Ultrathin heat homogenizing plate structure
A vapor chamber, ultra-thin technology, applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of easy dents on the shell plate, complicated manufacturing process, poor temperature uniformity of the vapor chamber, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
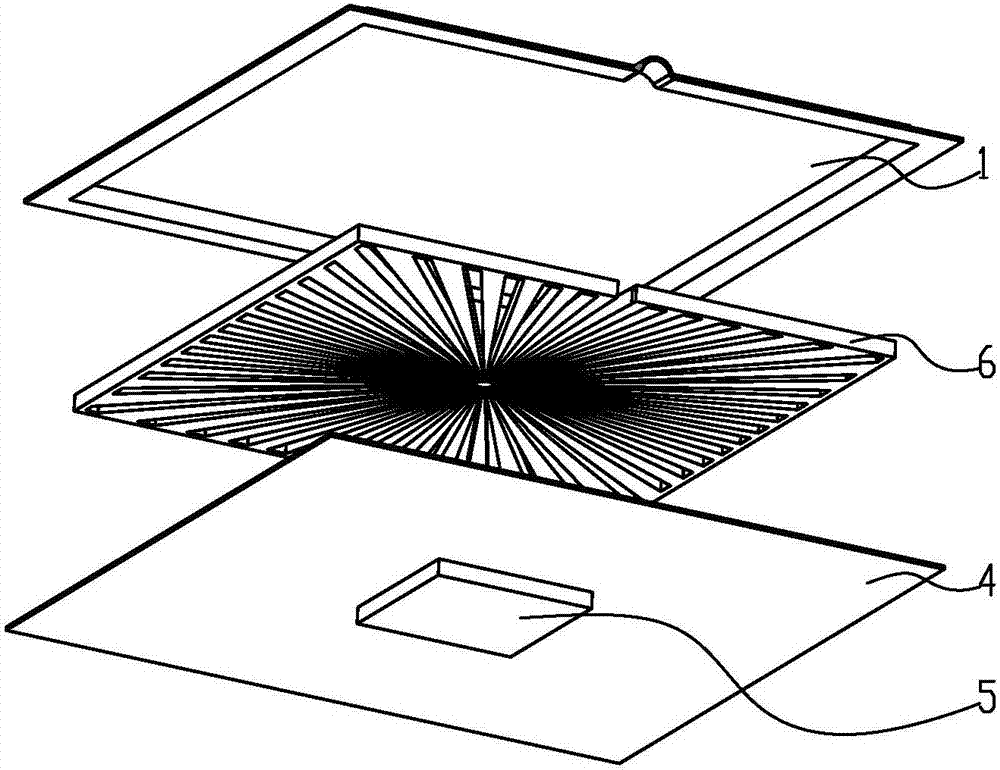
[0035] Such as figure 1 , image 3 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 As shown, an ultra-thin vapor chamber includes: an upper shell 1, a layer of liquid-absorbing core 2 and a lower shell 4 arranged in sequence, the lower surface of the upper shell 1 and the uppermost liquid-absorbing core 2 The upper surface is affixed, the bottom surface of the bottom liquid-absorbing core 2 is affixed to the upper surface of the lower shell 4, and the center of the heat source 5 located in the lower shell 4 or the upper shell 1 is centered on the liquid-absorbing core 2. The annular array is provided with several channels 22 that gradually widen outwards from the center, and between adjacent channels 22 are liquid-absorbing core strips 7, and this layer of liquid-absorbing core 2 is called channel liquid-absorbing core 6, and the grooves The ratio between the depth of the channel 22 and the total thickness of all the liquid-absorbing cores 2 is greater than 1:2, and the angle between the centerlin...
Embodiment 2
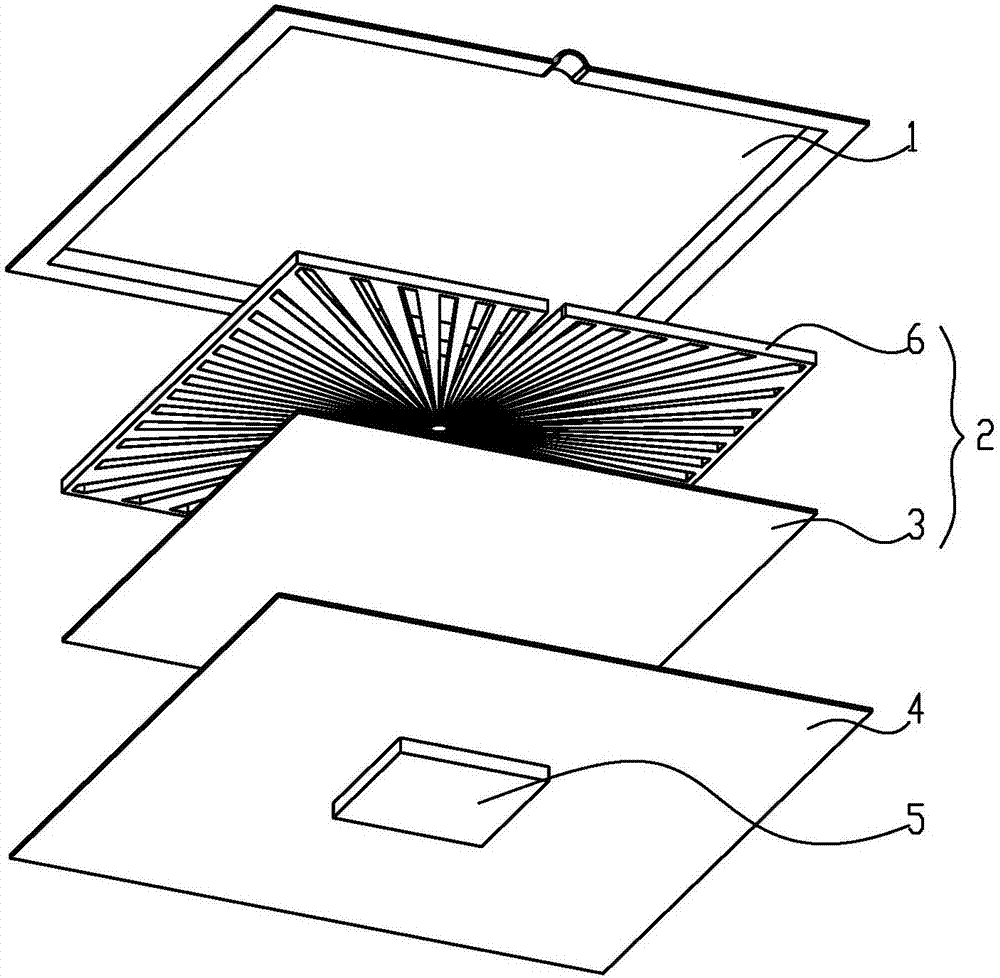
[0041] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be repeated here. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that: figure 2 , Figure 7 , Figure 8 As shown, the liquid-absorbent core 2 is arranged in two layers including the channel liquid-absorbent core 6 provided with the channel 22 and the conventional liquid-absorbent core 3 , and the channel liquid-absorbent core 6 provided with the channel 22 is arranged away from the heat source 5 .
