Method for preparing non-noble metal tungsten carbide photocatalyst by hydrothermal method
A non-precious metal and photocatalyst technology, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of disordered product appearance, incomplete agglomeration and reaction, irregular particle size, etc. Achieve the effect of controllable shape, uniform particle size and perfect crystal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Weigh 1.3g of sodium tungstate and 1.0g of ammonium sulfate in 30mL of deionized water, mix them evenly and dissolve them fully, use 3M HCl solution to adjust the pH=2, add the obtained clear mixed liquid into 50mL of polytetrafluoroethylene to react The reaction kettle was placed in an oven at 180°C for hydrothermal reaction for 8 hours, then cooled to room temperature naturally, and the product was centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain a tungsten trioxide precursor;
[0027] Put 0.15g of tungsten trioxide precursor and 0.9g of glucose in 30mL of deionized water and mix evenly, then add it into a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, put the reactor in a 180°C oven for hydrothermal reaction for 8 hours, and then Cool naturally to room temperature, and centrifuge, wash, and dry the product to obtain a carbon-coated tungsten trioxide precursor;
[0028] Put the carbon-coated tungsten trioxide precursor into the heat treatment equipment, fill it with argon, program the ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] In this example, the non-noble metal tungsten carbide photocatalyst was prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, except that the amount of glucose was changed to 0.45 g. The resulting target product is labeled as T2.
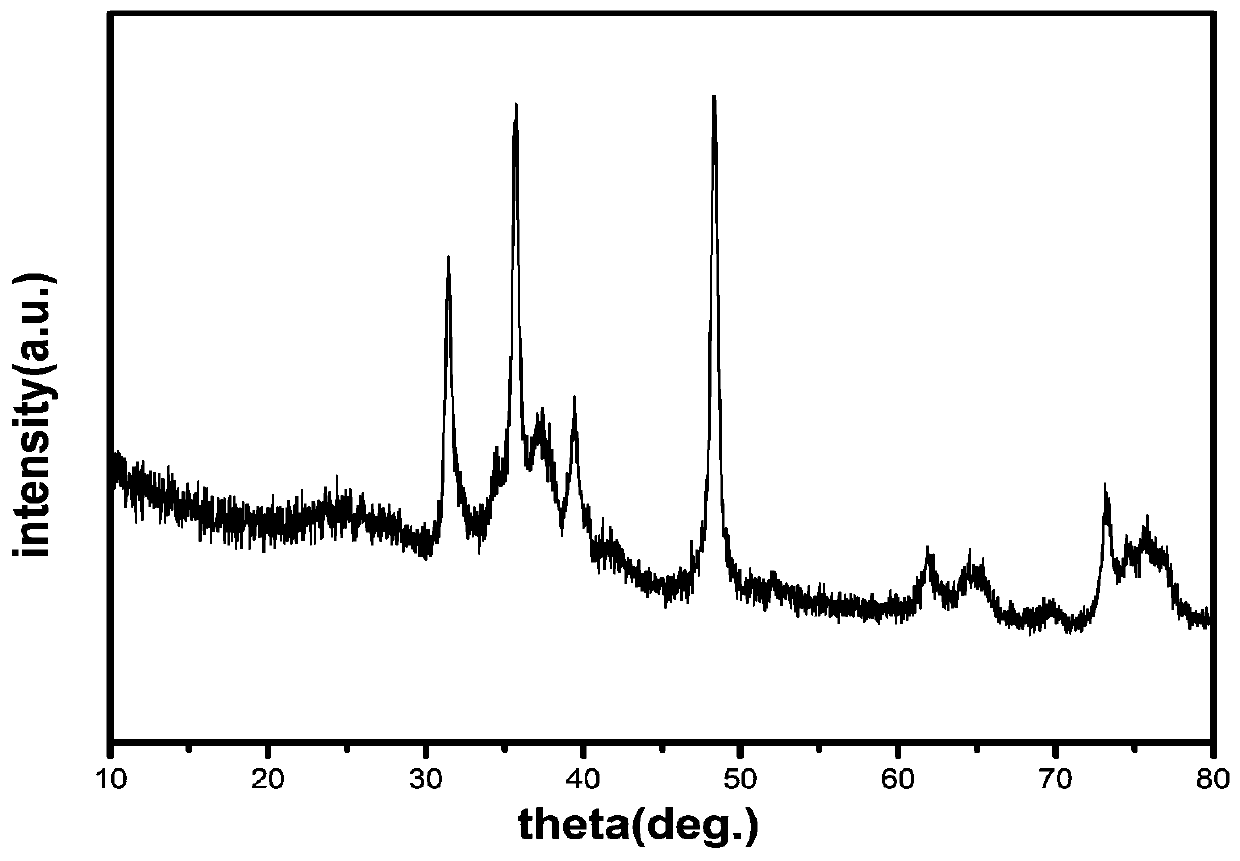
[0033] figure 1 Scanning electron micrograph of the target product tungsten carbide, figure 2 is the X-ray diffraction spectrum of the target product. from figure 1 It can be seen that the prepared tungsten carbide catalyst has a long rod-shaped structure with good dispersion, and its average length is about 600nm. from figure 2 It can be clearly seen that there are three strongest diffraction peaks at 2θ of 31.480, 35.760 and 48.400, corresponding to the (001), (100) and (101) crystal planes of WC (JCPDS: 51-0939) ; In addition, there are several relatively weak diffraction peaks, whose 2θ values are 64.040, 65.320, 73.200, 75.600 and 76.920, which are respectively WC crystal planes (110), (002), (111), (200) and ( 102) (JCPDS: 51...
