Method for performing adaptive variable waveform switching to track target
A tracking target and self-adaptive technology, applied in the direction of radio wave reflection/re-radiation, radio wave measurement system, use of re-radiation, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of continuous and stable tracking of the target, low interception performance, and low transmission power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
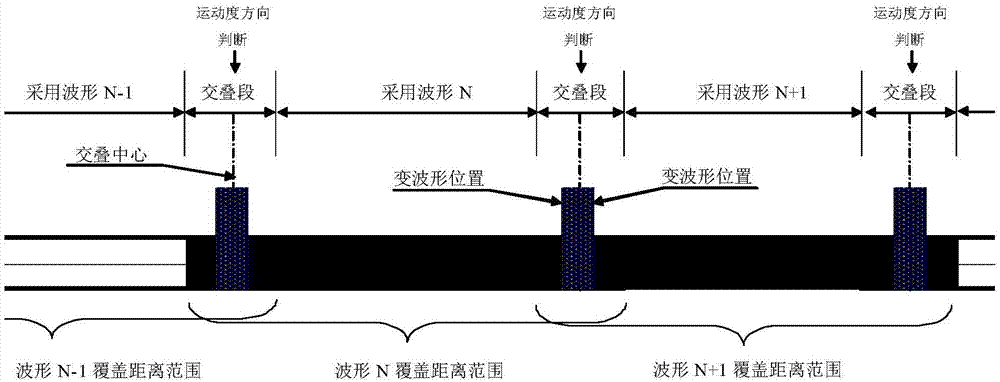
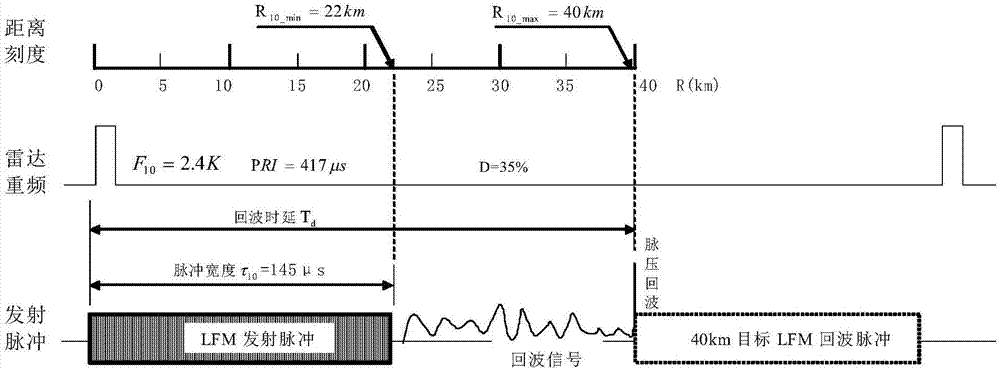
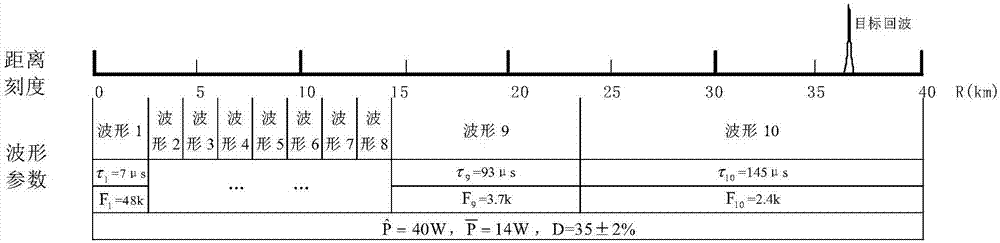
[0022] refer to Figure 1-3 . refer to Figure 1-3 . According to the present invention, according to the distance detection range R required by the radar and the allowable transmitter duty cycle D, the pulse width τ is calculated N and radar pulse repetition frequency F N ;According to the principle of radar, the detection range R required by the radar is divided into N sections, and the distance coverage of each section is R N_min ~R N_max , and the overlapping coverage of adjacent distance segments; then segment R according to the radar detection distance N , beam width θ, operating wavelength λ, radar repetition frequency F N , distance resolution unit △R, target velocity V and target acceleration a, calculate the maximum scan time T allowed for each segment N , to determine the coherent accumulated pulse number n and the required distance coverage R when the target flies from far to near or from near to far N As the target changes, the corresponding pulse width τ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com