A kind of application based on non-host plant volatiles as tea geometrid attractant
A technology of host plants and volatiles, applied in the direction of attracting pests, plant growth regulators, chemicals for biological control, etc., to achieve broad industrialization prospects, low cost, and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 : Extraction of volatiles
[0019] The test plants Nepeta chinensis and Artemisia annua were collected from Zhenlei Mountain in Xinyang and around the campus of Xinyang Agriculture and Forestry University respectively. Wash the test plants, cut them into pieces, dry them naturally, cut them into small pieces, put them in a steam distiller to distill and extract the volatile oil, and put the extracted volatile oil in a -4°C refrigerator for sealed storage for later use.
Embodiment 2
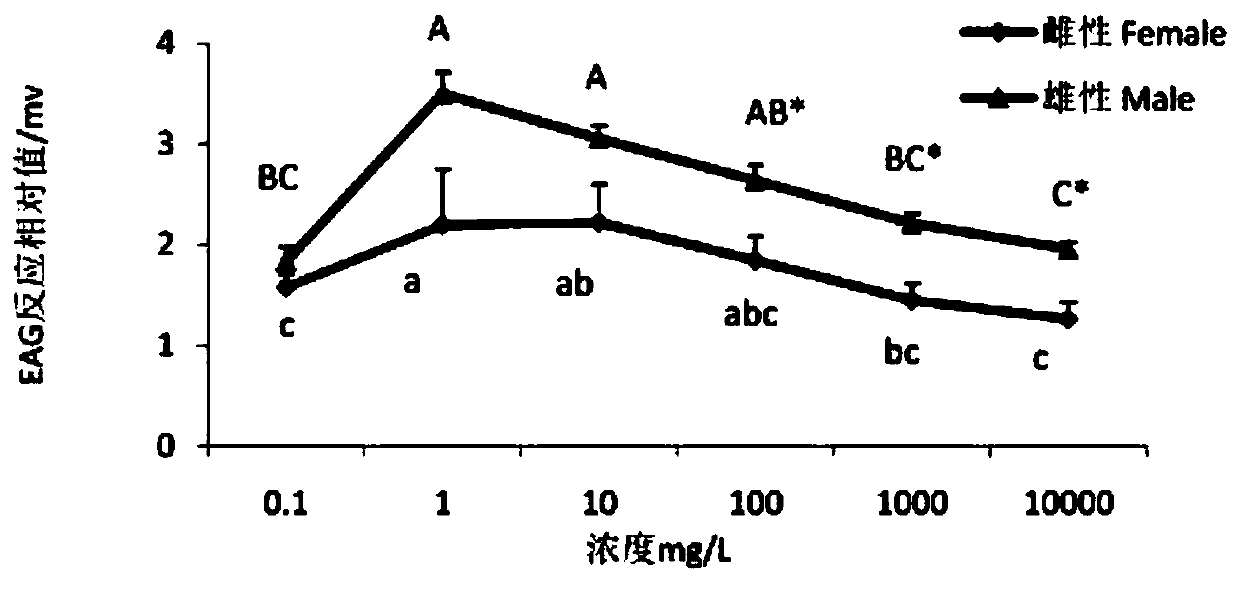
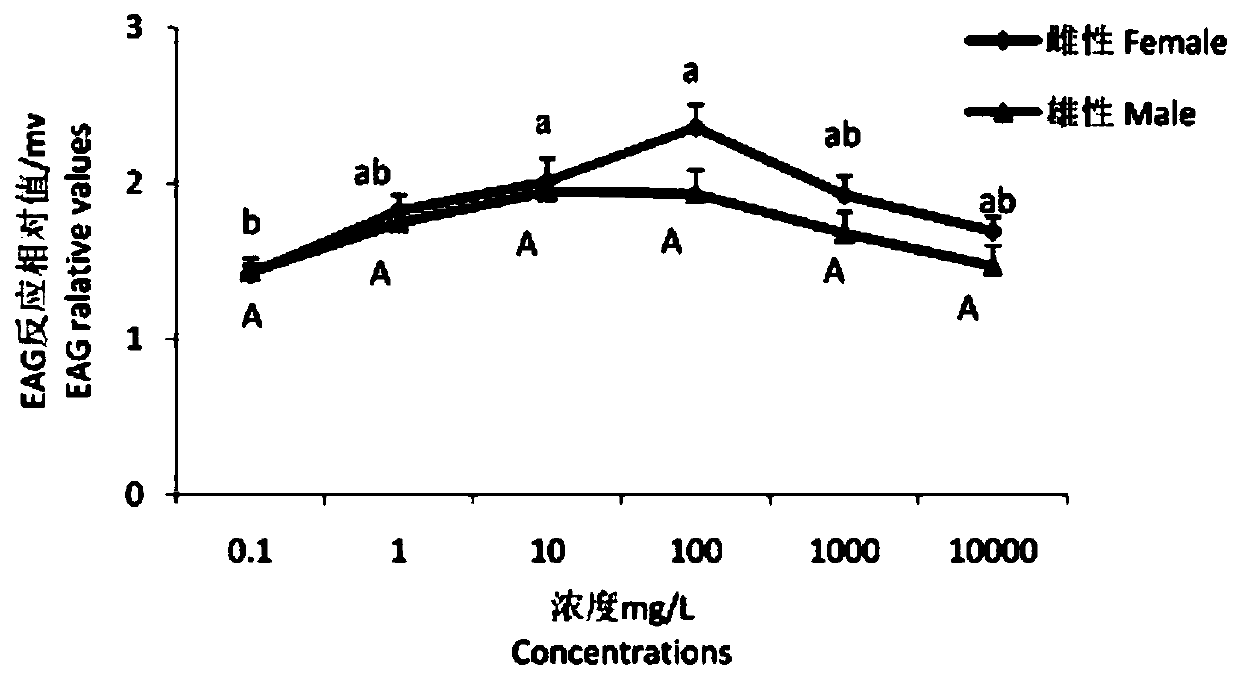
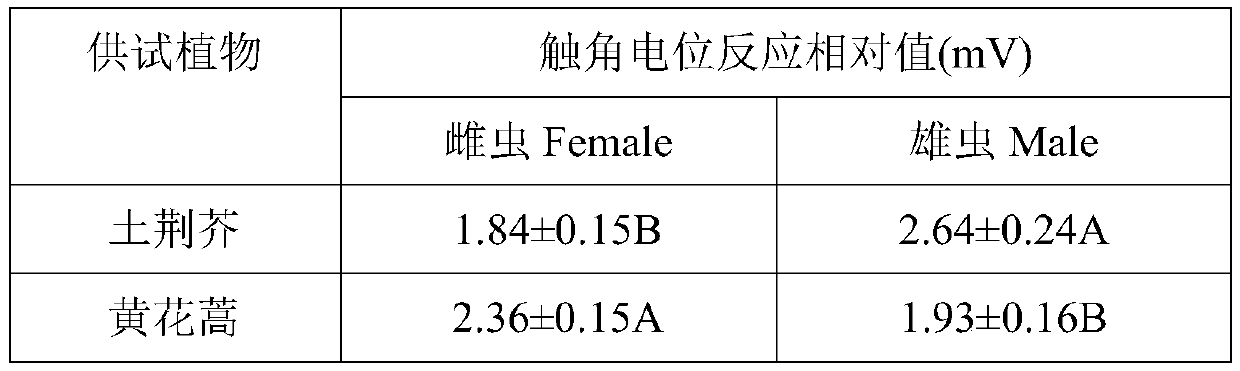
[0020] Example 2 : Antennapotential EAG responses of tea geometrid adults to volatiles
[0021] Pests tested: Tea geometrid larvae were collected from tea gardens around Ma'anshan, Xinyang, brought back to the laboratory and placed in an insect hood, where they were reared continuously for multiple generations. Insert the collected tea leaves with branches into the triangular bottle for 1-2 instar larvae to eat. When the larvae grow to 3-4 instar, they will be reared in an insect breeding box, and a layer of filter paper will be laid in the insect raising box to keep it moist and be replaced regularly. Fresh tea leaves and filter paper. The breeding temperature is 25±1°C, the relative humidity is 60%±5%, and the photoperiod is 16L:8D. After the larvae had pupated and emerged, the males and females were separated, fed with honey water with a volume concentration of 5%, and healthy adults 2-3 days after emergence were selected as test insects.
[0022] Test method: The anten...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 : Behavioral responses of tea geometrid adults to volatiles.
[0030] The "Y" type olfactometer was used to measure the chemotaxis response of tea geometrid adults to volatiles. During the olfactory measurement, the outlet of the atmospheric sampling bottle was used as the air source, and the air flow of each arm was controlled at 400 mL / min by the LZB-4 glass rotameter. Use a micro sampler to draw 5 μL of the substance solution to be tested, drop it onto a 2cm x 2cm filter paper strip, and put it into the side arm of the "Y" tube. Add acetone dropwise to the filter paper strip of the same specification, and put it into the other arm of the "Y" tube as a control.
[0031] The adults of tea geometrid were more active in the first half of the night, and the experiment was carried out from 18:00 to 23:00. The indoor temperature was kept at (25±1)℃ and the humidity was (60±5)%. 24 hours after the first eclosion, the female and male adults of tea geometrid with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com