Method for calculating probability of failure to operate on command of reactor protection system
A technology for reactor protection and probability calculation, which is applied in the field of reactor protection system rejection probability calculation, can solve problems such as low calculation efficiency, lack of consideration of common cause failure, and unguaranteed accuracy, so as to achieve improved calculation efficiency, simple process, accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
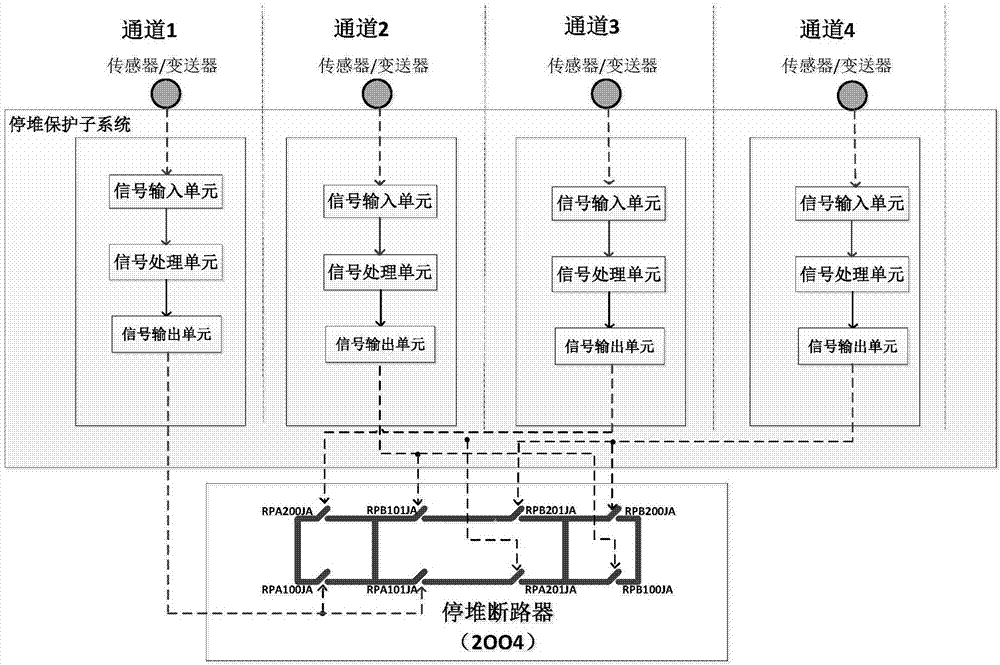
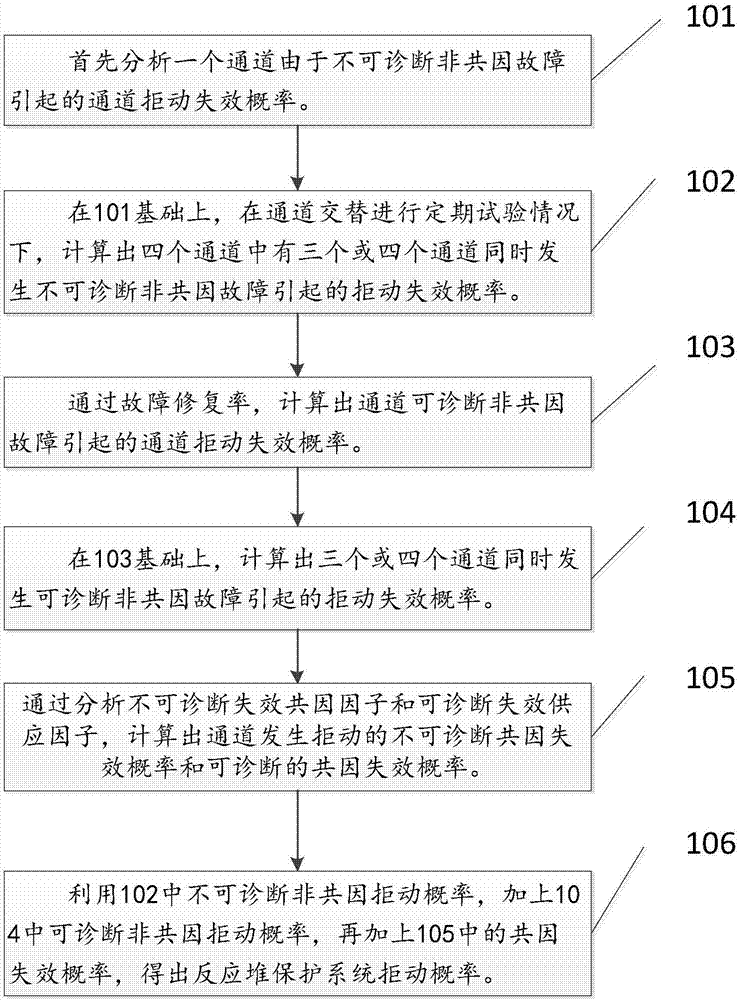
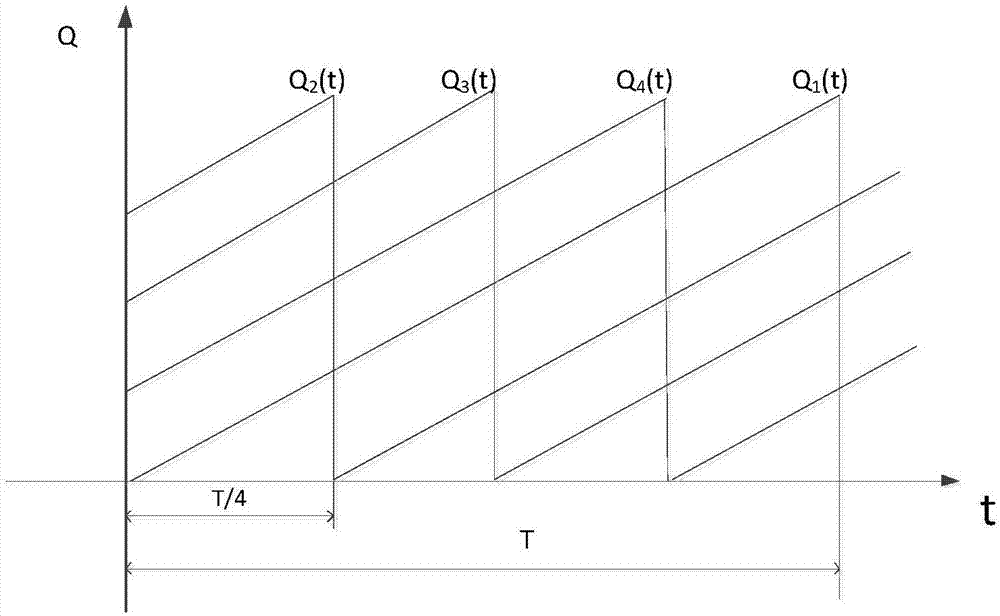
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown in the typical reactor protection system architecture, four channels constitute a two-out-of-four voting redundancy system, in which each channel includes a signal input unit, a signal processing unit and a signal output unit, and the output of the four channels is in the shutdown circuit breaker Realize two-out-of-four logic voting, that is, if two of the four channels are normal, the system is normal. The faults affecting the safety function of each channel include diagnosable faults and non-diagnosable faults, and the fault rates of diagnosable and non-diagnosable faults are expressed as λ D, lambda U , for diagnosable faults, repair immediately after the fault occurs, and the average repair time is MTTR (mean time to repair); for non-diagnosable faults, the fault needs to be detected and repaired during ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com