Nanometer modification method of lithium iron phosphate and prepared nanometer modified lithium iron phosphate and lithium ion battery
A lithium iron phosphate nanotechnology, applied in nanotechnology for materials and surface science, battery electrodes, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problem of low ion conductivity and electronic conductivity, affecting the energy density of power batteries, and difficult Ensure batch stability and other issues, to achieve the effect of small material particle size, good dynamic properties, and shallow embedding depth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0057] As a preferred technical solution, the preparation method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0058] (1), fully mixing the non-nanometerized lithium iron phosphate raw material with the carbon source to obtain the lithium iron phosphate raw material powder;
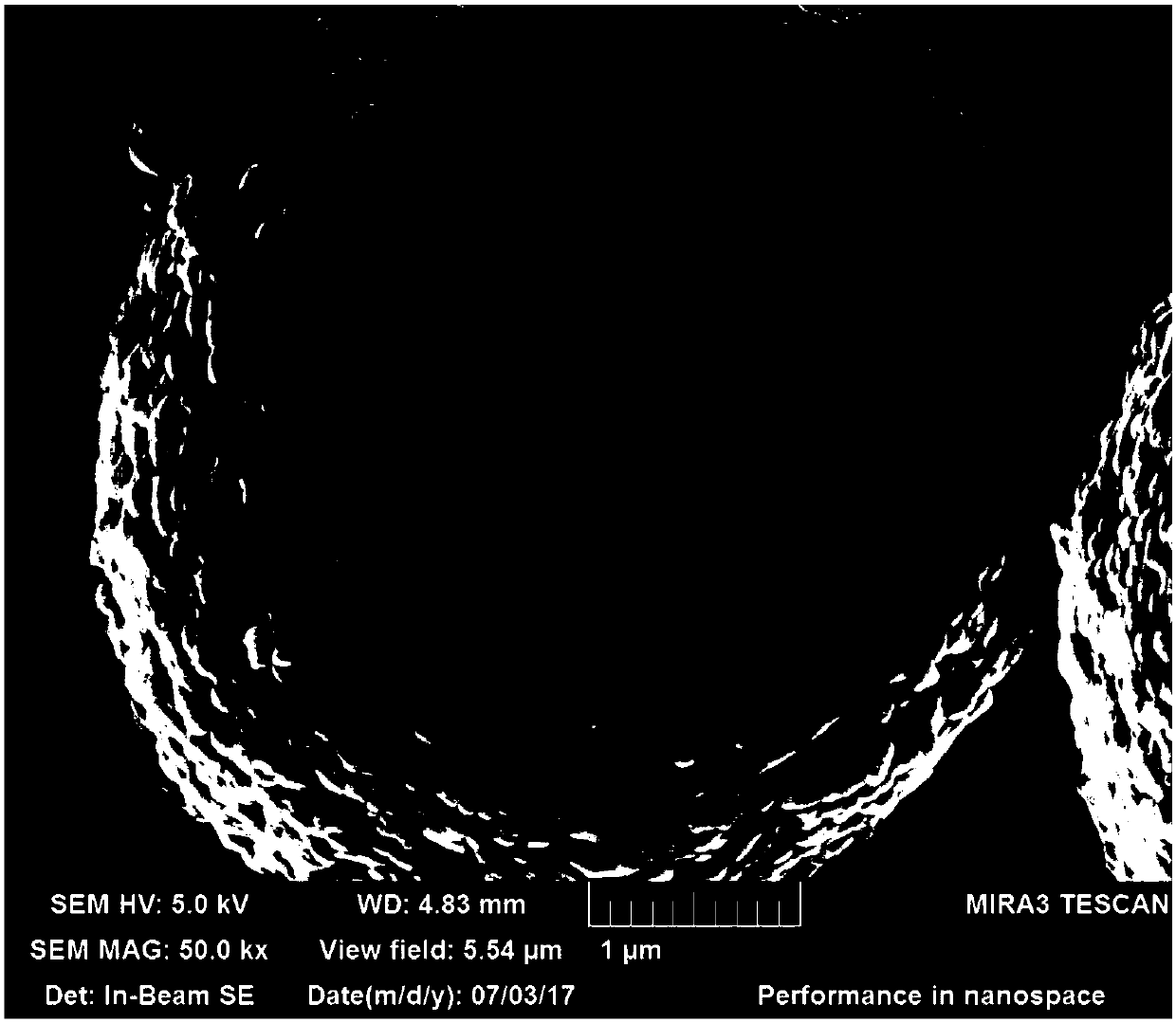
[0059] (2), using the method of wet ball milling, the raw material powder of lithium iron phosphate is ball milled to obtain nanoscale particles with a particle diameter D50 of 100 to 200 nm;
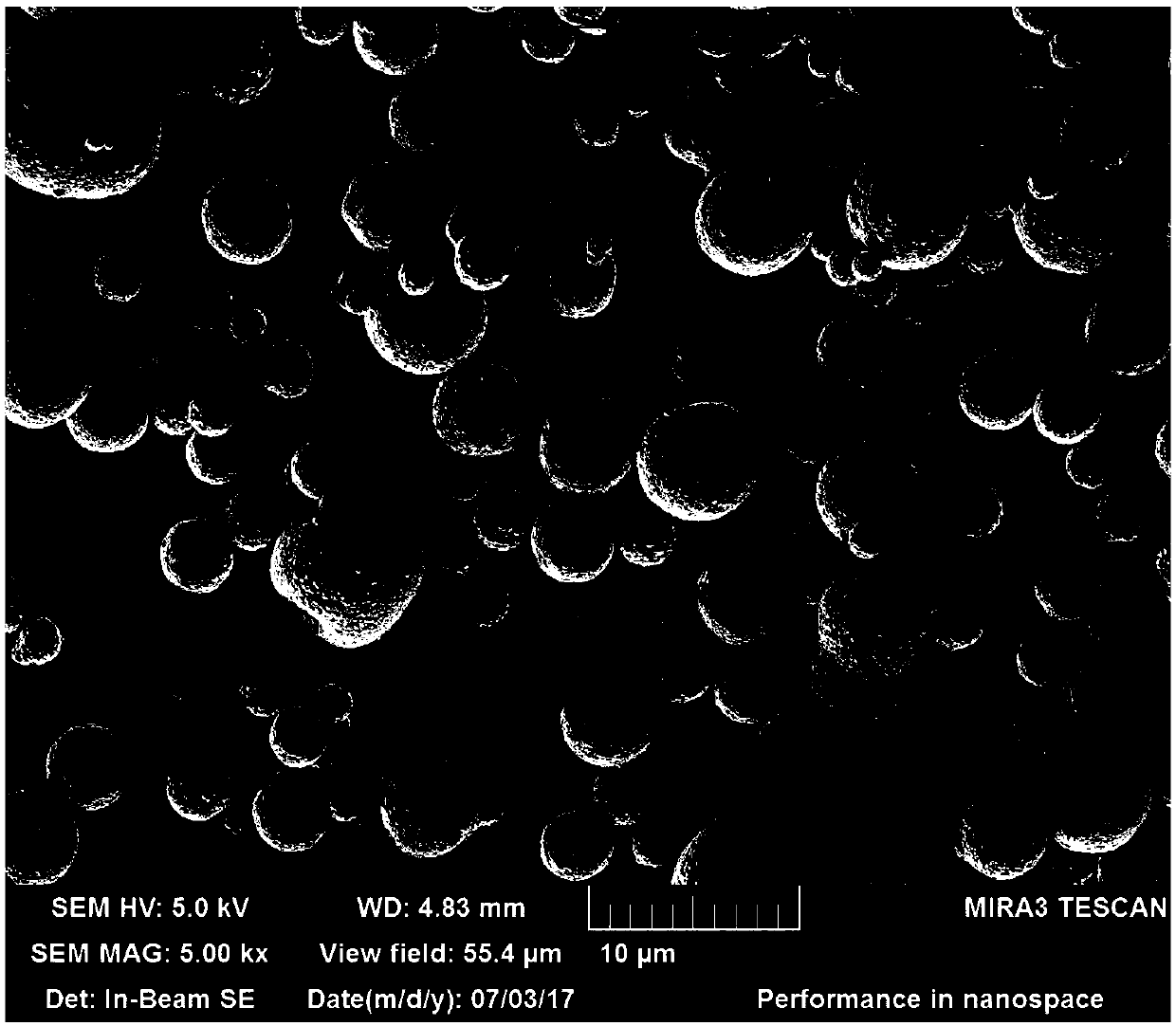
[0060] (3), the nano-scale particle that step (2) is made carries out spray granulation, and the obtained particle diameter D50 is the quasi-spherical lithium iron phosphate of 3~10 μ m;
[0061] The inlet temperature of the spray granulation is 200-350°C, and the outlet temperature is 60-120°C;
[0062] (4) Calcining the nano-sized lithium iron phosphate obtained by granulating in step (3) under a protective gas atmosphere at a constant temperature of 500-900°C for 2-10 hours to prepare nano-sized mod...
Embodiment 1
[0067] A nano-modification method of lithium iron phosphate, comprising the steps of:
[0068] (1), adding glucose to the non-nanometerized lithium iron phosphate raw material and fully mixing to obtain lithium iron phosphate raw material powder;
