Application of splicing cofactor AtU2AF65b in regulation and control of flowering phase of plant
A technology of cofactor and flowering period regulation, applied in the field of molecular biology and biology, can solve the problems of plant growth, difficulty in application, dwarf, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the growth process, solving the contradiction between low and peak seasons, wide application prospects and economic value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
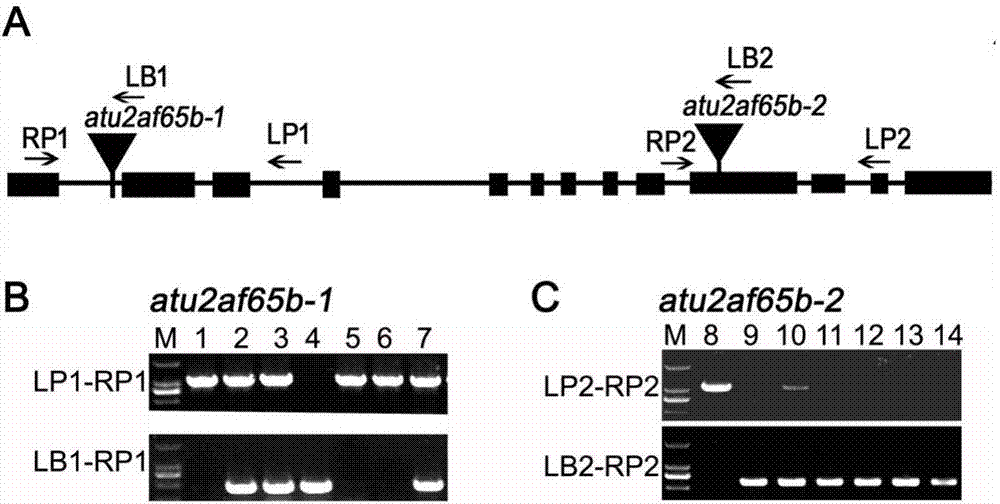
[0032] Example 1 Identification of homozygotes in mutants atu2af65b-1 and atu2af65b-2 of AtU2AF65b gene
[0033] (1) Take Arabidopsis thaliana grown for about 2 weeks in the greenhouse, cut one or two leaves from the plant, 5-10 mg, put them into a centrifuge tube, add 400 μL of extraction buffer (200mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 250mM NaCl, 25mM EDTA, 0.5% SDS), the genomic DNA was extracted by conventional methods.
[0034] (2) Using genomic DNA as a template, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was performed with primers LP and RP, LB and RP, respectively.
[0035] The reaction system for PCR amplification is: 2×Es Taq MasterMix 10 μL, upstream primer LP1 / LB1 (20 μmol / L) 0.5 μL, downstream primer RP1 (20 μmol / L) 0.5 μL, template 1.0 μL, add ddH 2 O to a total volume of 20 μL.
[0036] The reaction conditions for PCR amplification were as follows: first, pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes; 30 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 56°C for 30 secon...
Embodiment 2
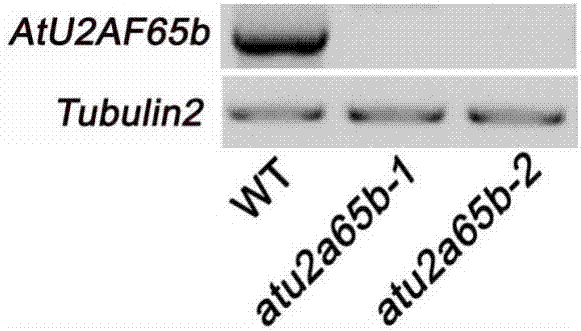
[0049] On the basis of Example 1, the gene expression level of AtU2AF65b in mutant atu2af65b-1 and atu2af65b-2 homozygous was detected
[0050] (1) Take 10 mg each of the homozygous mutants and wild-type Arabidopsis plants grown on MS medium for two weeks, and extract the wild-type respectively with a total RNA extraction kit (purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) and the total RNA of the mutant, the method was carried out according to the instructions. 1ug RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA with reverse transcriptase (Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.).
[0051] (2) Using cDNA as a template, using AtU2AF65b gene-specific primers, detect the amount of AtU2AF65b transcripts in the wild type and mutants by reverse transcription PCR (according to the general one-step RT- PCR kit instructions). The primer sequences are:
[0052] Upstream primer (AtU2AF65b F): 5'-ATGATGAGTTACGAAGGCAACGGAG-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in S...
Embodiment 3
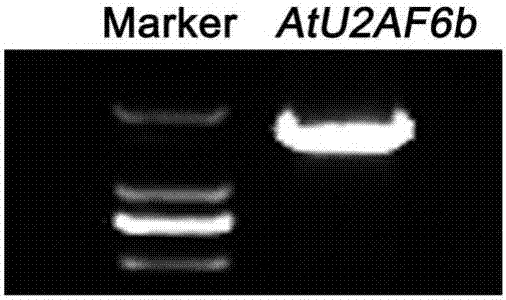
[0061] Construction of AtU2AF65b Overexpression Vector and Identification of Transgenic Plants
[0062] (1) Using the cDNA of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana in Example 2 as a template, use the same AtU2AF65b gene-specific primers (AtU2AF65b F and AtU2AF65b R) in Example 2 to amplify the full length of the AtU2AF65b coding region. The primer sequences are:
[0063] Upstream primer (AtU2AF65b F): 5'-ATGATGAGTTACGAAGGCAACGGAG-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.9;
[0064] Downstream primer (AtU2AF65bR): 5'-TCAGTCTTCGTAGTCGCCTTGG-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQID NO.10;
[0065] The reaction system of PCR amplification is: high-fidelity DNA polymerase 0.5 μL, 5×DNA polymerase buffer 10 μL, dNTP 1 μL, upstream primer (20 μmol / L) 1.5 μL, downstream primer (20 μmol / L) μL, add ddH 2 O to a total volume of 50 μL. The PCR amplification conditions were the same as in Example 2.
[0066] The length of the PCR product was detected by electro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com