[0042] The heat source 5 is placed at the center of the bottom of the lower shell plate 4 of the vapor chamber, which is also the center of the divergence of the liquid absorbing core 6 of the channel. The lower surface of the conventional liquid-absorbing core 3 is affixed to the upper surface, and the lower surface of the conventional liquid-absorbing core 3 is affixed to the upper surface of the lower shell plate 4. In this way, the channel 22 of the channel liquid-absorbing c...
Embodiment 3
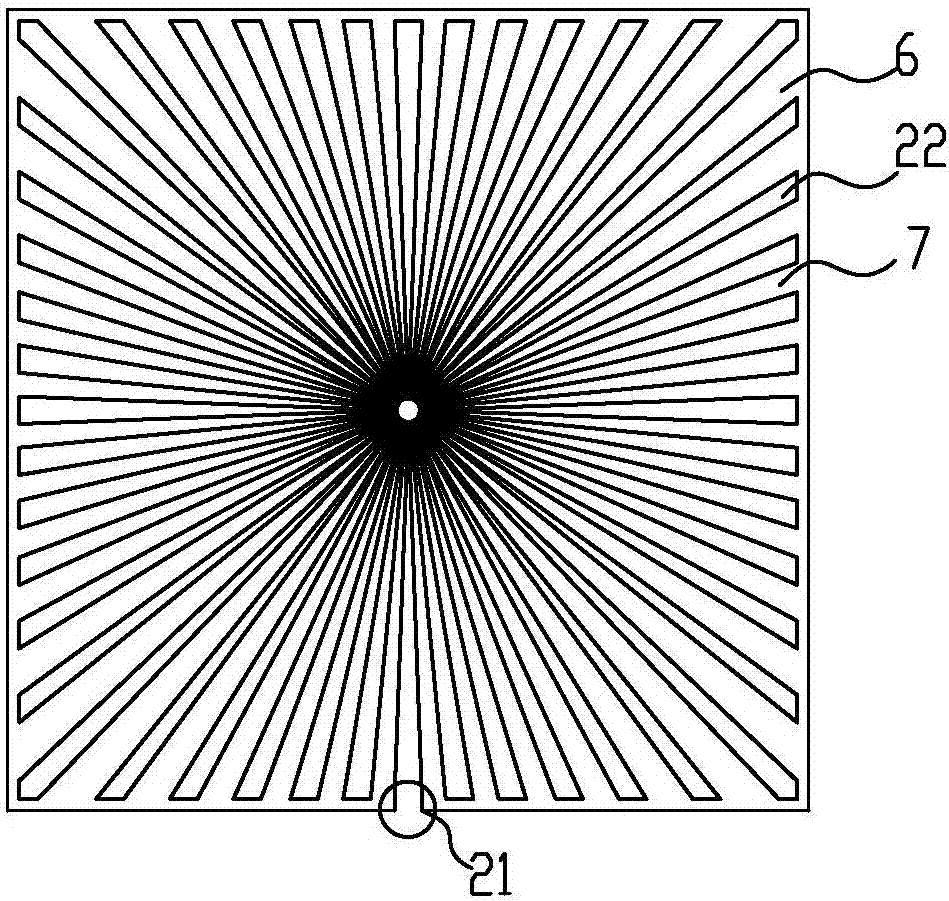
[0044] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be repeated here. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that: Figure 4 As shown, with the center as the center of the circle, the ratio of the total width of the channel 22 on the same circumference to the width of the total liquid-absorbent core strip 7 is less than or equal to 2:1, with the center as the center of the circle, the ratio of the total width of the channel 22 on the same circumference is less than or equal to 2:1. Where the ratio of the width to the width of the adjacent liquid-absorbing core side strip 7 is less than or equal to 1:3, a branch channel 23 is provided, and the maximum width of the channel 22 is ≤3mm. When the area of the vapor chamber is large, since the thickness of the upper and lower shell plates 4 is only 0.03-0.3mm, in order to ensure sufficient support strength, the maximum distance between the channels 22 shall not exceed 3mm, whi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com