UV devices, systems, and methods of making and use
A technology of equipment and control box, which is applied in the field of manufacturing portable UV equipment and portable UV equipment, and can solve the problems of verifying the sterilization level and not establishing protocols, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
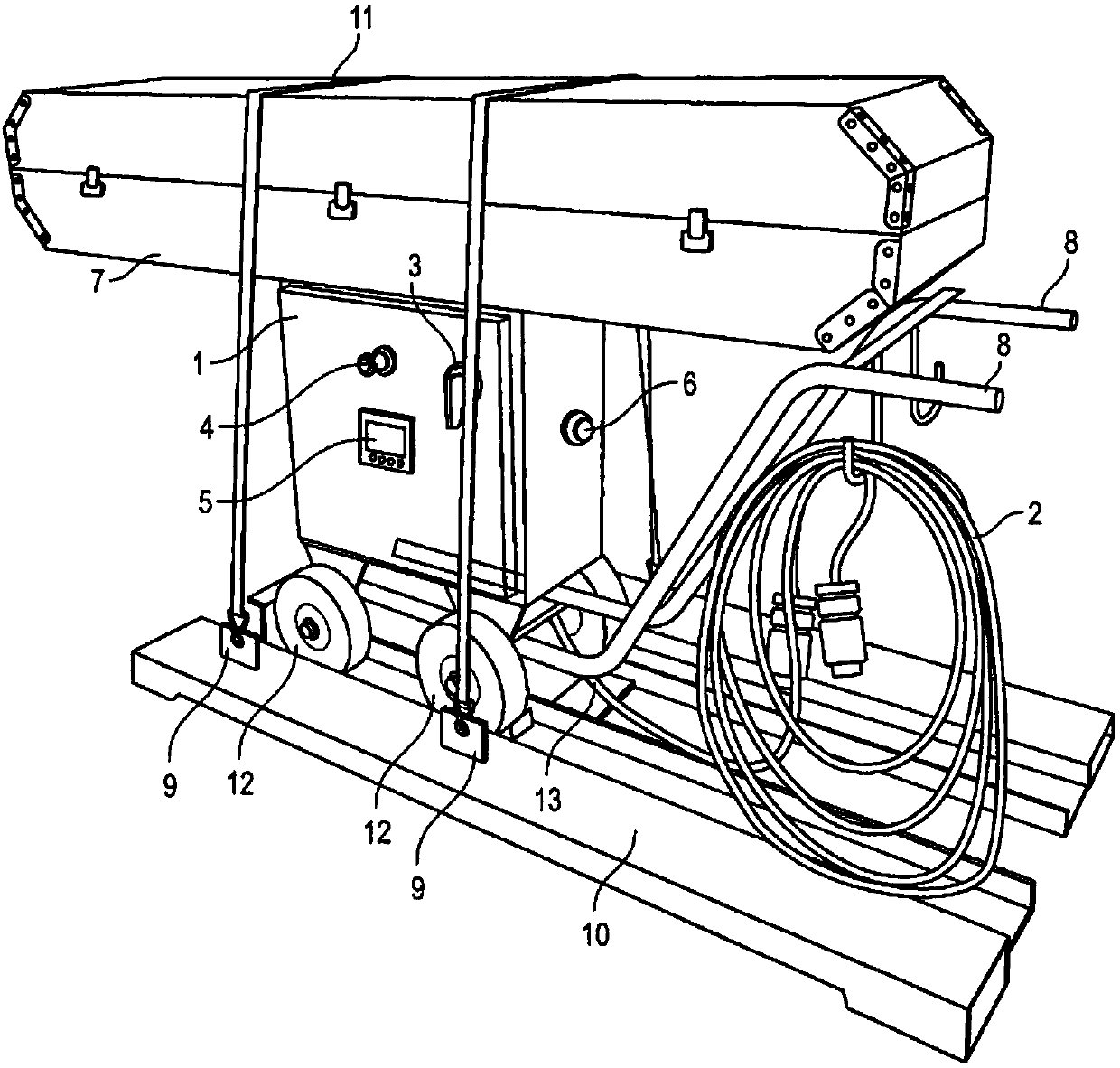
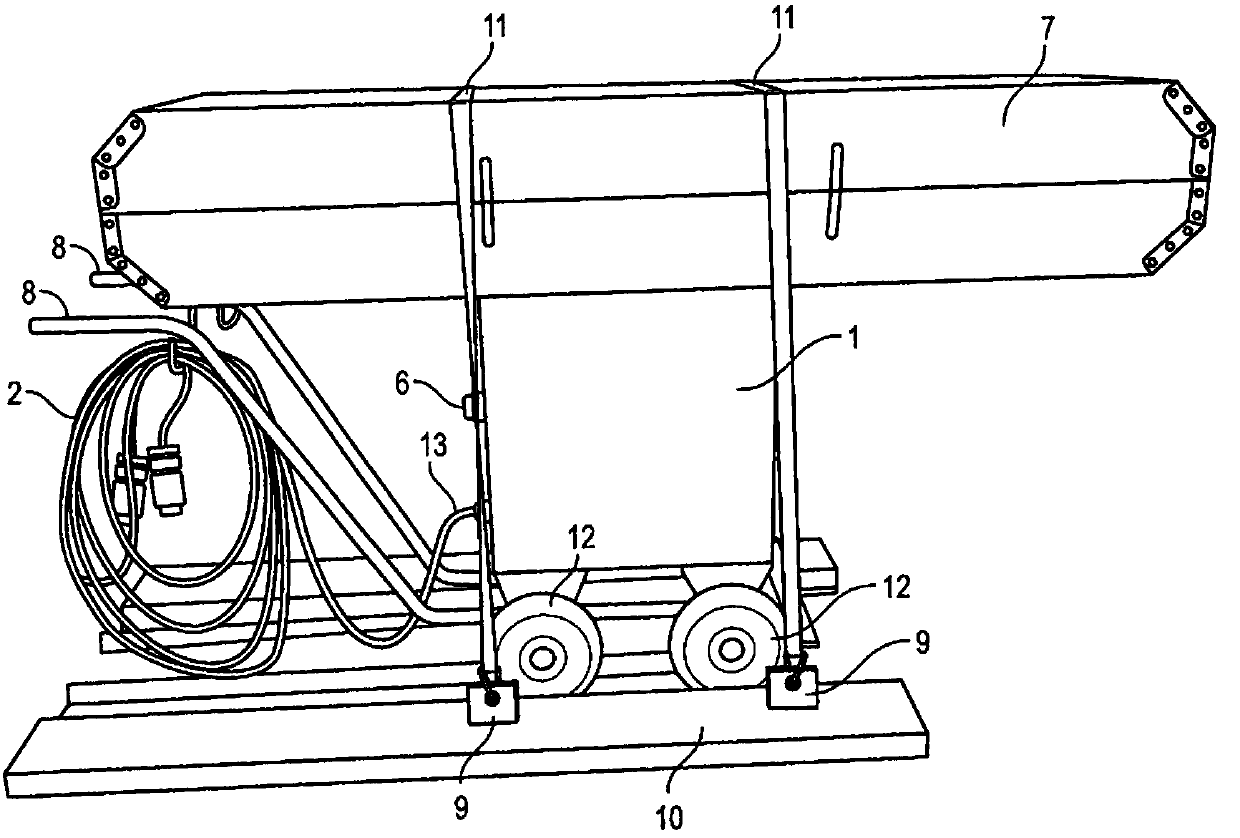
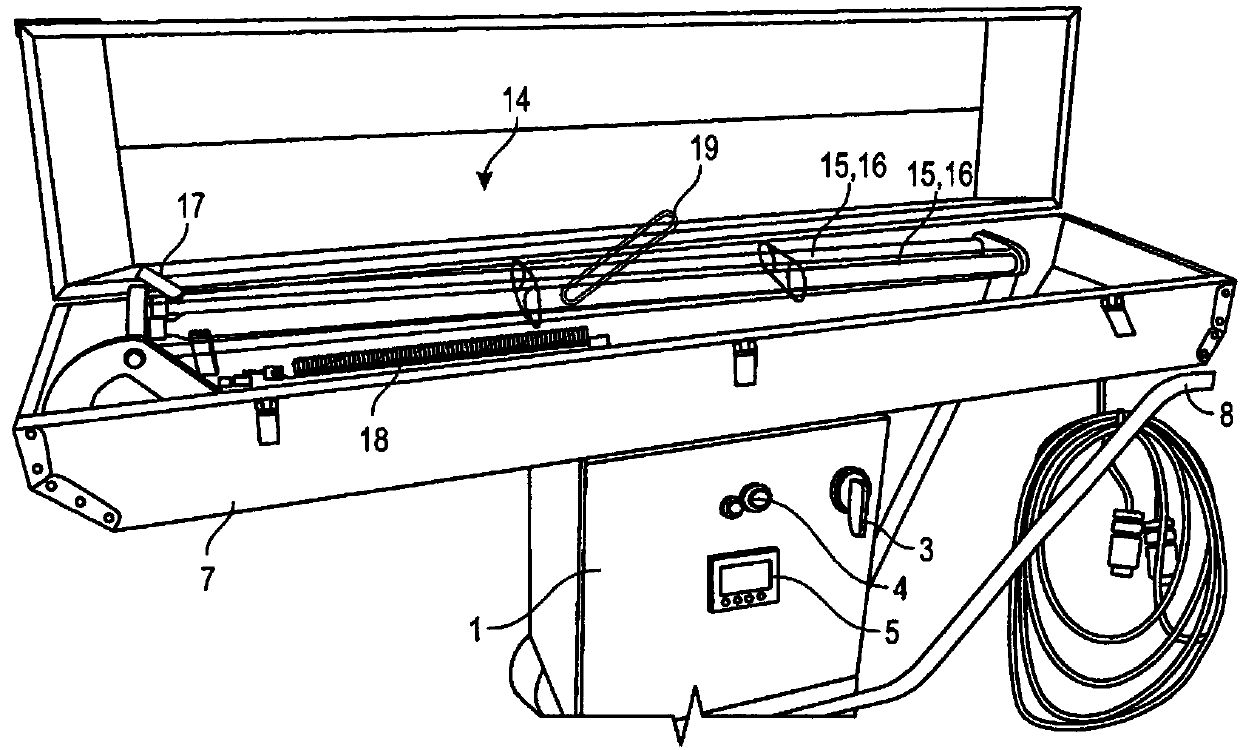
Image
Examples
example 1
[0735] Example 1. Calculate the kill rate of microorganisms
[0736] Provided below are the steps for calculating the UV intensity required to kill a desired microorganism, and therefore the time to kill, using the compositions, algorithms and methods of the present invention. Here, the required energy doses of UV radiation required for killing factors are provided in Tables 1 to 5 (UV dosage, in μWs / cm 2 )(microwatt / cm 2 ). As shown in Table 9 below, according to the algorithm presented here, to determine the UV intensity (UV dose) on a surface at various distances from the germicidal UV light source, the user will radiate energy (in microwatts per square centimeter at a distance of one meter shown) divided by the intensity factor.
