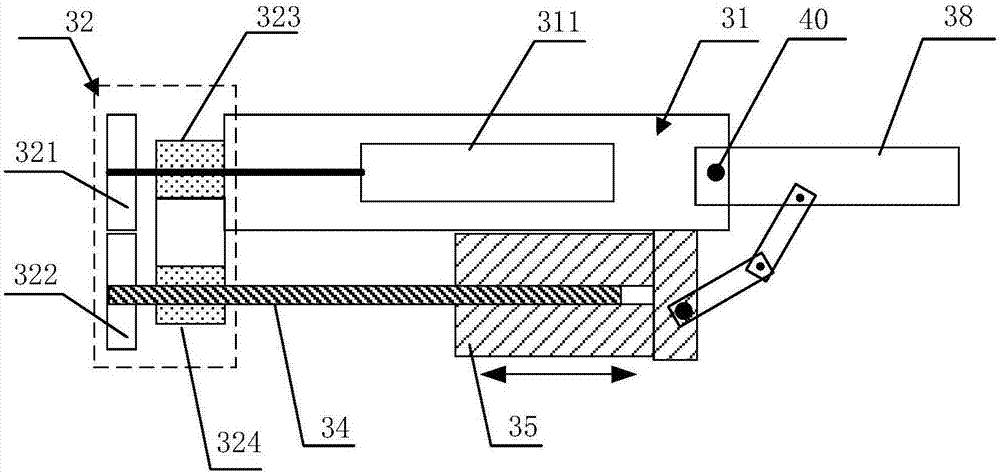
[0049] Compared with the first embodiment, the present embodiment provides an alternative solution to the implementation manner in which the nut 35 is fixed relative to the finger rack 31 in the radial direction in the first embodiment. The fact that the nut 35 is fixed relative to the finger frame 31 in the radial direction means that the nut 35 is restrained in the radial direction and released in the axial direction, and when the screw 34 is rotated, the nut 35 can move in the radial direction. The lower part of the finger frame 31 is provided with a sliding guide rail, and the nut 35 is connected with the finger frame 31 through the sliding guide rail, so that the nut 35 is fixedly connected with the finger frame 31 in the radial direction and can slide in the axial direction. The sliding guide rail may also not have a bearing function, but only provide a restraining effect in the radial direction. Preferably, the nut 35 is clamped on the sliding guide rail, so that the sli...
Embodiment 3
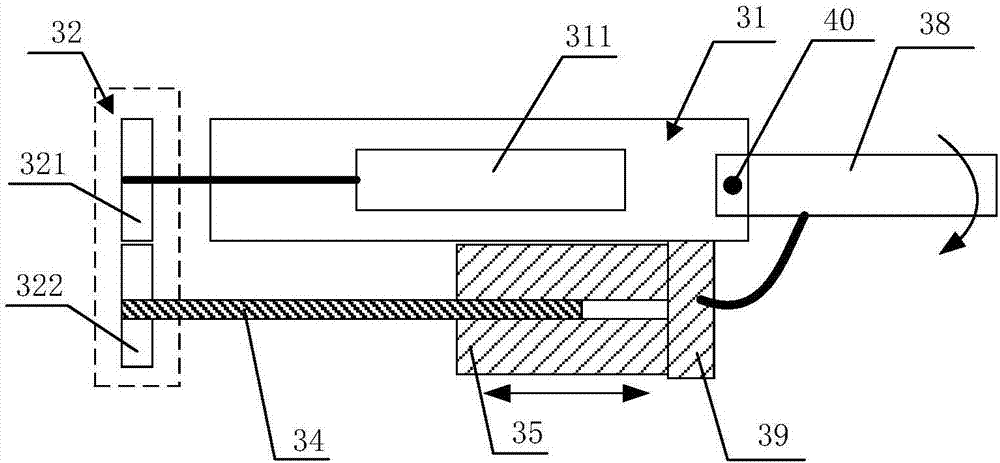
[0051] like Figure 6 to Figure 11 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the principle of the finger mechanism driven by the double-layer folding back according to the third embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is that the finger body of this embodiment includes a base phalanx and a proximal phalanx, and correspondingly, the driving manner of the nut is also different.
[0052] The above-mentioned base phalanx 42 is rotatably connected to the finger frame 31 through the first rotating shaft 40, and the base phalanx 42 and the proximal phalanx 43 are rotatably connected through the second rotating shaft 44, and are arranged between the proximal phalanx 43 and the finger frame 31. There is a first pull rod 45, one end of the first pull rod 45 is rotatably connected to the finger frame 31 through a third rotating shaft 46, and the other end of the first pull rod 45 is rotatably connected to the proximal knuckle 43 through a fourth rotating...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com