Arterial fibrillation detecting method based on single lead electrocardiosignal time-frequency characteristic
A technology of time-frequency characteristics and ECG signals, applied in diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, sensors, etc., can solve the problems of discrimination and low detection accuracy of atrial fibrillation, and achieve improved accuracy, high accuracy, and good robustness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
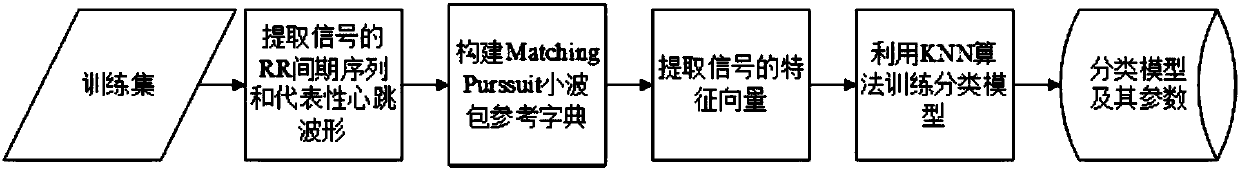
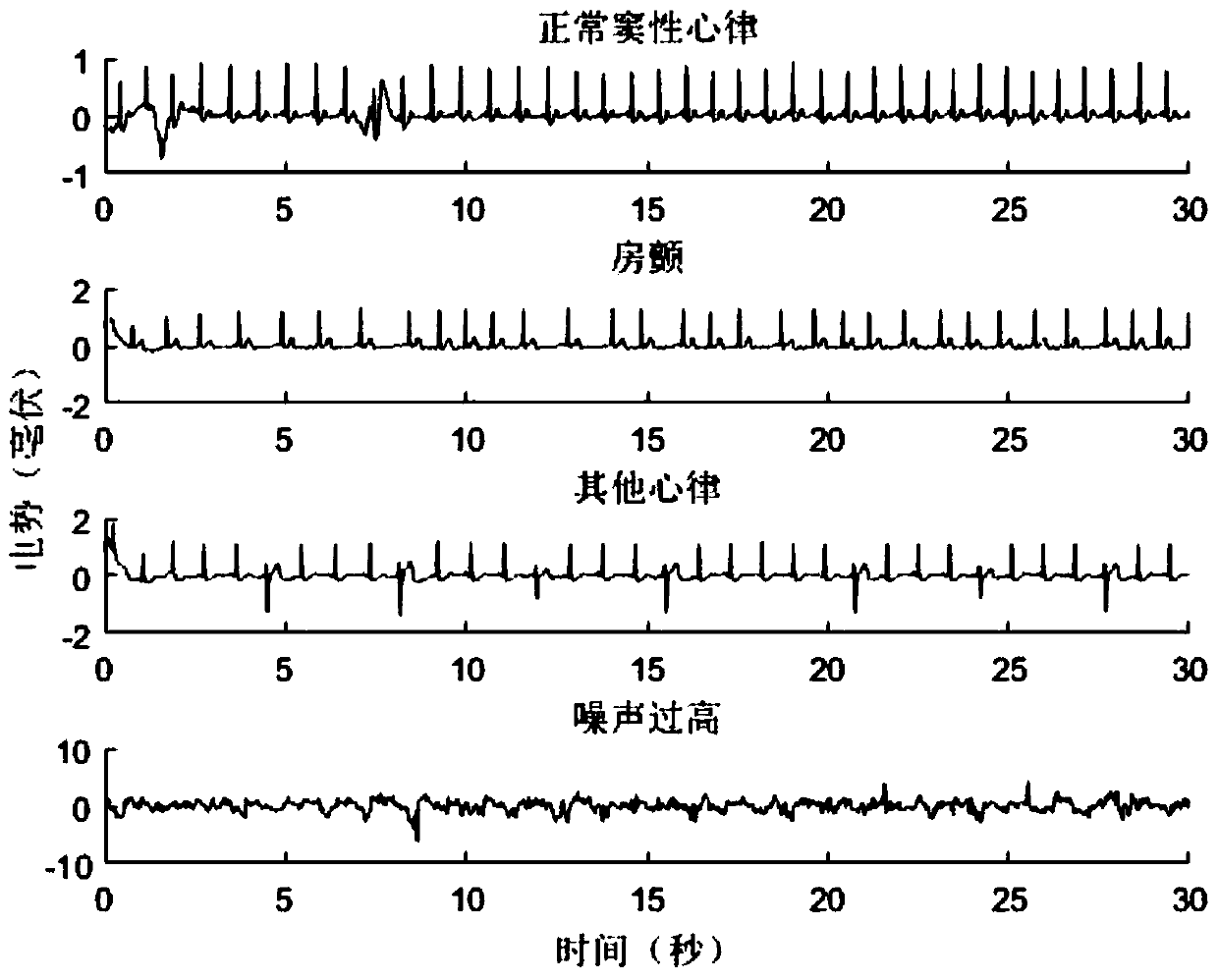
[0026] Embodiment 1: This embodiment describes an atrial fibrillation detection method based on the time-frequency characteristics of a single-lead ECG signal, which divides the original ECG signal into normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, other arrhythmias or excessive noise. Four categories, the method includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: For the single-lead surface ECG signal (the signal length is in the range of 10-60 seconds), first perform a preprocessing operation to remove the baseline drift and some noise interference in the ECG signal;
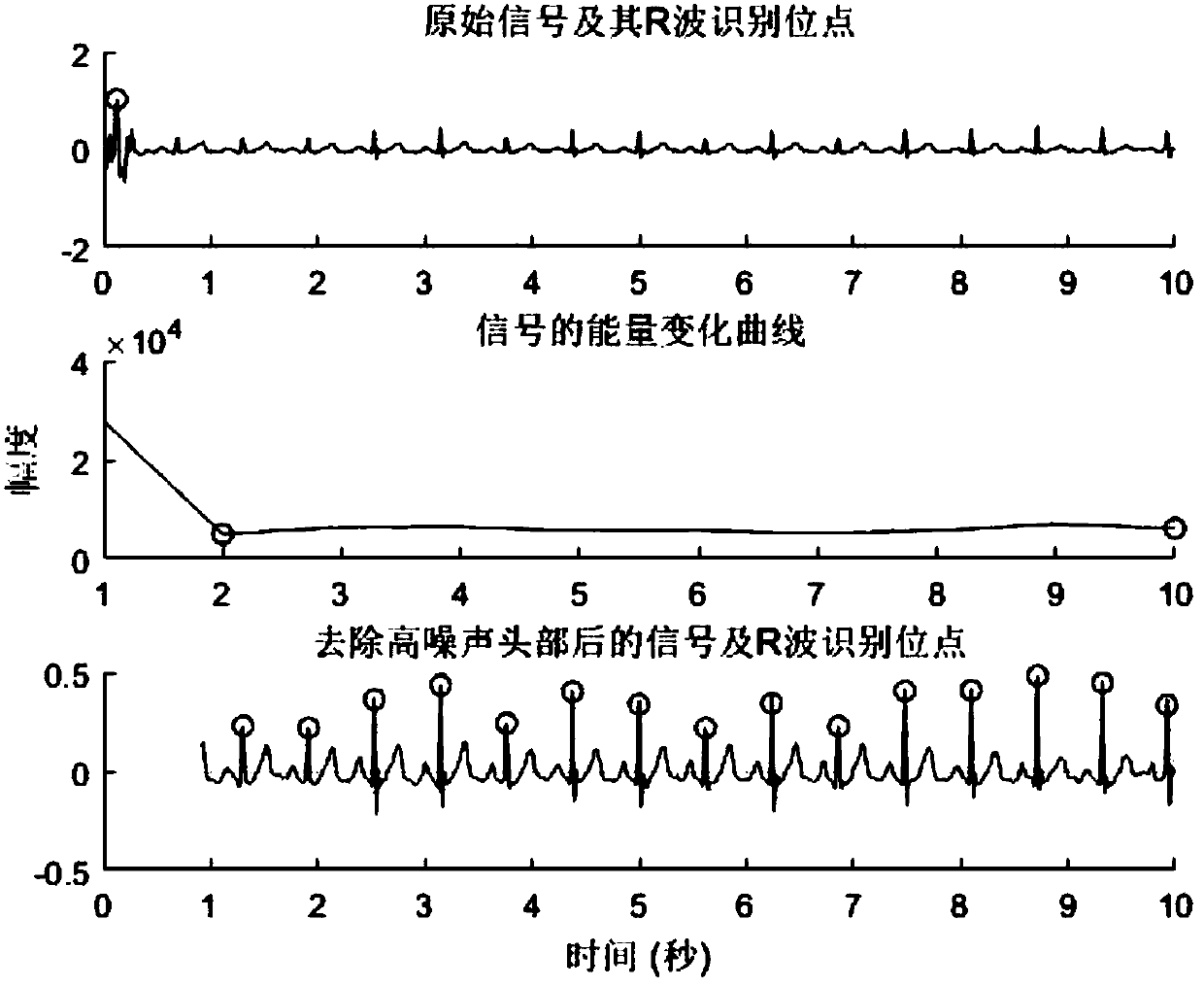
[0028] Step 2: Calculate the change of signal energy in the time domain based on the sliding window method, and find the first window whose energy is not higher than the median value of the energy of each subsequent window. The corresponding part is removed from the signal, and the third step is performed; if the window does not exist, the signal is considered to be too noisy, and the detection process ends;
[0029] ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: In the method for detecting atrial fibrillation based on the time-frequency characteristics of a single-lead ECG signal according to Embodiment 1, the specific steps of the second step are as follows:
