Biomarkers for diagnosing vascular stenotic diseases and their uses
A technology for use and vitamins, applied in the field of biomarkers for diagnosing vascular stenosis diseases and its uses, can solve the problem of unreliable speculation of cardiovascular diseases in diabetic patients, and achieve the effect of simple and effective early diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Preparation of patient's blood sample
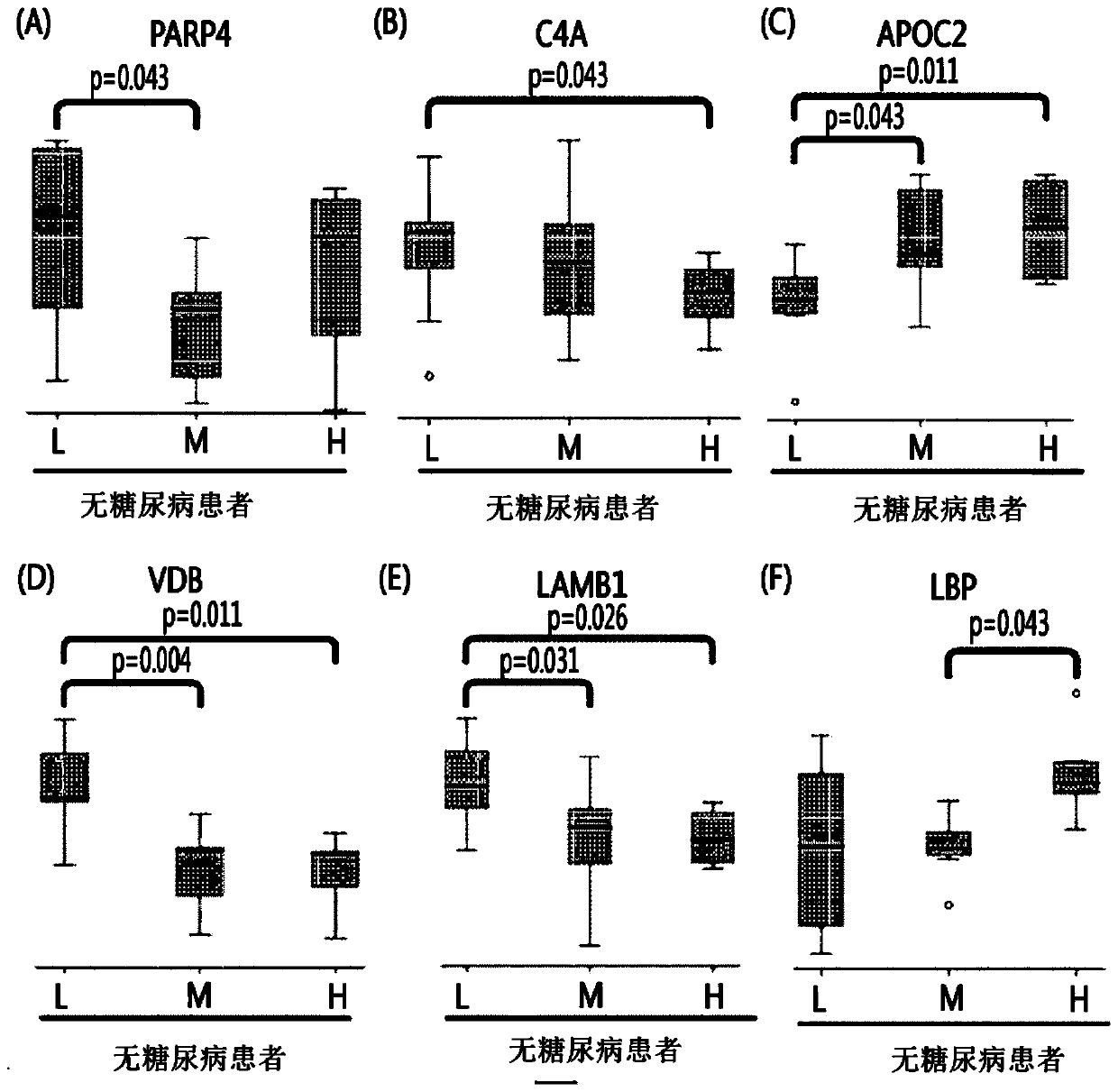
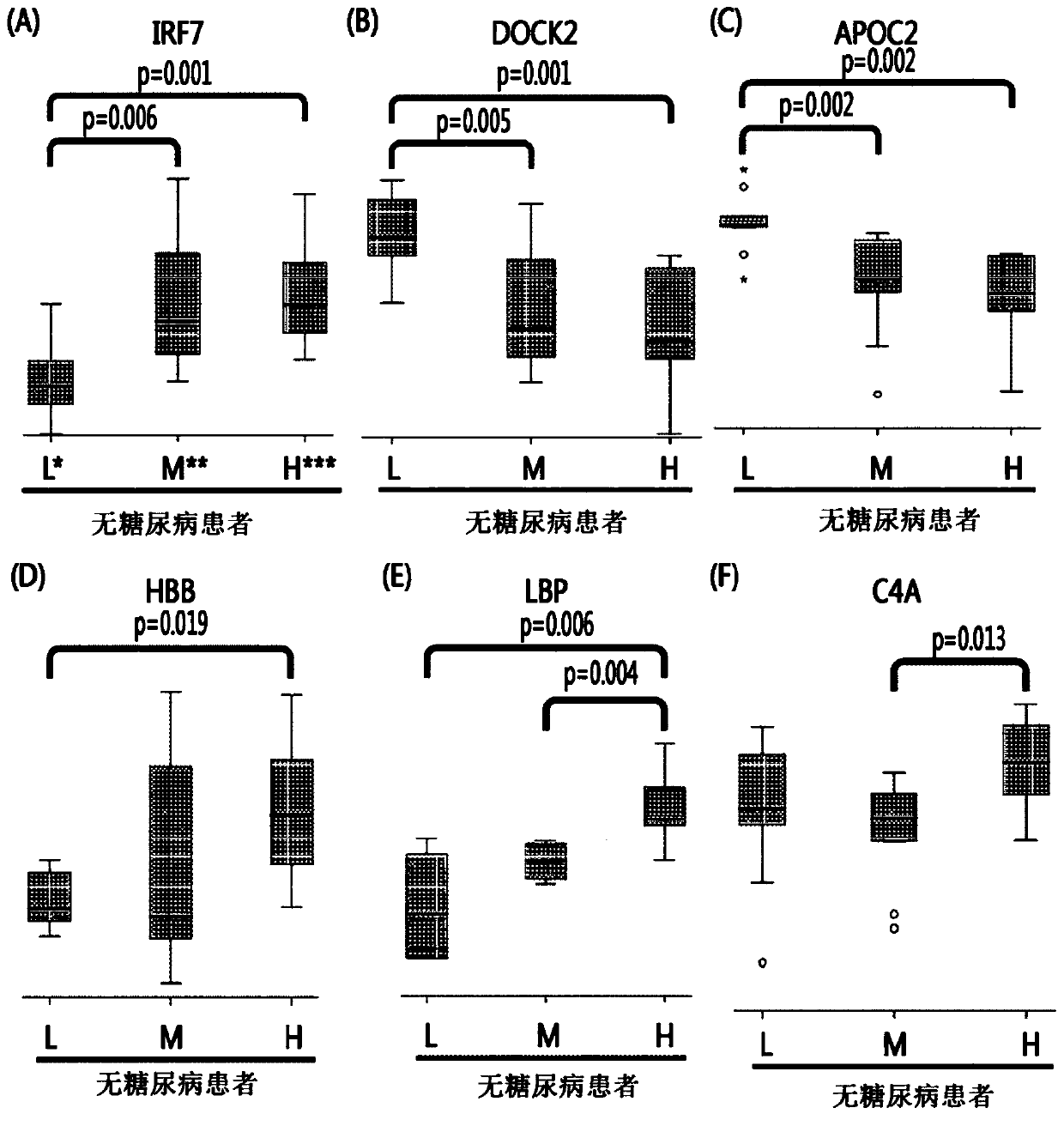
[0067] According to the blockage degree of vascular stenosis, non-diabetic patients were divided into low-risk group patients (0%), medium-risk group patients (0-50%), and high-risk group patients (above 50%). Diabetic patients are divided into low-risk group patients, intermediate-risk group patients, and high-risk group patients. Thereafter, blood samples were collected from these patients.
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: Removal of Abundant Proteins from Patient Blood Samples
[0069] Among the proteins of the blood samples collected in Example 1, 14 high-abundance proteins (albumin, IgG, antitrypsin, IgA, transferrin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, α2-macrosphere Protein, α1 acid glycoprotein, IgM, apolipoprotein AI, apolipoprotein AII, complement C3, transthyretin) accounted for 95% of the total protein. Therefore, when analyzing the low-abundance proteins of interest, the sensitivity of these 14 high-abundance proteins is greatly reduced, so the MARS (Multiple Affinity Removal System (Multiple Affinity Removal System)) column (P / N 5188 -6558, Agilent) to remove the 14 proteins, and only the remaining proteins were used for subsequent analysis.
