Inertial navigation-based indoor positioning method and device
An indoor positioning and base station technology, used in measurement devices, navigation, surveying and navigation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
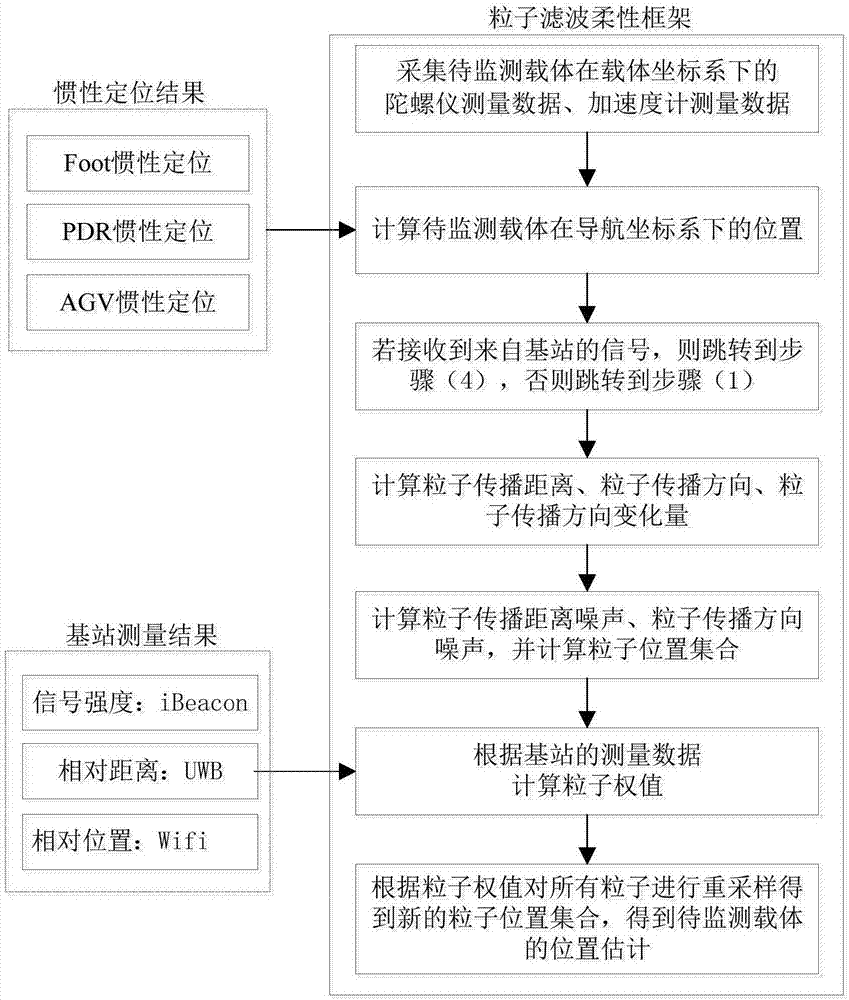
[0081] The carrier to be monitored is a person, and the position of the carrier to be monitored is calculated by using the person's foot dead reckoning (Foot-INS); at this time k is the sampling time. Preferably, an accelerometer and a gyroscope are arranged on the foot of the person.
