Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as gate oxide layer breakdown damage, achieve the effect of avoiding breakdown damage and ensuring overall performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, which is used for manufacturing a semiconductor device.
[0039] Such as figure 2 Shown is a schematic flow chart of the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device according to this embodiment. The manufacturing method of the semiconductor device includes:
[0040] Step 201, forming a gate oxide layer on a semiconductor substrate.
[0041] The semiconductor substrate in this embodiment can be a silicon substrate, a sapphire substrate, or any other semiconductor substrate, which can be selected according to actual needs.
[0042] The gate oxide layer in this embodiment may be silicon dioxide. For example, if the semiconductor substrate is a silicon substrate, the gate oxide layer may be formed by oxidizing the silicon substrate. The growth temperature of the gate oxide layer is 900° C. to 1200° C. ℃, the thickness is 0.01 micron to 1.0 micron.
[0043] Step 202, forming a gate material...
Embodiment 2
[0053] In this embodiment, a further supplementary description is given to the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in the first embodiment.
[0054] Such as Figures 3A to 3F Shown is a schematic structural view of each step of the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device according to this embodiment.
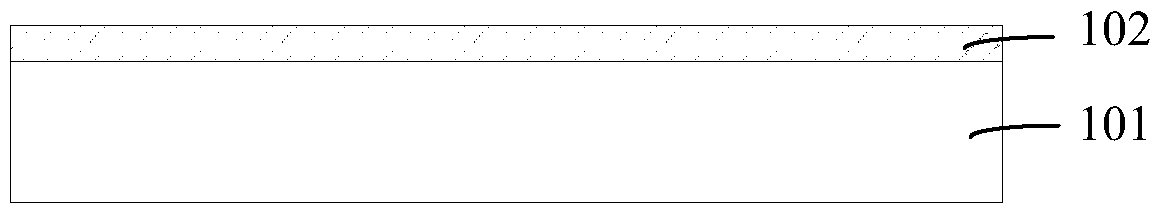
[0055] Such as Figure 3A As shown, a gate oxide layer 302 is formed on a semiconductor substrate 301 .
[0056] The semiconductor substrate 301 in this embodiment may be a silicon substrate, a sapphire substrate, or any other semiconductor substrate, which may be selected according to actual needs.
[0057] The gate oxide layer 302 in this embodiment may be silicon dioxide. For example, if the semiconductor substrate 301 is a silicon substrate, the gate oxide layer may be formed by oxidizing the silicon substrate. The growth temperature of the gate oxide layer 302 is 900° C.˜1200° C., and the thickness is 0.01 μm˜1.0 μm.
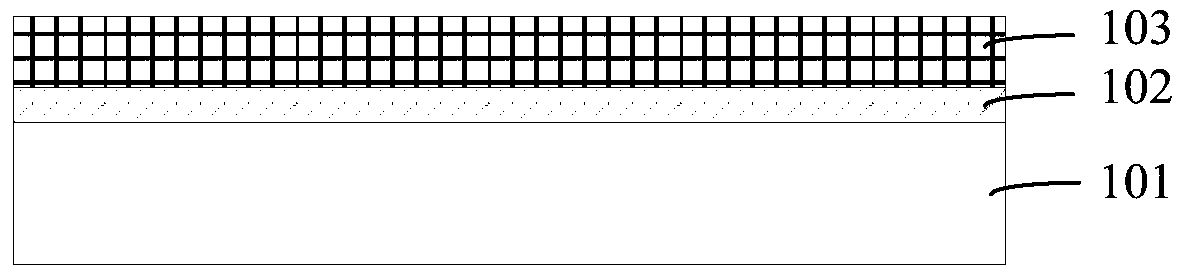
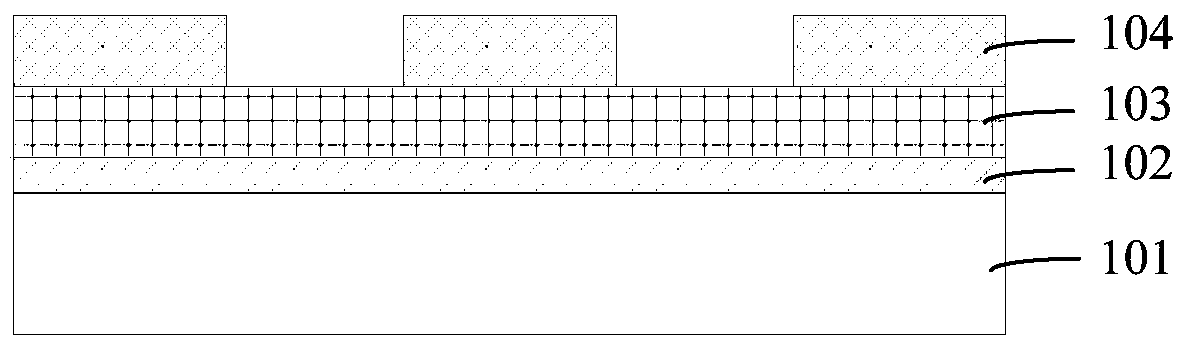
[0058] Such as Figure 3B As s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com