[0036] (1) Divide the ECG signal into a series of windows, each window has a length of 1.8 seconds, and there is an overlapping area of 0.9 seconds between adjacent windows;
[0037] (2) Calculate the energy of the signal in each window, the formula is as follows:
[0038]
[0039] Among them, x is the discrete signal sequence in the window, x[n] represents the value of the nth sampling point in the window, T is the window duration, and N represents the number of sampling points in the window;
[0040] (3) Starting from the first window, compare its energy with the median value of the energy of each window in the signal, until a window is found so that its energy is not higher than the median energy of each subsequent window; set the window at The ser...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: In the method for detecting atrial fibrillation based on the time-frequency characteristics of a single-lead ECG signal according to Embodiment 1, the specific steps of step 5 are as follows:
[0045] (1) Define the lower limit of the similarity within the group, that is, the minimum Pearson correlation coefficient of the heartbeat waveform within the group, and the value is about 0.8 (adjusted according to the signal noise intensity);
[0046] (2) Calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between the heartbeat waveforms in the same signal, the formula is as follows
[0047]
[0048] Among them, X and Y respectively represent the sampling point sequence corresponding to the two heartbeat waveforms, E represents the mathematical expectation, μ X represents the average value of each sampling point in X, μ Y Represents the average value of each sampling point in Y, σ X represents the standard deviation of each sampling point in X, σ Y Represents the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com