[0082] In this embodiment, the specific steps of the indoor positioning method based on inertial navigation are as follows:
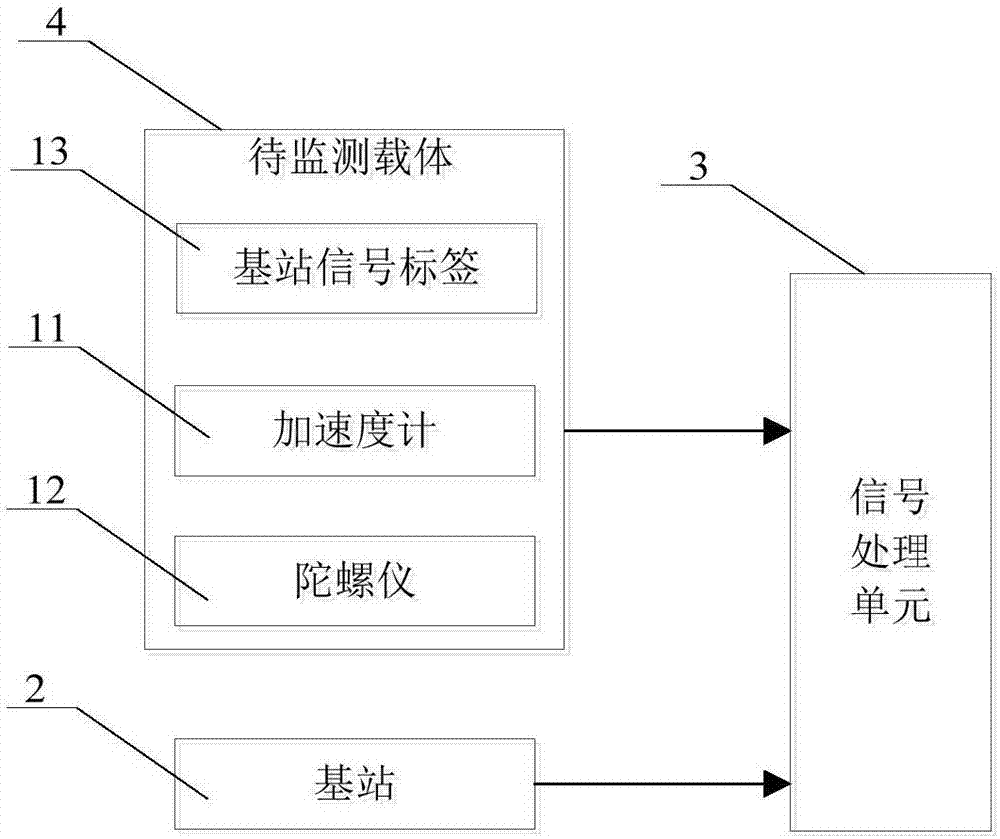
[0083] (1) While the carrier to be monitored is moving, the gyroscope measurement data of the carrier to be monitored 4 in the carrier coordinate system is collected at a fixed period Accelerometer measurement data in the carrier coordinate system It is preferably the accelerometer and gyroscope measurement data of the foot; wherein, the superscript b or subscript b indicates that the data is in the carrier coordinate system;
[0084] (2) Use gyroscope to measure data Accelerometer measurement data Calculate the position (x k ,y k ); if the carrier 4 to be moni...
Embodiment 2
[0134] The carrier 4 to be monitored is a person, and the position of the carrier to be monitored is calculated by using the waist dead reckoning (PDR-INS); at this time, k is the number of steps the person is traveling. The steps in this embodiment are the same as those in other embodiments, and the content in the steps in other embodiments can be adopted. In the second embodiment, in step (2), the PDR-INS uses the dead reckoning model to calculate the movement position change of the carrier. The accelerometer and gyroscope are preferably installed on the waist of the person, and the inertial measurement data obtained are the gyroscope measurement data of the waist of the person and accelerometer measurements
[0135] In the present embodiment, the specific sub-steps in step (2) are as follows:
[0136] (2.1) Use the following formula to calculate the step length L of the k-th step in the process of personnel moving k
[0137]
[0138] in, is the step frequency of...
Embodiment 3
[0145] The carrier 4 to be monitored is a wheeled robot, and the position of the carrier 4 to be monitored is calculated by using the wheeled robot dead reckoning (AGV-INS). In this embodiment, k is the sampling time. The steps in this embodiment are the same as those in other embodiments, and the content in the steps in other embodiments can be adopted. In this embodiment, in step (2), the AGV-INS uses a dead reckoning algorithm to obtain the position change of the wheeled robot.
[0146] In this embodiment, in step (2), the position of the wheeled robot in the navigation coordinate system (x k ,y k )
[0147]
[0148] Among them, L k is the horizontal displacement increment of the wheeled robot from time k-1 to time k, is the wheel orientation angle at time k, and k is the sampling point at a fixed sampling frequency. (x k ,y k ) is the AGV-INS inertial track data.
[0149] Among them, the pulse number n of the wheel encoder wheel encoder from k-1 time to k time...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com