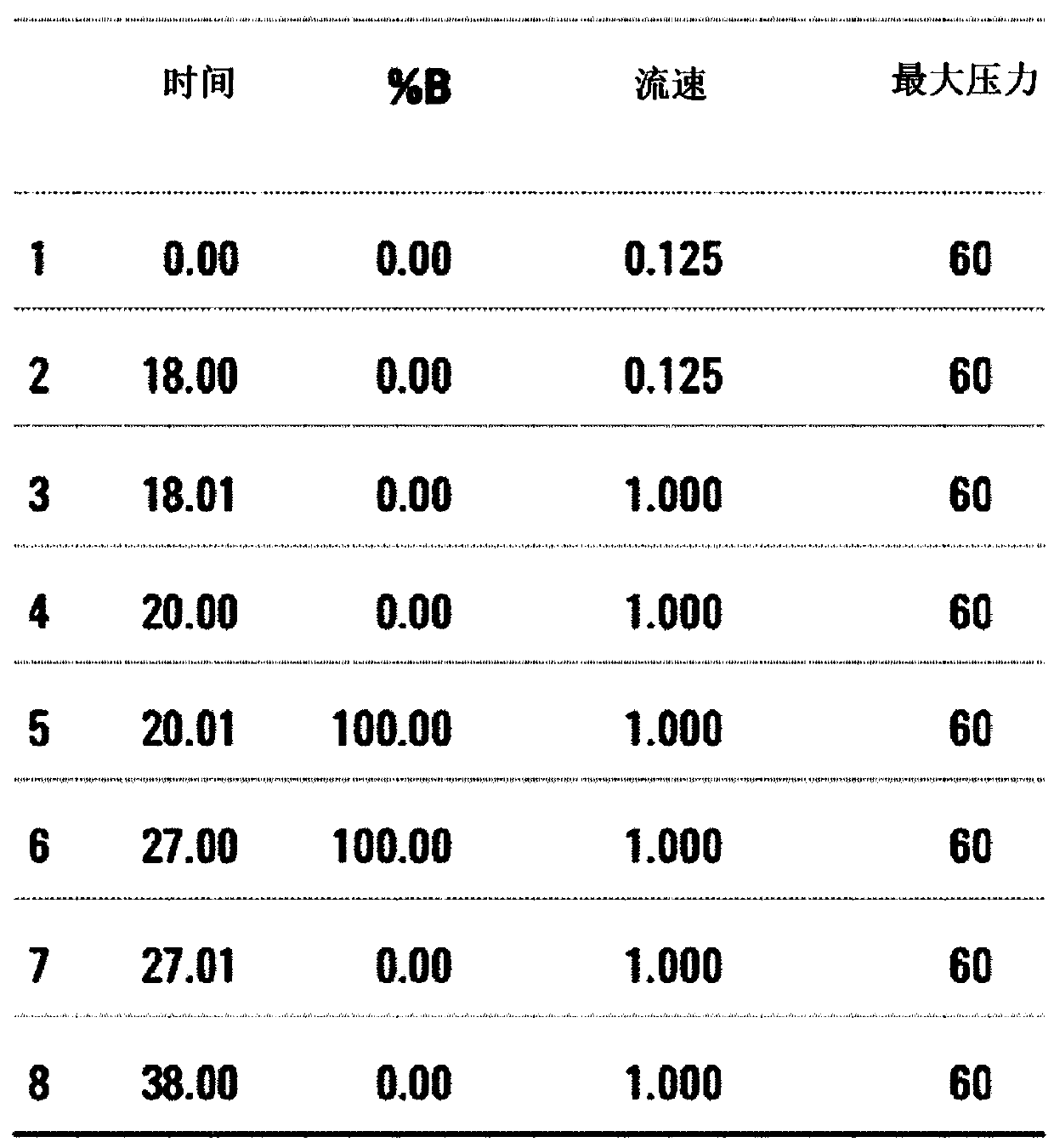
[0070] Specifically, the process of removing high-abundance proteins using MARS (Multiple Affinity Removal System) column (P / N 5188-6558, Agilent) is as follows.
[0071] 2 μl of 50x protease inhibitor (Roche) was added to 40 μl of the...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3: Peptidation of protein samples
[0078] In order to perform analysis with a mass spectrometer, a process of cleavage of protein in peptide units by an enzyme (trypsin) is required first, so peptide cleavage of protein is carried out by the following process.
[0079] 150 μl of DTT solution (final concentration: 6M urea, 10 mM DTT, 50 mM tris) was added to 50 μl of blood sample with a concentration of 60 μg to remove abundant protein, and reacted (reduced) at 37° C. for 1 hour. After treating 20 μl of IAA solution (final concentration: 5.45 M of urea, 50 M of IAA, 50 mM tris) in 200 μl of the reacted (reduced) sample, reacted (alkylated) at room temperature for 30 minutes in the dark, Then, 1 ml of Tris solution (50 mM, pH 8) (final concentration: 1 M urea, 50 mM tris, final volume: 1.2 ml) was added to the sample. Thereafter, the trypsin solution was dispensed in units of 5 μl and reacted at 37° C. for 12 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com