[0737] Table 9: Intensity Factors (Ultraviolet Corporation (Lebanon, IN, USA 46052)).
[0738]
[0739] 190 microwatts / cm output using (at a distance of one meter) 254nm 2 A UV light source placed 36" from the inner surface in the ferme...
example 2
[0743] Example 2. Inhibits the growth of Bacillus subtilis
[0744] In order to determine the effectiveness of the method of the present invention and the efficacy of the UV device of the present invention in sanitizing stainless steel tanks used in the winemaking process, Bacillus subtilis (American Type Culture Collection, ATCC No.: 82TM; Designation: AMC[ ATCC 8037, NRS 315]) kill / growth arrest. Bacillus subtilis forms spores, thereby making it a more UV resistant microorganism than non-spore forming microorganisms. In this experiment, as the UV light source, a 30" SE UV-C lamp (Steri-Aire) was used. Three identical UV lamps were placed on a stand and placed in a helical configuration with each UV lamp at 15 angle set.
[0745] With the Bacillus subtilis suspension two samples (each time point) were pierced with a sharp to give 9.6 x 10 for the first three time points 6 CFU (colony forming unit) / final concentration of sample taken. Using 1.3×10 6 The CFU / sample suspe...
example 3
[0756] Example 3. Microbial population reduction on stainless steel tanks using UVC (UVT-4 model) versus steam and peracetic acid Disinfection Contrast Efficacy Test
[0757] A comparative efficacy trial of three different tank sanitization methods was conducted at a winery in St. Helena, California (CA). The purpose of this comparative trial was to evaluate the sanitizing efficacy of various sanitizers (steam, peracetic acid (PAA)) and ultraviolet light C (UVC) for the reduction of wine and ambient microbial populations on the interior surfaces of stainless steel production tanks. Trials were performed on four different cans. Briefly, the method of testing was as follows: (i) the tanks were emptied of wine; (ii) pre-treatment microbial swab samples were collected from the ceiling, wall, and floor of each tank; (iii) Tanks were subjected to an appropriate sanitization protocol; (iv) post-treatment microbial swab samples were collected from the roof, walls, and floor of ea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com