[0069] The mass percent of lithium iron phosphate powder in the lithium iron phosphate raw material powder is 95%, and the mass percent of glucose as a carbon source is 5%;
[0070] (2), utilize the method for wet ball milling to carry out ball milling to obtain particle diameter D50 to be the nanoscale particle of 100nm with lithium iron phosphate raw material powder;
[0071] (3), the nanoscale particle that step (2) is made carries out spray granulation, and the obtained particle diameter D50 is the quasi-spherical lithium iron phosphate of 3 μm;
[0072] The inlet temperature of the spray granulation is 200°C, and the outlet temperature is 60°C;
[0073] (4) The nanoscale lithium iron phosphate obtained by granulating in step ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] A nano-modification method of lithium iron phosphate, comprising the steps of:
[0076] (1), fully mixing the non-nanometerized lithium iron phosphate raw material with sucrose to obtain the lithium iron phosphate raw material powder;
[0077] The mass percent of lithium iron phosphate powder in the lithium iron phosphate raw material powder is 97%, and the mass percent of sucrose as a carbon source is 3%;
[0078] (2), utilize the method for wet ball milling to carry out ball milling to obtain particle diameter D50 and be the nanoscale particle of 200nm with lithium iron phosphate raw material powder;
[0079] (3), the nanoscale particle that step (2) is made carries out spray granulation, and the obtained particle diameter D50 is the quasi-spherical lithium iron phosphate of 10 μm;
[0080] The inlet temperature of the spray granulation is 350°C, and the outlet temperature is 120°C;
[0081] (4) The nanoscale lithium iron phosphate obtained by granulating in step (3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com