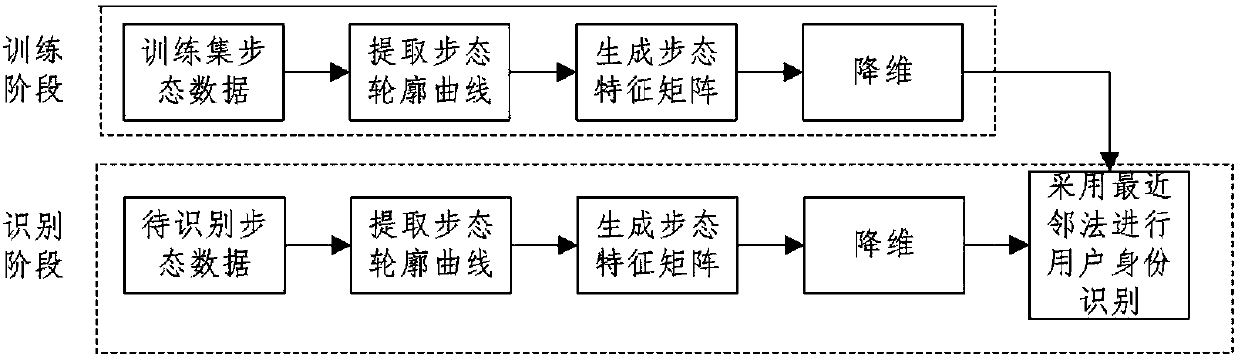
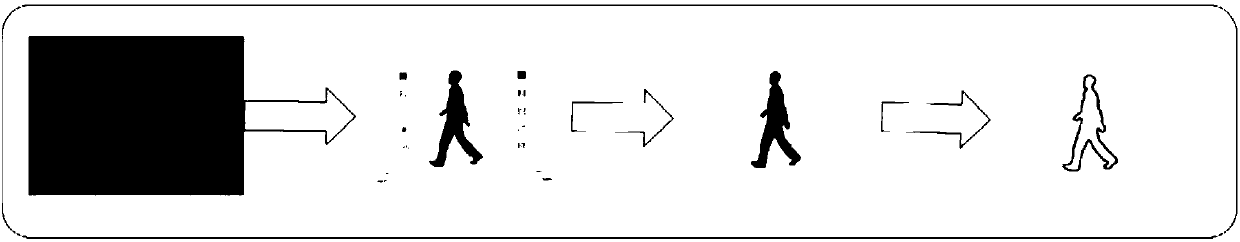
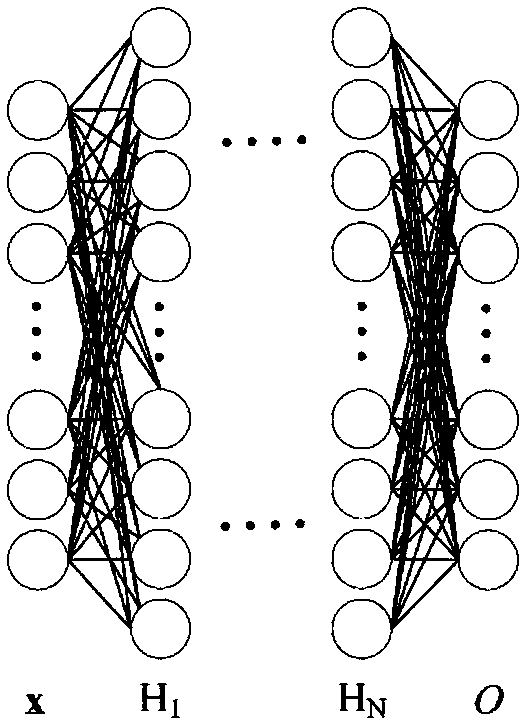
Gait data-based identity recognition method
A technology of identity recognition and gait, applied in digital data authentication, character and pattern recognition, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of application and promotion of gait recognition methods, achieve strong sparsity, improve accuracy, and maintain local The effect of details
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0061] Example 1: Using Dataset B of the CASIA gait database to test the accuracy of identification
[0062] CASIA Dataset B is a large-scale multi-view gait dataset. The dataset was collected in 2005 and contains 15,004 gait videos of 124 individuals. The gait of each person is collected from 11 viewing angles (0, 18, 36, ..., 180 degrees), and the walking conditions include three types: normal conditions, wearing a coat and backpack. The recognition results of this embodiment were compared with methods based on HMM (Hidden Markov Model), CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), and VTM (View Transformation Matrix). Training data acquisition method: Randomly select gait data of different proportions of each person's 90-degree viewing angle under normal conditions for training, and the remaining 90-degree viewing angle data and other viewing angle data are used for identity recognition testing. The method that the application proposes and the comparative experiment result of thre...
example 2
[0063] Example 2: Using Dataset C of the CASIA gait database to test the accuracy of identification
[0064] CASIA Dataset C is a large-scale gait dataset collected with infrared cameras for nighttime scenes. The dataset was collected in 2005 and contains 1583 gait videos of 153 individuals. Each person's walking conditions include four types: normal walking, fast walking, slow walking and walking with bags. The recognition results of this embodiment were compared with methods based on HMM (Hidden Markov Model), CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), and VTM (View Transformation Matrix). Training data acquisition method: Randomly select different proportions of gait data from normal walking data for training, and the remaining normal walking data and other conditional data are used for identity recognition testing. The method that the application proposes and the comparative experiment result of three kinds of existing methods are as follows Figure 5 As shown, the horizontal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com