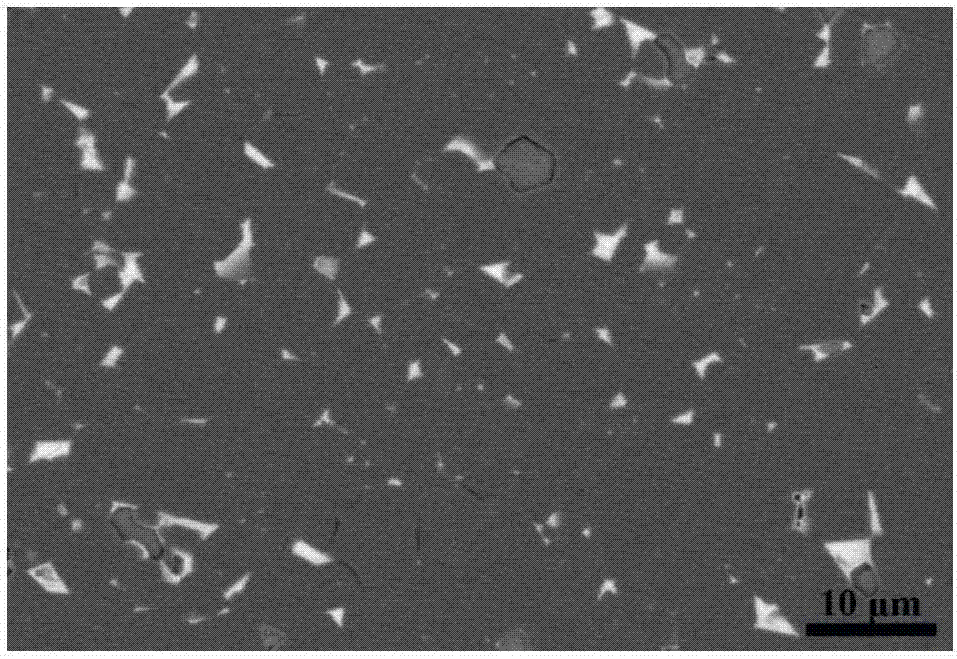
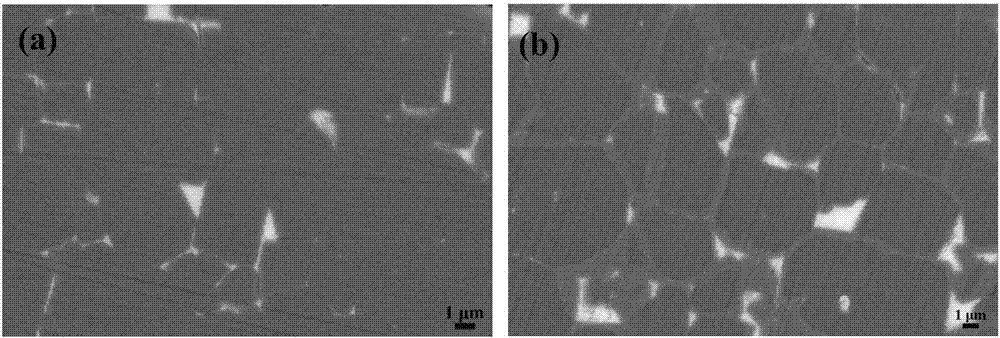
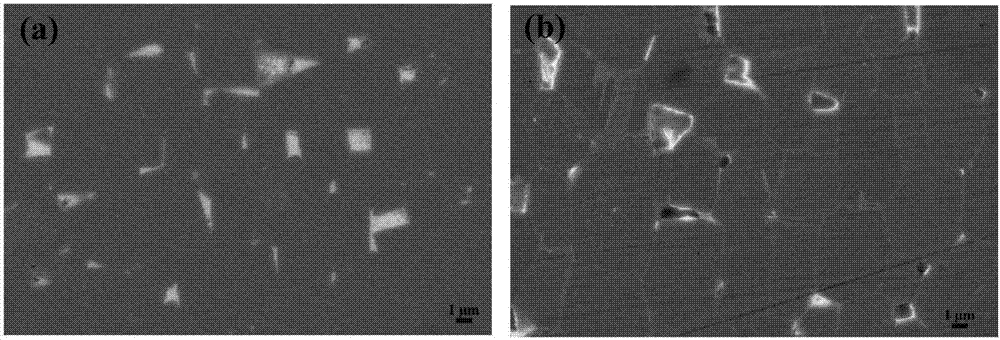
Method for preparing high-performance sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet by using two-step grain boundary diffusion technique
A grain boundary diffusion, NdFeB technology, applied in magnetic objects, solid diffusion coating, metal material coating process, etc., can solve the problem of high concentration gradient of heavy rare earth elements on the surface of magnets, consumption of heavy rare earth elements, and grain growth. and other problems, to avoid abnormal growth of crystal grains and improve the utilization rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Select an N50 commercial magnet, process it into a sample with a size of φ8mm×5mm, and clean the surface. The composition is Pr prepared by the quick-setting process 50 Tb 20 Cu 15 Al 15 (atomic percent) alloy thin strip (30 μm thick) as a diffusion source; directly covering the upper and lower surfaces of the magnet after surface cleaning; place the treated sample in the furnace, and evacuate to (3-5)×10 -3 Pa is subjected to a first-stage heat treatment, that is, holding at 700°C for 6h; then performing a second-stage heat treatment, that is, holding at 900°C for 1h; and finally performing a third-stage heat treatment at 500°C for 2h under vacuum annealing; to obtain a high coercive force sintered NdFeB magnetic material . The coercive force of the magnet is increased from 12.2kOe before grain boundary diffusion to 22.5kOe after diffusion, while the remanence hardly decreases. The magnetic properties of the original magnet and the diffused magnet are as follows: ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Select an N50 commercial magnet, process it into a sample with a size of φ8mm×5mm, and clean the surface. The composition is Pr prepared by the quick-setting process 60 Tb 10 Cu 10 Al 10 co 10 (atomic percent) alloy thin strip (30μm thick) as a diffusion source; directly cover the upper and lower surfaces of the magnet after surface cleaning; place the treated sample in the furnace, and evacuate to (3-5)×10-3Pa Carry out the primary heat treatment, that is, hold at 650°C for 6 hours; then carry out the second stage of heat treatment, that is, hold at 900°C for 1 hour; finally carry out the third stage of heat treatment at 500°C for 2 hours in vacuum annealing; obtain high coercive force sintered NdFeB magnetic materials. The coercive force of the magnet increases from 12.5kOe before grain boundary diffusion to 20.5kOe after diffusion, while the remanence hardly decreases. The magnetic properties of the original magnet and the diffused magnet are as follows:
[002...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com