Embodiment 3
[0036] In this example, the non-noble metal tungsten carbide photocatalyst was prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, except that the amount of glucose was changed to 0.225 g. The resulting target product was labeled as T3.
[0037] The morphology of the sample obtained in this example is similar to that of Example 2, with uniform particle size, excellent appearance and good performance.
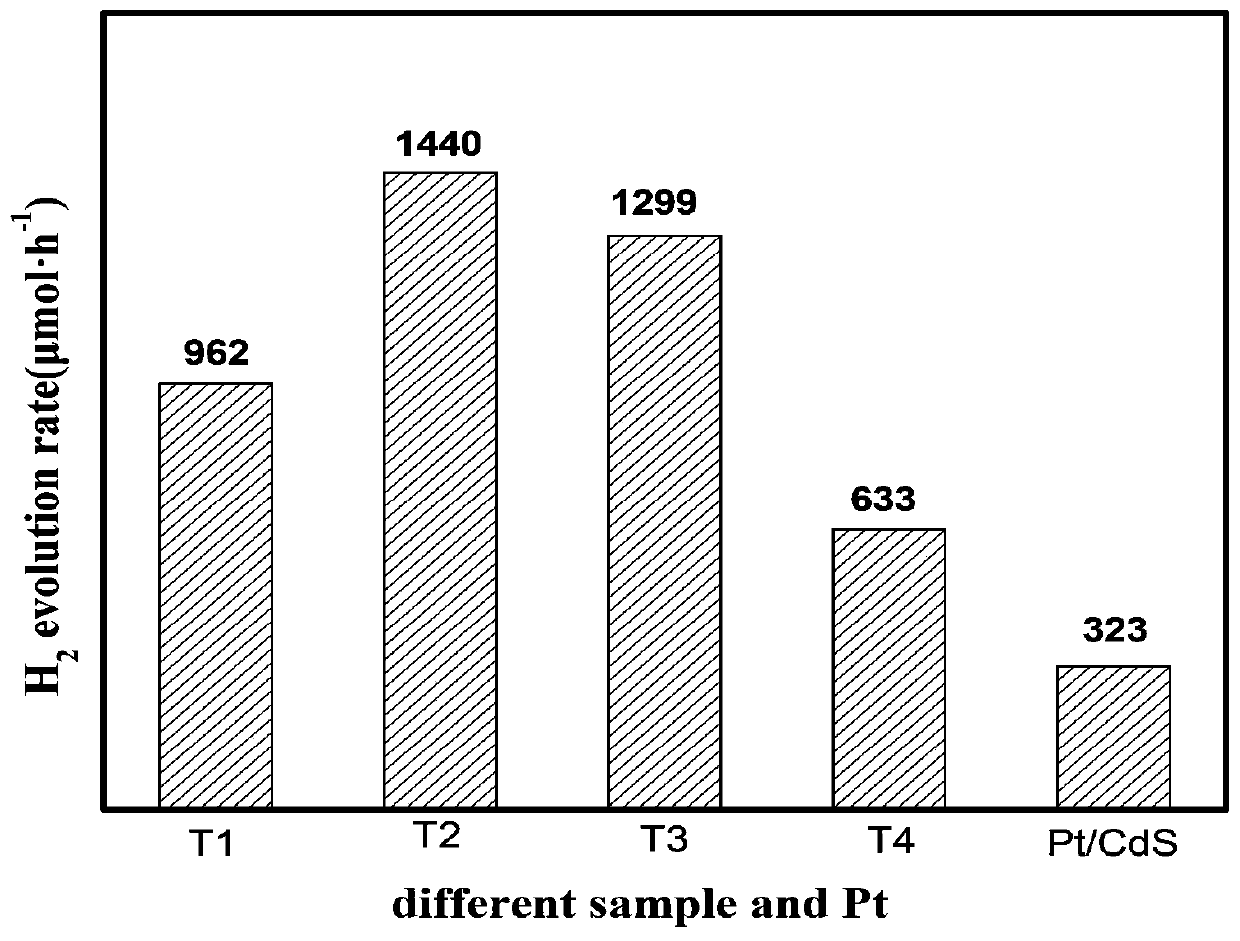
[0038] The T3 sample was used in the photocatalytic water splitting hydrogen production reaction according to the same method as in Example 1, and the noble metal Pt was used as the photocatalyst for comparison to test its catalytic performance. After testing, the hydrogen production of the T3 sample is as follows image 3 As shown, the calculated hydrogen production rate of the T3 sample is 1299 μmol / h, which is higher than that of the noble metal-based photocatalyst (about 323 μmol / h).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com